Elmer V Bernstam
Generalized and Transferable Patient Language Representation for Phenotyping with Limited Data
Feb 24, 2021



Abstract:The paradigm of representation learning through transfer learning has the potential to greatly enhance clinical natural language processing. In this work, we propose a multi-task pre-training and fine-tuning approach for learning generalized and transferable patient representations from medical language. The model is first pre-trained with different but related high-prevalence phenotypes and further fine-tuned on downstream target tasks. Our main contribution focuses on the impact this technique can have on low-prevalence phenotypes, a challenging task due to the dearth of data. We validate the representation from pre-training, and fine-tune the multi-task pre-trained models on low-prevalence phenotypes including 38 circulatory diseases, 23 respiratory diseases, and 17 genitourinary diseases. We find multi-task pre-training increases learning efficiency and achieves consistently high performance across the majority of phenotypes. Most important, the multi-task pre-training is almost always either the best-performing model or performs tolerably close to the best-performing model, a property we refer to as robust. All these results lead us to conclude that this multi-task transfer learning architecture is a robust approach for developing generalized and transferable patient language representations for numerous phenotypes.
A frame semantic overview of NLP-based information extraction for cancer-related EHR notes
Apr 02, 2019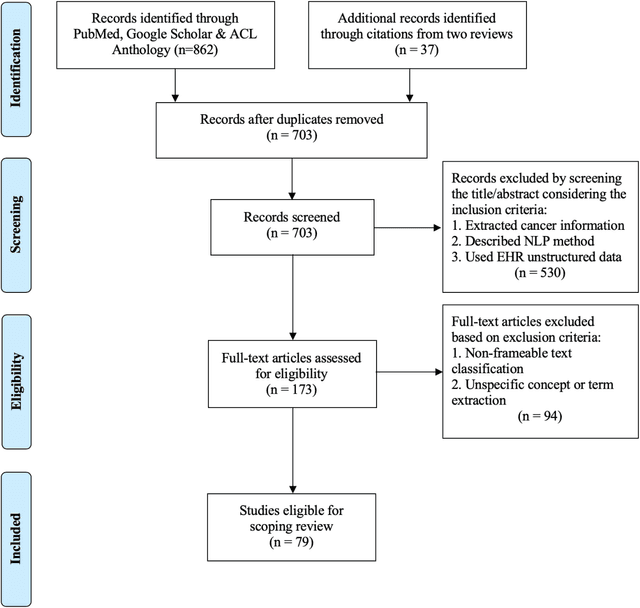
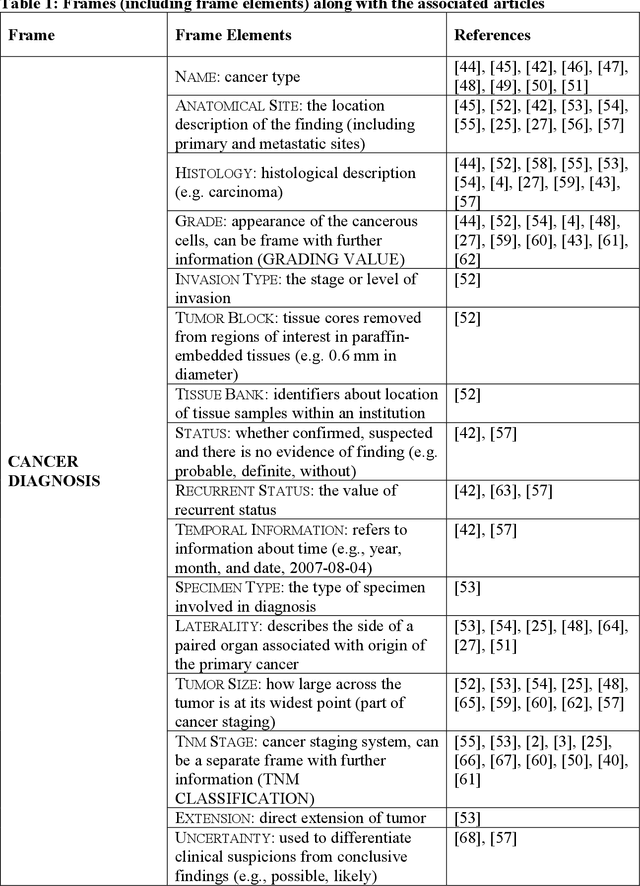
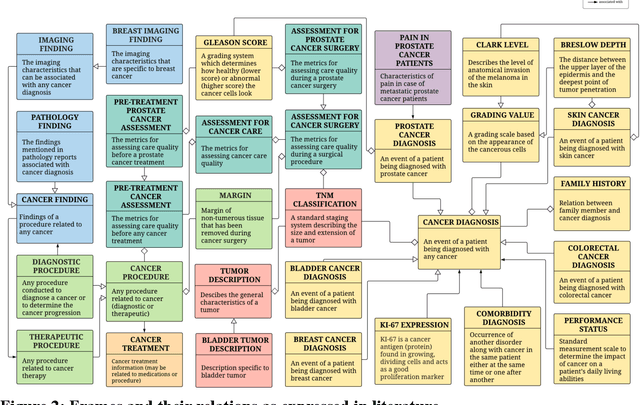
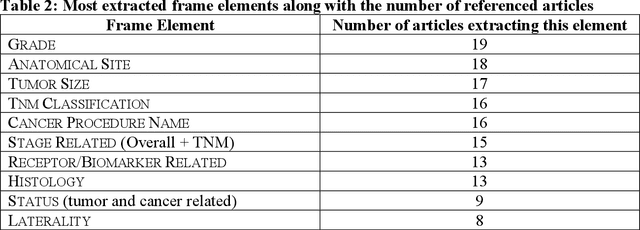
Abstract:Objective: There is a lot of information about cancer in Electronic Health Record (EHR) notes that can be useful for biomedical research provided natural language processing (NLP) methods are available to extract and structure this information. In this paper, we present a scoping review of existing clinical NLP literature for cancer. Methods: We identified studies describing an NLP method to extract specific cancer-related information from EHR sources from PubMed, Google Scholar, ACL Anthology, and existing reviews. Two exclusion criteria were used in this study. We excluded articles where the extraction techniques used were too broad to be represented as frames and also where very low-level extraction methods were used. 79 articles were included in the final review. We organized this information according to frame semantic principles to help identify common areas of overlap and potential gaps. Results: Frames were created from the reviewed articles pertaining to cancer information such as cancer diagnosis, tumor description, cancer procedure, breast cancer diagnosis, prostate cancer diagnosis and pain in prostate cancer patients. These frames included both a definition as well as specific frame elements (i.e. extractable attributes). We found that cancer diagnosis was the most common frame among the reviewed papers (36 out of 79), with recent work focusing on extracting information related to treatment and breast cancer diagnosis. Conclusion: The list of common frames described in this paper identifies important cancer-related information extracted by existing NLP techniques and serves as a useful resource for future researchers requiring cancer information extracted from EHR notes. We also argue, due to the heavy duplication of cancer NLP systems, that a general purpose resource of annotated cancer frames and corresponding NLP tools would be valuable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge