Dmitrijs Trizna
SLIFER: Investigating Performance and Robustness of Malware Detection Pipelines
May 23, 2024

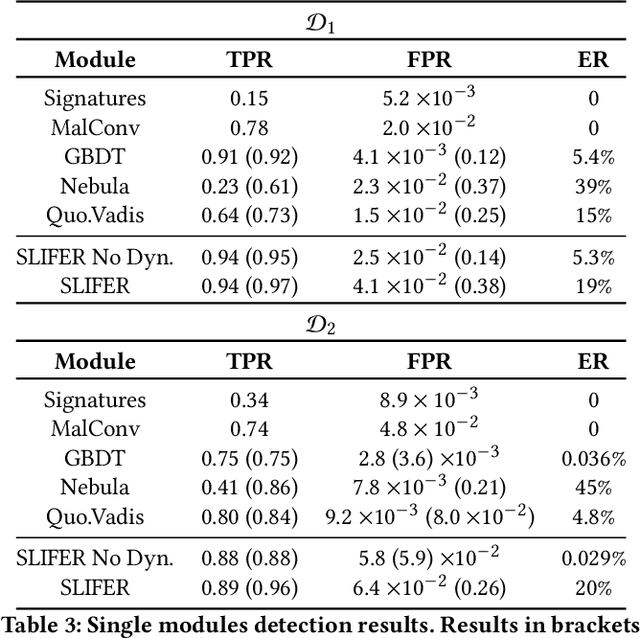

Abstract:As a result of decades of research, Windows malware detection is approached through a plethora of techniques. However, there is an ongoing mismatch between academia -- which pursues an optimal performances in terms of detection rate and low false alarms -- and the requirements of real-world scenarios. In particular, academia focuses on combining static and dynamic analysis within a single or ensemble of models, falling into several pitfalls like (i) firing dynamic analysis without considering the computational burden it requires; (ii) discarding impossible-to-analyse samples; and (iii) analysing robustness against adversarial attacks without considering that malware detectors are complemented with more non-machine-learning components. Thus, in this paper we propose SLIFER, a novel Windows malware detection pipeline sequentially leveraging both static and dynamic analysis, interrupting computations as soon as one module triggers an alarm, requiring dynamic analysis only when needed. Contrary to the state of the art, we investigate how to deal with samples resistance to analysis, showing how much they impact performances, concluding that it is better to flag them as legitimate to not drastically increase false alarms. Lastly, we perform a robustness evaluation of SLIFER leveraging content-injections attacks, and we show that, counter-intuitively, attacks are blocked more by YARA rules than dynamic analysis due to byte artifacts created while optimizing the adversarial strategy.
Living-off-The-Land Reverse-Shell Detection by Informed Data Augmentation
Feb 28, 2024



Abstract:The living-off-the-land (LOTL) offensive methodologies rely on the perpetration of malicious actions through chains of commands executed by legitimate applications, identifiable exclusively by analysis of system logs. LOTL techniques are well hidden inside the stream of events generated by common legitimate activities, moreover threat actors often camouflage activity through obfuscation, making them particularly difficult to detect without incurring in plenty of false alarms, even using machine learning. To improve the performance of models in such an harsh environment, we propose an augmentation framework to enhance and diversify the presence of LOTL malicious activity inside legitimate logs. Guided by threat intelligence, we generate a dataset by injecting attack templates known to be employed in the wild, further enriched by malleable patterns of legitimate activities to replicate the behavior of evasive threat actors. We conduct an extensive ablation study to understand which models better handle our augmented dataset, also manipulated to mimic the presence of model-agnostic evasion and poisoning attacks. Our results suggest that augmentation is needed to maintain high-predictive capabilities, robustness to attack is achieved through specific hardening techniques like adversarial training, and it is possible to deploy near-real-time models with almost-zero false alarms.
Quo Vadis: Hybrid Machine Learning Meta-Model based on Contextual and Behavioral Malware Representations
Aug 20, 2022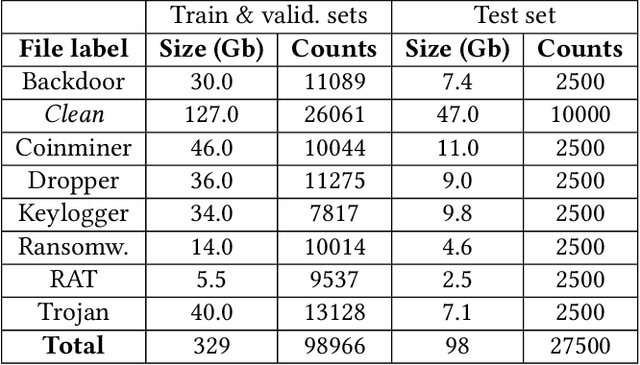

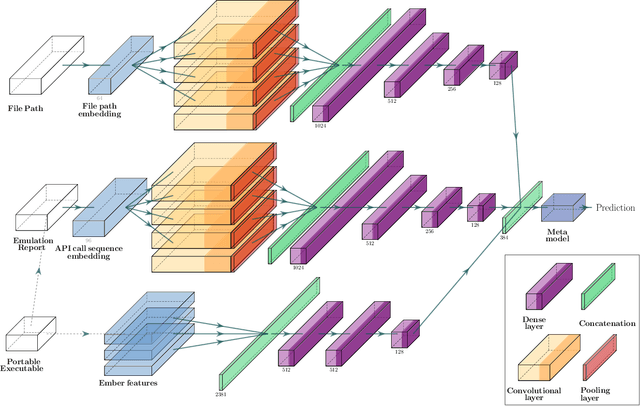
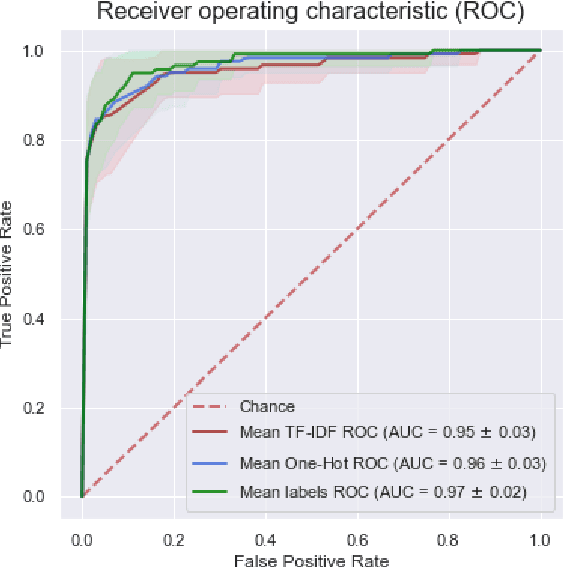
Abstract:We propose a hybrid machine learning architecture that simultaneously employs multiple deep learning models analyzing contextual and behavioral characteristics of Windows portable executable, producing a final prediction based on a decision from the meta-model. The detection heuristic in contemporary machine learning Windows malware classifiers is typically based on the static properties of the sample since dynamic analysis through virtualization is challenging for vast quantities of samples. To surpass this limitation, we employ a Windows kernel emulation that allows the acquisition of behavioral patterns across large corpora with minimal temporal and computational costs. We partner with a security vendor for a collection of more than 100k int-the-wild samples that resemble the contemporary threat landscape, containing raw PE files and filepaths of applications at the moment of execution. The acquired dataset is at least ten folds larger than reported in related works on behavioral malware analysis. Files in the training dataset are labeled by a professional threat intelligence team, utilizing manual and automated reverse engineering tools. We estimate the hybrid classifier's operational utility by collecting an out-of-sample test set three months later from the acquisition of the training set. We report an improved detection rate, above the capabilities of the current state-of-the-art model, especially under low false-positive requirements. Additionally, we uncover a meta-model's ability to identify malicious activity in validation and test sets even if none of the individual models express enough confidence to mark the sample as malevolent. We conclude that the meta-model can learn patterns typical to malicious samples from representation combinations produced by different analysis techniques. We publicly release pre-trained models and anonymized dataset of emulation reports.
Shell Language Processing: Unix command parsing for Machine Learning
Jul 06, 2021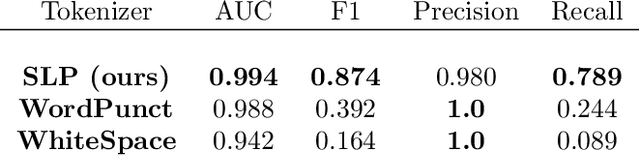
Abstract:In this article, we present a Shell Language Preprocessing (SLP) library, which implements tokenization and encoding directed on the parsing of Unix and Linux shell commands. We describe the rationale behind the need for a new approach with specific examples when conventional Natural Language Processing (NLP) pipelines fail. Furthermore, we evaluate our methodology on a security classification task against widely accepted information and communications technology (ICT) tokenization techniques and achieve significant improvement of an F1-score from 0.392 to 0.874.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge