Donghee Han
Rethinking LLM-Based Recommendations: A Query Generation-Based, Training-Free Approach
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:Existing large language model LLM-based recommendation methods face several challenges, including inefficiency in handling large candidate pools, sensitivity to item order within prompts ("lost in the middle" phenomenon) poor scalability, and unrealistic evaluation due to random negative sampling. To address these issues, we propose a Query-to-Recommendation approach that leverages LLMs to generate personalized queries for retrieving relevant items from the entire candidate pool, eliminating the need for candidate pre-selection. This method can be integrated into an ID-based recommendation system without additional training, enhances recommendation performance and diversity through LLMs' world knowledge, and performs well even for less popular item groups. Experiments on three datasets show up to 57 percent improvement, with an average gain of 31 percent, demonstrating strong zero-shot performance and further gains when ensembled with existing models.
Closer through commonality: Enhancing hypergraph contrastive learning with shared groups
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Hypergraphs provide a superior modeling framework for representing complex multidimensional relationships in the context of real-world interactions that often occur in groups, overcoming the limitations of traditional homogeneous graphs. However, there have been few studies on hypergraphbased contrastive learning, and existing graph-based contrastive learning methods have not been able to fully exploit the highorder correlation information in hypergraphs. Here, we propose a Hypergraph Fine-grained contrastive learning (HyFi) method designed to exploit the complex high-dimensional information inherent in hypergraphs. While avoiding traditional graph augmentation methods that corrupt the hypergraph topology, the proposed method provides a simple and efficient learning augmentation function by adding noise to node features. Furthermore, we expands beyond the traditional dichotomous relationship between positive and negative samples in contrastive learning by introducing a new relationship of weak positives. It demonstrates the importance of fine-graining positive samples in contrastive learning. Therefore, HyFi is able to produce highquality embeddings, and outperforms both supervised and unsupervised baselines in average rank on node classification across 10 datasets. Our approach effectively exploits high-dimensional hypergraph information, shows significant improvement over existing graph-based contrastive learning methods, and is efficient in terms of training speed and GPU memory cost. The source code is available at https://github.com/Noverse0/HyFi.git.
ProbGate at EHRSQL 2024: Enhancing SQL Query Generation Accuracy through Probabilistic Threshold Filtering and Error Handling
Apr 25, 2024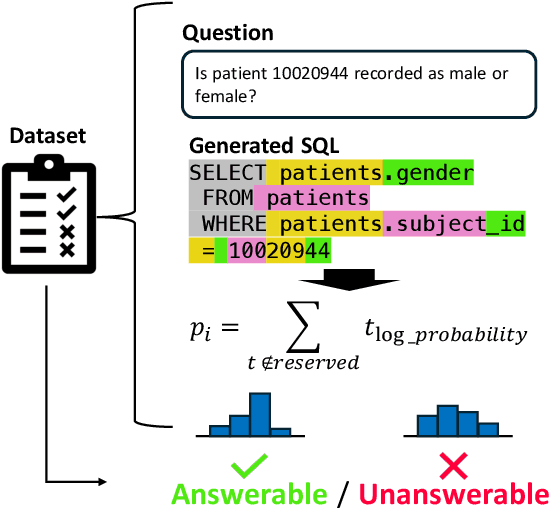
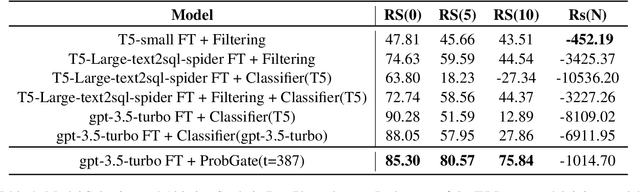
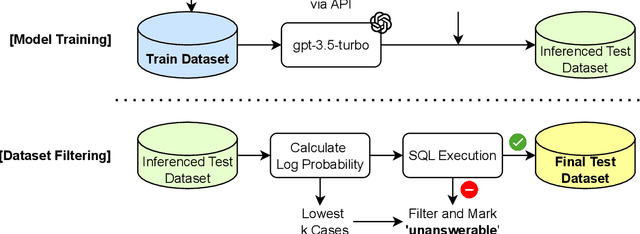
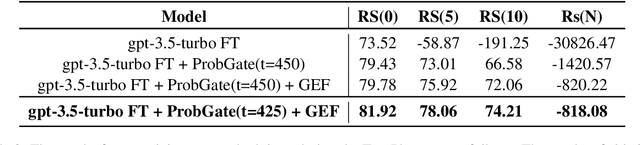
Abstract:Recently, deep learning-based language models have significantly enhanced text-to-SQL tasks, with promising applications in retrieving patient records within the medical domain. One notable challenge in such applications is discerning unanswerable queries. Through fine-tuning model, we demonstrate the feasibility of converting medical record inquiries into SQL queries. Additionally, we introduce an entropy-based method to identify and filter out unanswerable results. We further enhance result quality by filtering low-confidence SQL through log probability-based distribution, while grammatical and schema errors are mitigated by executing queries on the actual database. We experimentally verified that our method can filter unanswerable questions, which can be widely utilized even when the parameters of the model are not accessible, and that it can be effectively utilized in practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge