Dr. Anil Kumar Singh
A Comparative Study of Transformers on Word Sense Disambiguation
Nov 30, 2021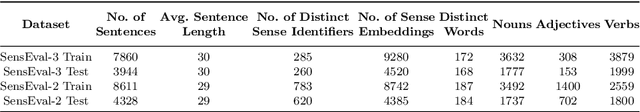
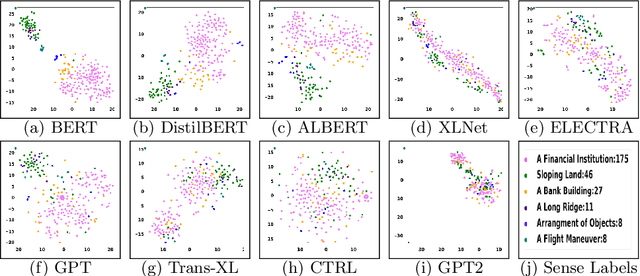
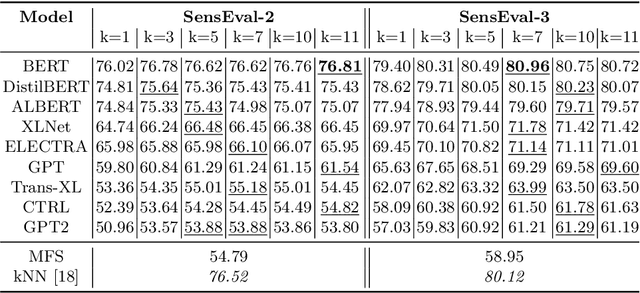
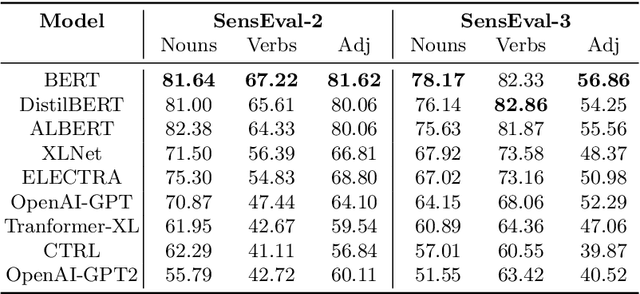
Abstract:Recent years of research in Natural Language Processing (NLP) have witnessed dramatic growth in training large models for generating context-aware language representations. In this regard, numerous NLP systems have leveraged the power of neural network-based architectures to incorporate sense information in embeddings, resulting in Contextualized Word Embeddings (CWEs). Despite this progress, the NLP community has not witnessed any significant work performing a comparative study on the contextualization power of such architectures. This paper presents a comparative study and an extensive analysis of nine widely adopted Transformer models. These models are BERT, CTRL, DistilBERT, OpenAI-GPT, OpenAI-GPT2, Transformer-XL, XLNet, ELECTRA, and ALBERT. We evaluate their contextualization power using two lexical sample Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) tasks, SensEval-2 and SensEval-3. We adopt a simple yet effective approach to WSD that uses a k-Nearest Neighbor (kNN) classification on CWEs. Experimental results show that the proposed techniques also achieve superior results over the current state-of-the-art on both the WSD tasks
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge