EL Houcine Bergou
School of Computer Science-Mohammed VI Polytechnic University
EUREKHA: Enhancing User Representation for Key Hackers Identification in Underground Forums
Nov 08, 2024Abstract:Underground forums serve as hubs for cybercriminal activities, offering a space for anonymity and evasion of conventional online oversight. In these hidden communities, malicious actors collaborate to exchange illicit knowledge, tools, and tactics, driving a range of cyber threats from hacking techniques to the sale of stolen data, malware, and zero-day exploits. Identifying the key instigators (i.e., key hackers), behind these operations is essential but remains a complex challenge. This paper presents a novel method called EUREKHA (Enhancing User Representation for Key Hacker Identification in Underground Forums), designed to identify these key hackers by modeling each user as a textual sequence. This sequence is processed through a large language model (LLM) for domain-specific adaptation, with LLMs acting as feature extractors. These extracted features are then fed into a Graph Neural Network (GNN) to model user structural relationships, significantly improving identification accuracy. Furthermore, we employ BERTopic (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers Topic Modeling) to extract personalized topics from user-generated content, enabling multiple textual representations per user and optimizing the selection of the most representative sequence. Our study demonstrates that fine-tuned LLMs outperform state-of-the-art methods in identifying key hackers. Additionally, when combined with GNNs, our model achieves significant improvements, resulting in approximately 6% and 10% increases in accuracy and F1-score, respectively, over existing methods. EUREKHA was tested on the Hack-Forums dataset, and we provide open-source access to our code.
Minibatch Stochastic Three Points Method for Unconstrained Smooth Minimization
Sep 16, 2022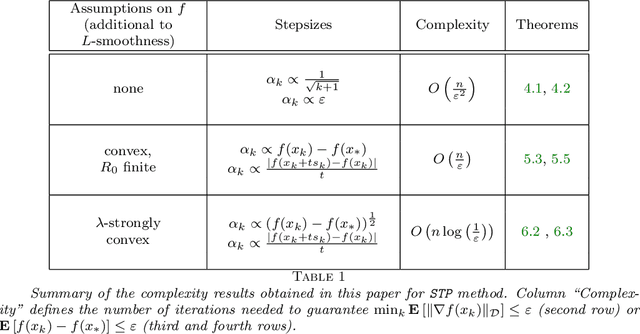
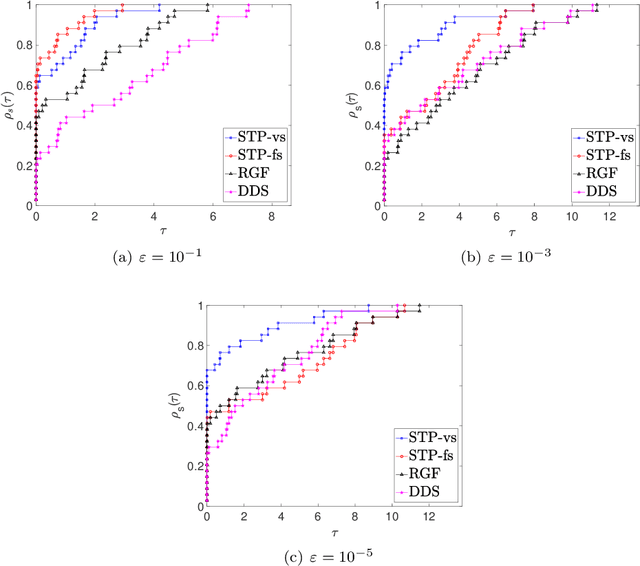
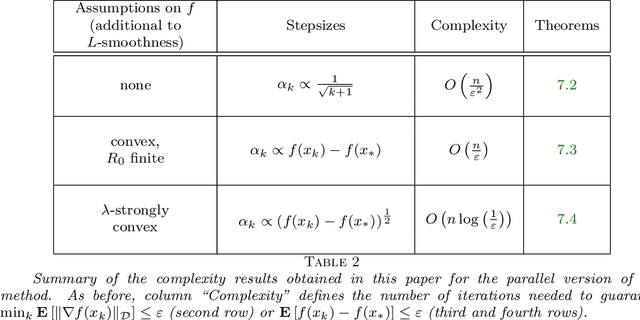
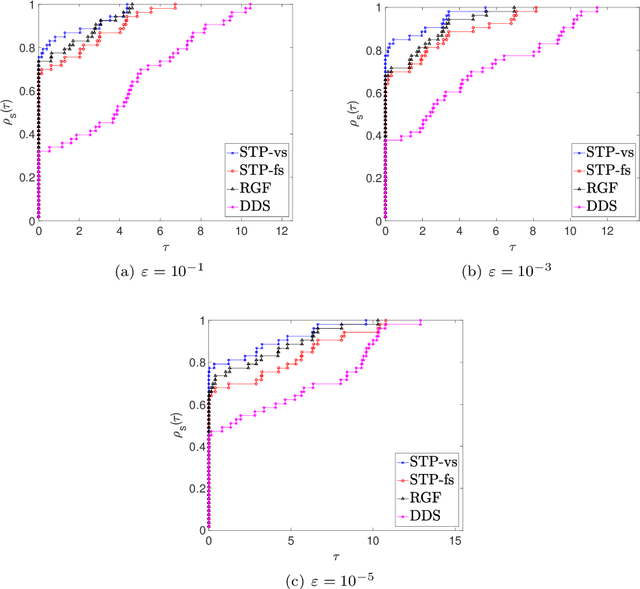
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new zero order optimization method called minibatch stochastic three points (MiSTP) method to solve an unconstrained minimization problem in a setting where only an approximation of the objective function evaluation is possible. It is based on the recently proposed stochastic three points (STP) method (Bergou et al., 2020). At each iteration, MiSTP generates a random search direction in a similar manner to STP, but chooses the next iterate based solely on the approximation of the objective function rather than its exact evaluations. We also analyze our method's complexity in the nonconvex and convex cases and evaluate its performance on multiple machine learning tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge