Edwin Weill
Vehicle Re-Identification: an Efficient Baseline Using Triplet Embedding
Jan 16, 2019



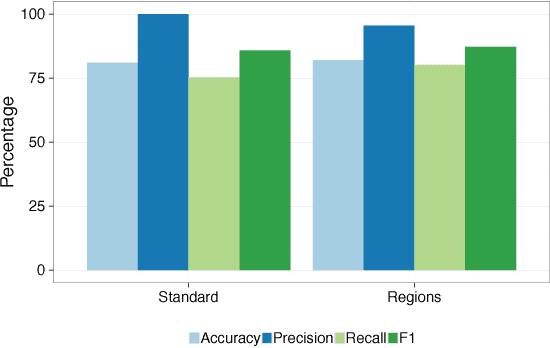
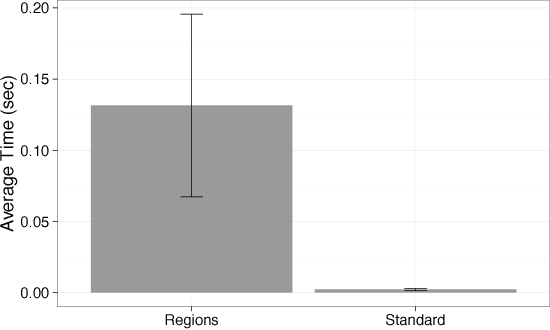
Abstract:In this paper we tackle the problem of vehicle re-identification in a camera network utilizing triplet embeddings. Re-identification is the problem of matching appearances of objects across different cameras. With the proliferation of surveillance cameras enabling smart and safer cities, there is an ever-increasing need to re-identify vehicles across cameras. Typical challenges arising in smart city scenarios include variations of viewpoints, illumination and self occlusions. Most successful approaches for re-identification involve (deep) learning an embedding space such that the vehicles of same identities are projected closer to one another, compared to the vehicles representing different identities. Popular loss functions for learning an embedding (space) include contrastive or triplet loss. In this paper we provide an extensive evaluation of these losses applied to vehicle re-identification and demonstrate that using the best practices for learning embeddings outperform most of the previous approaches proposed in the vehicle re-identification literature. Compared to most existing state-of-the-art approaches, our approach is simpler and more straightforward for training utilizing only identity-level annotations, along with one of the smallest published embedding dimensions for efficient inference. Furthermore in this work we introduce a formal evaluation of a triplet sampling variant (batch sample) into the re-identification literature.
Deep Learning in the Automotive Industry: Applications and Tools
Apr 30, 2017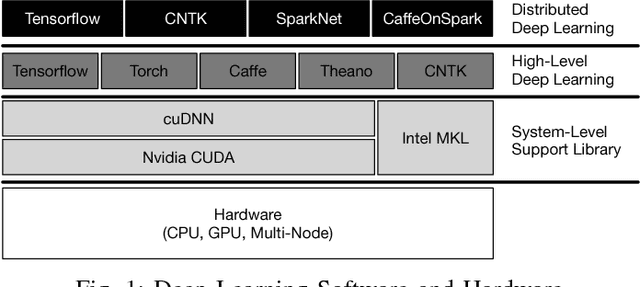
Abstract:Deep Learning refers to a set of machine learning techniques that utilize neural networks with many hidden layers for tasks, such as image classification, speech recognition, language understanding. Deep learning has been proven to be very effective in these domains and is pervasively used by many Internet services. In this paper, we describe different automotive uses cases for deep learning in particular in the domain of computer vision. We surveys the current state-of-the-art in libraries, tools and infrastructures (e.\,g.\ GPUs and clouds) for implementing, training and deploying deep neural networks. We particularly focus on convolutional neural networks and computer vision use cases, such as the visual inspection process in manufacturing plants and the analysis of social media data. To train neural networks, curated and labeled datasets are essential. In particular, both the availability and scope of such datasets is typically very limited. A main contribution of this paper is the creation of an automotive dataset, that allows us to learn and automatically recognize different vehicle properties. We describe an end-to-end deep learning application utilizing a mobile app for data collection and process support, and an Amazon-based cloud backend for storage and training. For training we evaluate the use of cloud and on-premises infrastructures (including multiple GPUs) in conjunction with different neural network architectures and frameworks. We assess both the training times as well as the accuracy of the classifier. Finally, we demonstrate the effectiveness of the trained classifier in a real world setting during manufacturing process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge