Day-Ahead Hourly Forecasting of Power Generation from Photovoltaic Plants
Paper and Code
Feb 26, 2019
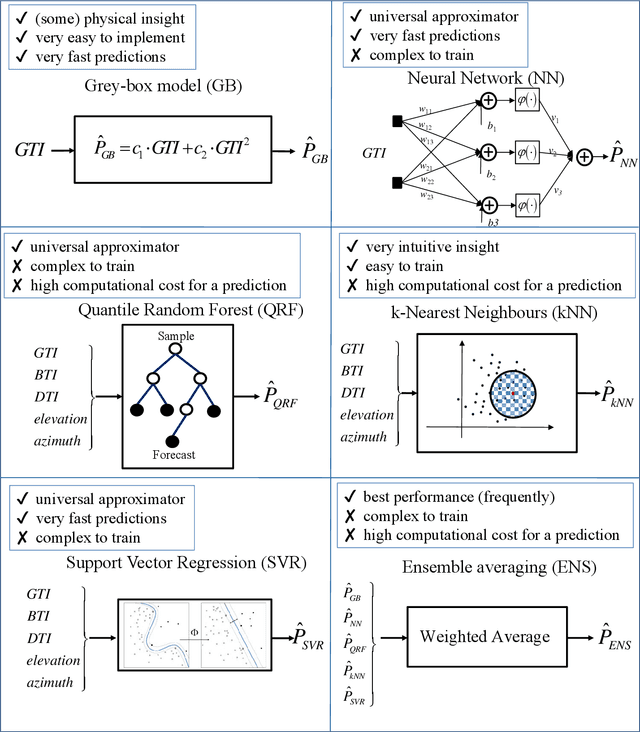
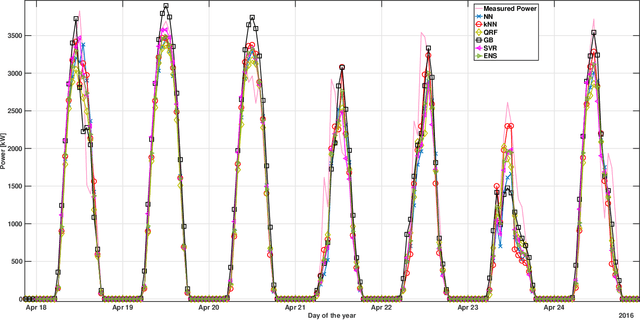
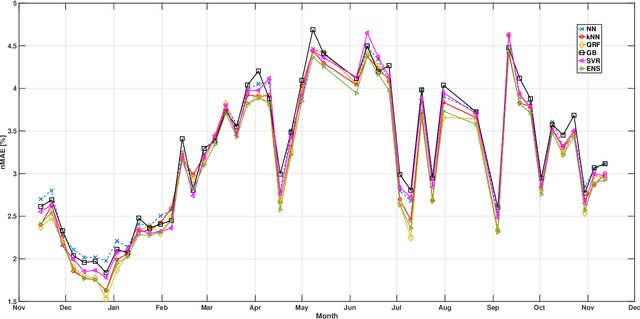
The ability to accurately forecast power generation from renewable sources is nowadays recognised as a fundamental skill to improve the operation of power systems. Despite the general interest of the power community in this topic, it is not always simple to compare different forecasting methodologies, and infer the impact of single components in providing accurate predictions. In this paper we extensively compare simple forecasting methodologies with more sophisticated ones over 32 photovoltaic plants of different size and technology over a whole year. Also, we try to evaluate the impact of weather conditions and weather forecasts on the prediction of PV power generation.
* IEEE Transactions of Sustainable Energy, Vol. 9, Issue 2, pp. 831
- 842 (2018) * Preprint of IEEE Transactions of Sustainable Energy, Vol. 9, Issue 2,
pp. 831 - 842 (2018)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge