Dongmei Liu
Morphy: A Datamorphic Software Test Automation Tool
Dec 20, 2019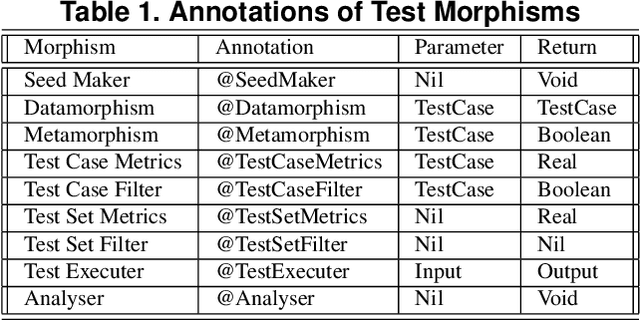
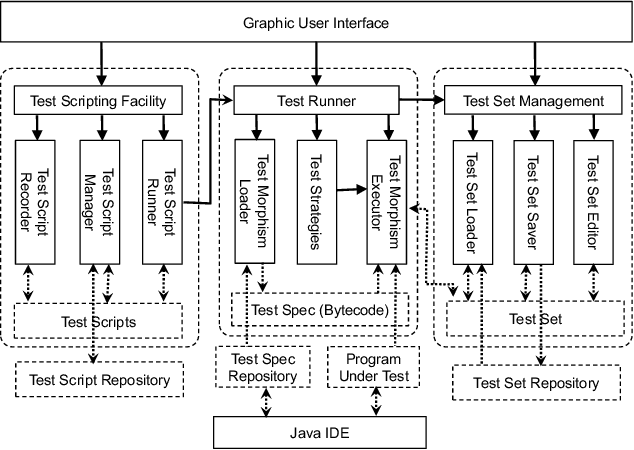
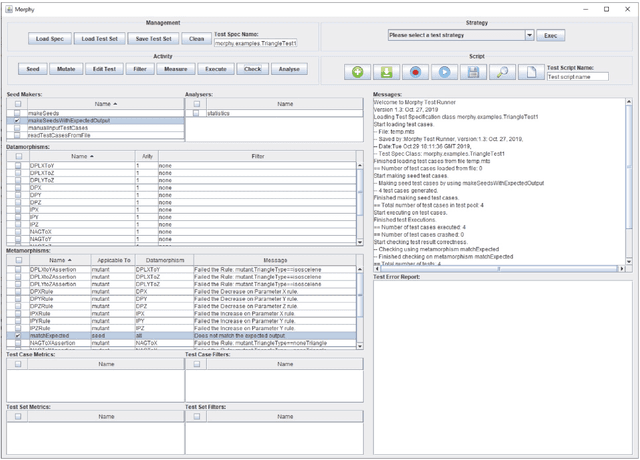
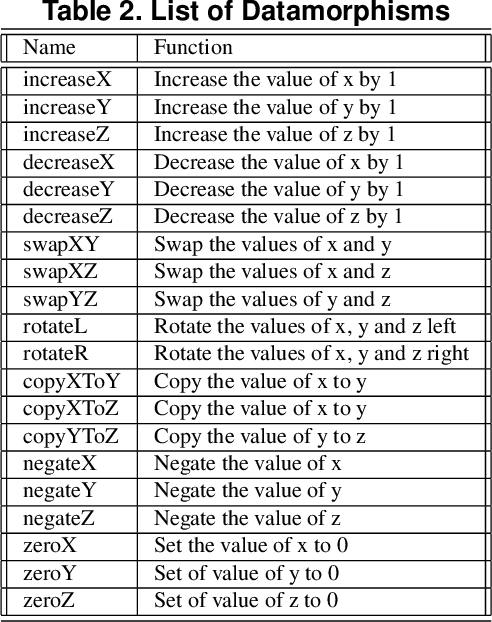
Abstract:This paper presents an automated tool called Morphy for datamorphic testing. It classifies software test artefacts into test entities and test morphisms, which are mappings on testing entities. In addition to datamorphisms, metamorphisms and seed test case makers, Morphy also employs a set of other test morphisms including test case metrics and filters, test set metrics and filters, test result analysers and test executers to realise test automation. In particular, basic testing activities can be automated by invoking test morphisms. Test strategies can be realised as complex combinations of test morphisms. Test processes can be automated by recording, editing and playing test scripts that invoke test morphisms and strategies. Three types of test strategies have been implemented in Morphy: datamorphism combination strategies, cluster border exploration strategies and strategies for test set optimisation via genetic algorithms. This paper focuses on the datamorphism combination strategies by giving their definitions and implementation algorithms. The paper also illustrates their uses for testing both traditional software and AI applications with three case studies.
Datamorphic Testing: A Methodology for Testing AI Applications
Dec 10, 2019



Abstract:With the rapid growth of the applications of machine learning (ML) and other artificial intelligence (AI) techniques, adequate testing has become a necessity to ensure their quality. This paper identifies the characteristics of AI applications that distinguish them from traditional software, and analyses the main difficulties in applying existing testing methods. Based on this analysis, we propose a new method called datamorphic testing and illustrate the method with an example of testing face recognition applications. We also report an experiment with four real industrial application systems of face recognition to validate the proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge