Elie Bursztein
Evaluating the Robustness of a Production Malware Detection System to Transferable Adversarial Attacks
Oct 02, 2025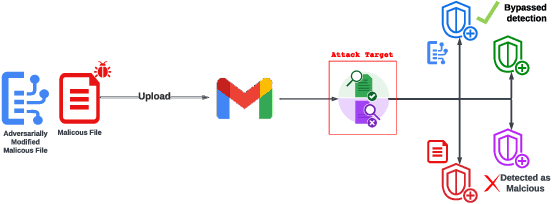
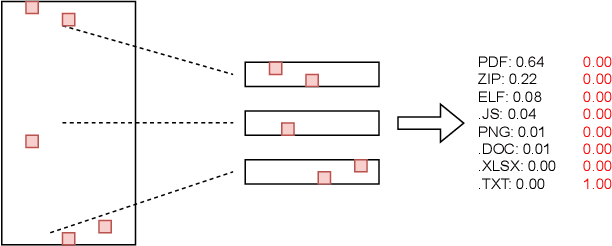
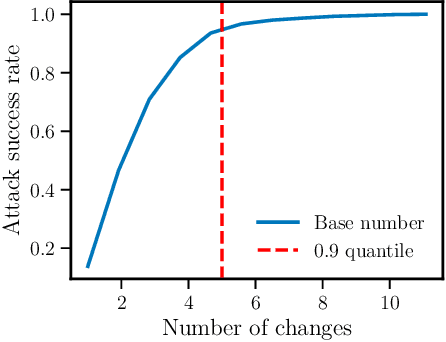
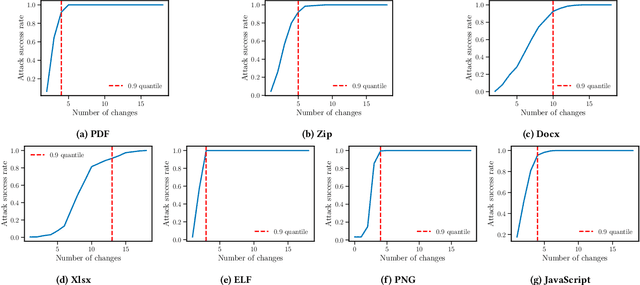
Abstract:As deep learning models become widely deployed as components within larger production systems, their individual shortcomings can create system-level vulnerabilities with real-world impact. This paper studies how adversarial attacks targeting an ML component can degrade or bypass an entire production-grade malware detection system, performing a case study analysis of Gmail's pipeline where file-type identification relies on a ML model. The malware detection pipeline in use by Gmail contains a machine learning model that routes each potential malware sample to a specialized malware classifier to improve accuracy and performance. This model, called Magika, has been open sourced. By designing adversarial examples that fool Magika, we can cause the production malware service to incorrectly route malware to an unsuitable malware detector thereby increasing our chance of evading detection. Specifically, by changing just 13 bytes of a malware sample, we can successfully evade Magika in 90% of cases and thereby allow us to send malware files over Gmail. We then turn our attention to defenses, and develop an approach to mitigate the severity of these types of attacks. For our defended production model, a highly resourced adversary requires 50 bytes to achieve just a 20% attack success rate. We implement this defense, and, thanks to a collaboration with Google engineers, it has already been deployed in production for the Gmail classifier.
Imagen 3
Aug 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce Imagen 3, a latent diffusion model that generates high quality images from text prompts. We describe our quality and responsibility evaluations. Imagen 3 is preferred over other state-of-the-art (SOTA) models at the time of evaluation. In addition, we discuss issues around safety and representation, as well as methods we used to minimize the potential harm of our models.
RETSim: Resilient and Efficient Text Similarity
Nov 28, 2023Abstract:This paper introduces RETSim (Resilient and Efficient Text Similarity), a lightweight, multilingual deep learning model trained to produce robust metric embeddings for near-duplicate text retrieval, clustering, and dataset deduplication tasks. We demonstrate that RETSim is significantly more robust and accurate than MinHash and neural text embeddings, achieving new state-of-the-art performance on dataset deduplication, adversarial text retrieval benchmarks, and spam clustering tasks. We also introduce the W4NT3D benchmark (Wiki-40B 4dversarial Near-T3xt Dataset) for evaluating multilingual, near-duplicate text retrieval capabilities under adversarial settings. RETSim and the W4NT3D benchmark are open-sourced under the MIT License at https://github.com/google/unisim.
RetVec: Resilient and Efficient Text Vectorizer
Feb 18, 2023Abstract:This paper describes RetVec, a resilient multilingual embedding scheme designed for neural-based text processing, including small-text classification and large-language models. RetVec combines a novel character encoding with an optional small model to embed words into a 256-dimensional vector space. These embeddings enable training competitive multilingual text models resilient to typos and adversarial attacks. In this paper, we evaluate and compare RetVec to state-of-the-art tokenizers and word embeddings on common model architectures. These comparisons demonstrate that RetVec leads to competitive models that are significantly more resilient to text perturbations across a variety of common tasks. RetVec is available under Apache 2 license at \url{https://github.com/[anonymized]}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge