Ebrahim Karami
Estimation and Tracking of AP-diameter of the Inferior Vena Cava in Ultrasound Images Using a Novel Active Circle Algorithm
Aug 08, 2018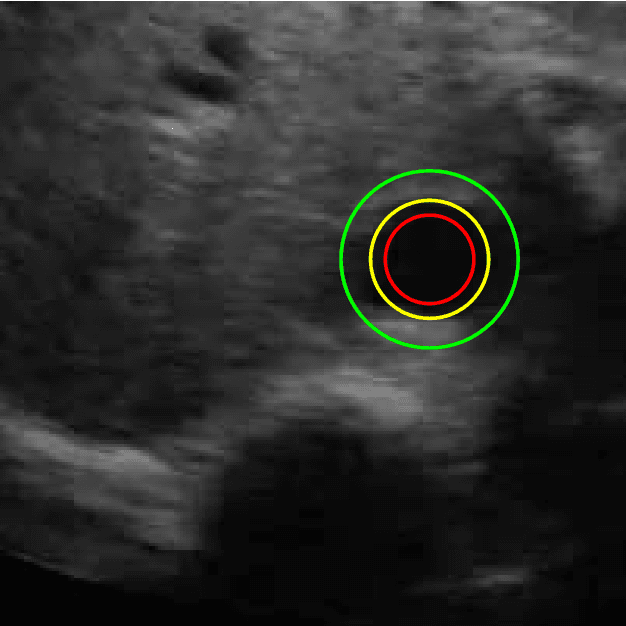
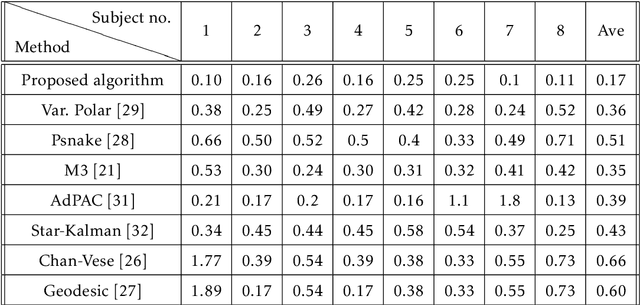
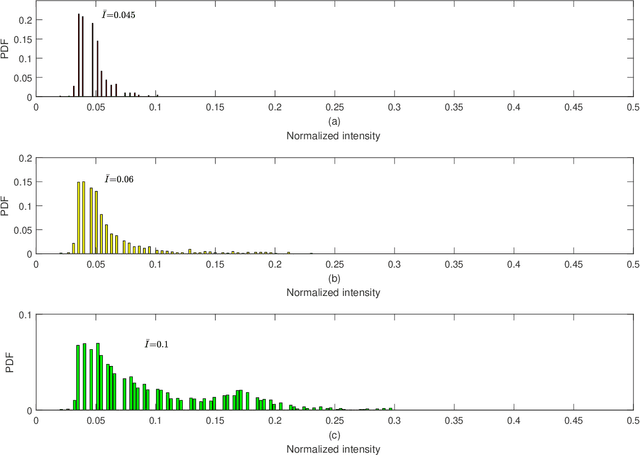
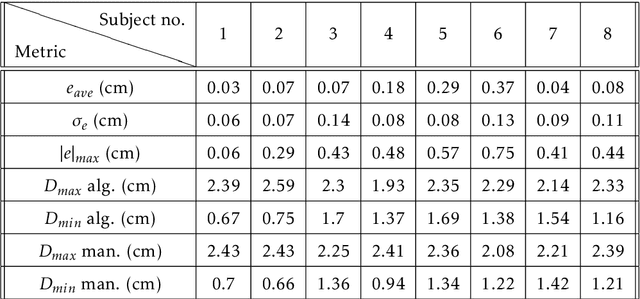
Abstract:Medical research suggests that the anterior-posterior (AP)-diameter of the inferior vena cava (IVC) and its associated temporal variation as imaged by bedside ultrasound is useful in guiding fluid resuscitation of the critically-ill patient. Unfortunately, indistinct edges and gaps in vessel walls are frequently present which impede accurate estimation of the IVC AP-diameter for both human operators and segmentation algorithms. The majority of research involving use of the IVC to guide fluid resuscitation involves manual measurement of the maximum and minimum AP-diameter as it varies over time. This effort proposes using a time-varying circle fitted inside the typically ellipsoid IVC as an efficient, consistent and novel approach to tracking and approximating the AP-diameter even in the context of poor image quality. In this active-circle algorithm, a novel evolution functional is proposed and shown to be a useful tool for ultrasound image processing. The proposed algorithm is compared with an expert manual measurement, and state-of-the-art relevant algorithms. It is shown that the algorithm outperforms other techniques and performs very close to manual measurement.
* Published in Computers in Biology and Medicine
Adaptive Polar Active Contour for Segmentation and Tracking in Ultrasound Videos
Mar 19, 2018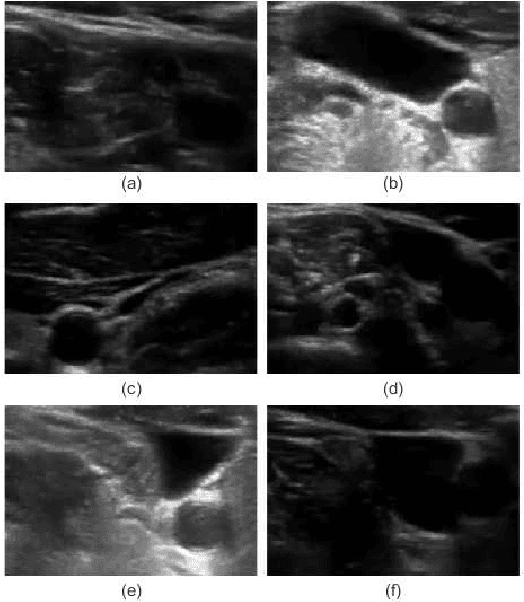
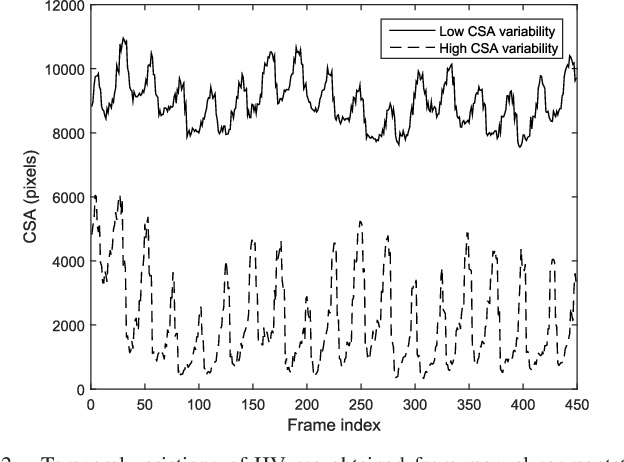
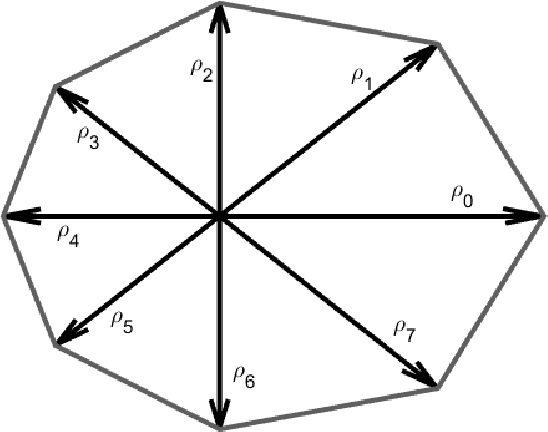
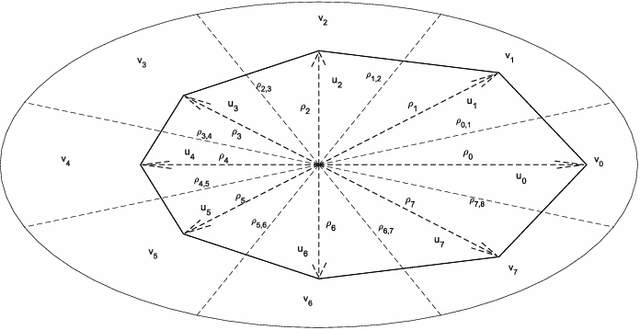
Abstract:Detection of relative changes in circulating blood volume is important to guide resuscitation and manage a variety of medical conditions including sepsis, trauma, dialysis and congestive heart failure. Recent studies have shown that estimates of circulating blood volume can be obtained from the cross-sectional area (CSA) of the internal jugular vein (IJV) from ultrasound images. However, accurate segmentation and tracking of the IJV in ultrasound imaging is a challenging task and is significantly influenced by a number of parameters such as the image quality, shape, and temporal variation. In this paper, we propose a novel adaptive polar active contour (Ad-PAC) algorithm for the segmentation and tracking of the IJV in ultrasound videos. In the proposed algorithm, the parameters of the Ad-PAC algorithm are adapted based on the results of segmentation in previous frames. The Ad-PAC algorithm is applied to 65 ultrasound videos captured from 13 healthy subjects, with each video containing 450 frames. The results show that spatial and temporal adaptation of the energy function significantly improves segmentation performance when compared to current state-of-the-art active contour algorithms.
Image Identification Using SIFT Algorithm: Performance Analysis against Different Image Deformations
Mar 13, 2018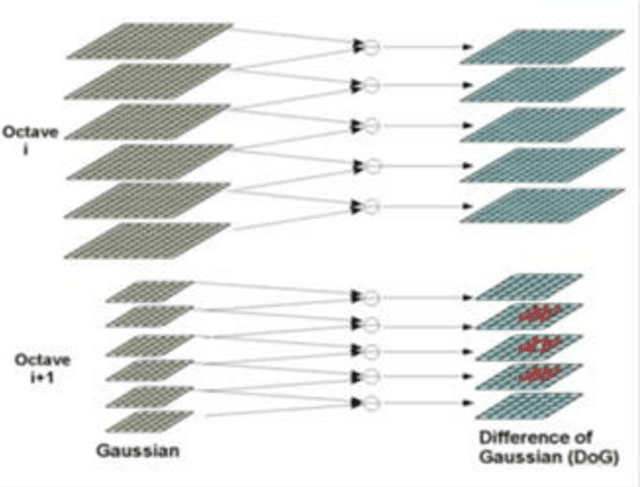
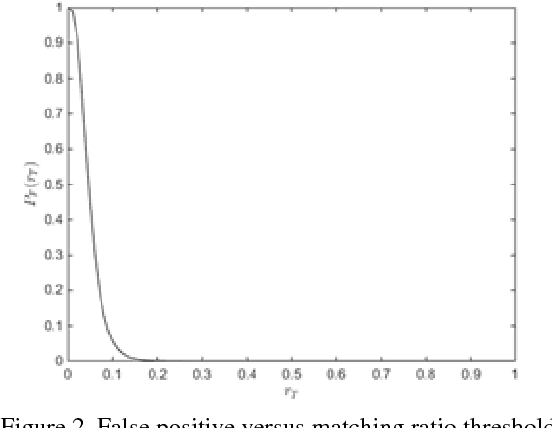
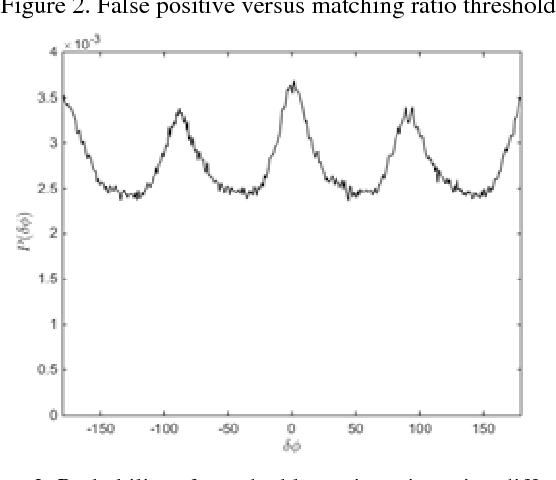
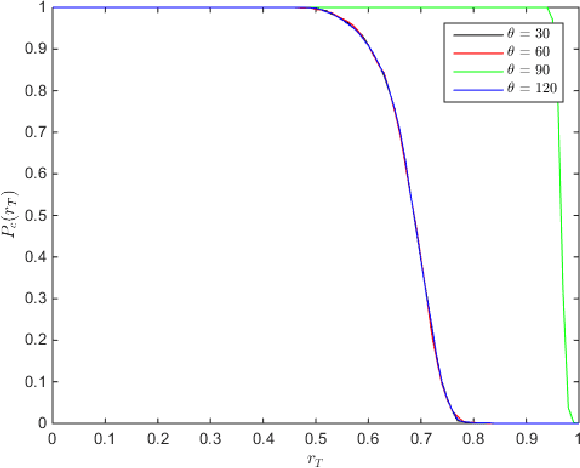
Abstract:Image identification is one of the most challenging tasks in different areas of computer vision. Scale-invariant feature transform is an algorithm to detect and describe local features in images to further use them as an image matching criteria. In this paper, the performance of the SIFT matching algorithm against various image distortions such as rotation, scaling, fisheye and motion distortion are evaluated and false and true positive rates for a large number of image pairs are calculated and presented. We also evaluate the distribution of the matched keypoint orientation difference for each image deformation.
Image Matching Using SIFT, SURF, BRIEF and ORB: Performance Comparison for Distorted Images
Oct 07, 2017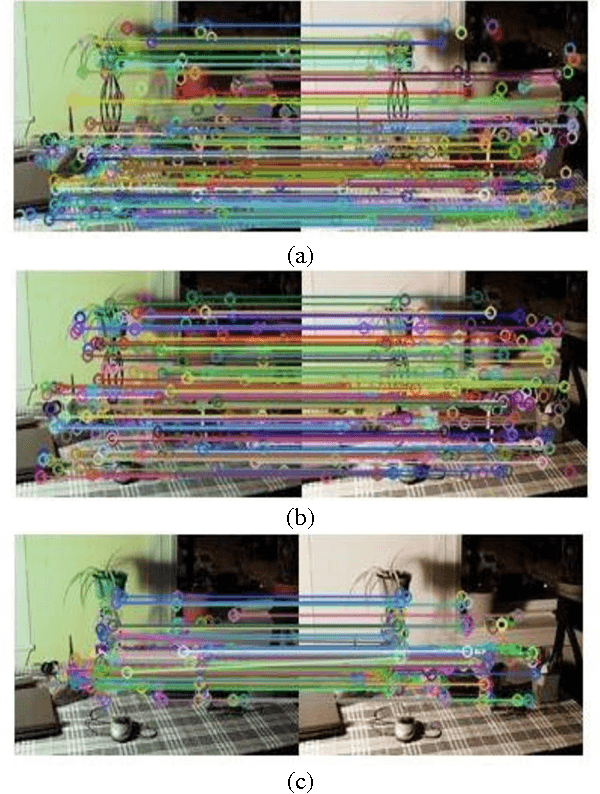
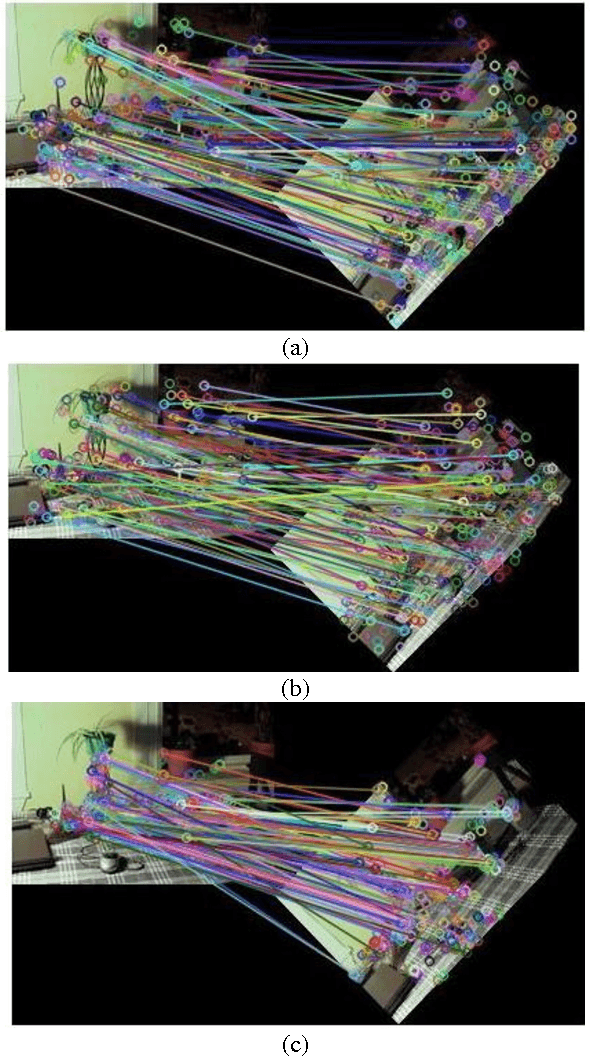

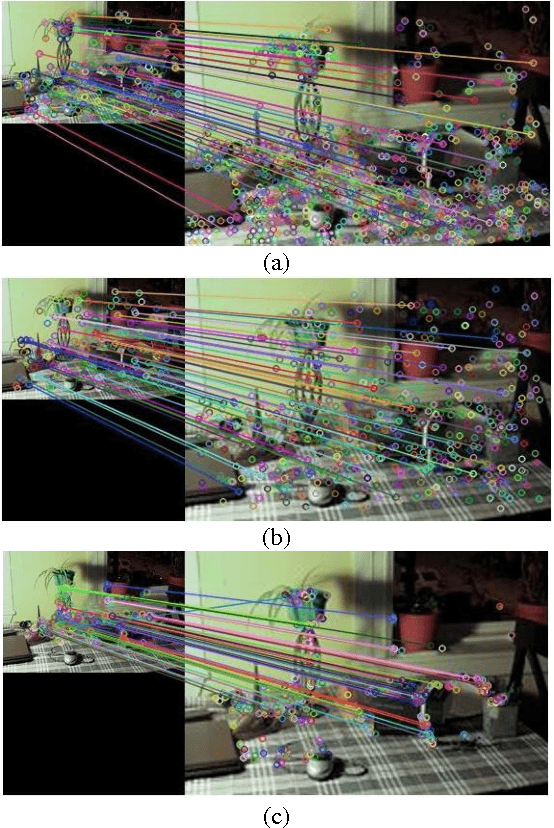
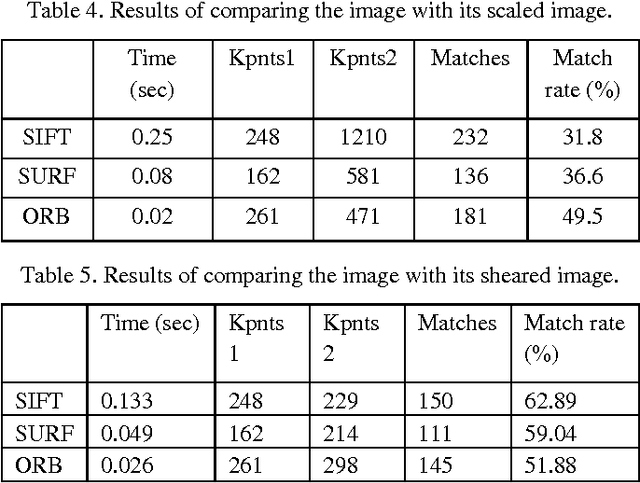
Abstract:Fast and robust image matching is a very important task with various applications in computer vision and robotics. In this paper, we compare the performance of three different image matching techniques, i.e., SIFT, SURF, and ORB, against different kinds of transformations and deformations such as scaling, rotation, noise, fish eye distortion, and shearing. For this purpose, we manually apply different types of transformations on original images and compute the matching evaluation parameters such as the number of key points in images, the matching rate, and the execution time required for each algorithm and we will show that which algorithm is the best more robust against each kind of distortion. Index Terms-Image matching, scale invariant feature transform (SIFT), speed up robust feature (SURF), robust independent elementary features (BRIEF), oriented FAST, rotated BRIEF (ORB).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge