Divya Bhargavi
Impression-Informed Multi-Behavior Recommender System: A Hierarchical Graph Attention Approach
Sep 07, 2023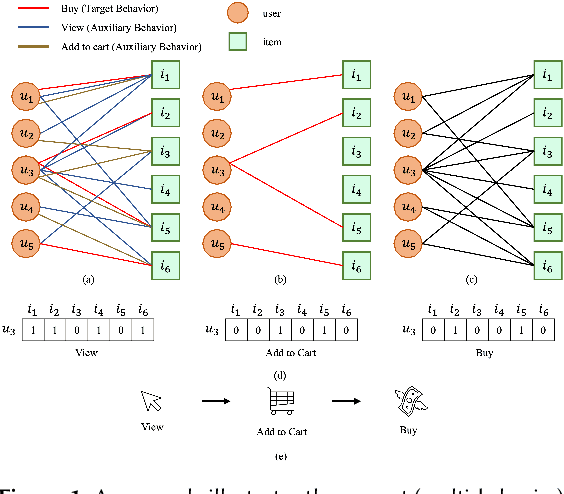

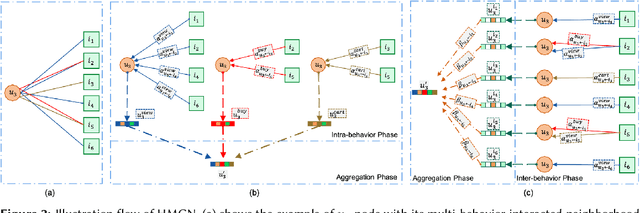

Abstract:While recommender systems have significantly benefited from implicit feedback, they have often missed the nuances of multi-behavior interactions between users and items. Historically, these systems either amalgamated all behaviors, such as \textit{impression} (formerly \textit{view}), \textit{add-to-cart}, and \textit{buy}, under a singular 'interaction' label, or prioritized only the target behavior, often the \textit{buy} action, discarding valuable auxiliary signals. Although recent advancements tried addressing this simplification, they primarily gravitated towards optimizing the target behavior alone, battling with data scarcity. Additionally, they tended to bypass the nuanced hierarchy intrinsic to behaviors. To bridge these gaps, we introduce the \textbf{H}ierarchical \textbf{M}ulti-behavior \textbf{G}raph Attention \textbf{N}etwork (HMGN). This pioneering framework leverages attention mechanisms to discern information from both inter and intra-behaviors while employing a multi-task Hierarchical Bayesian Personalized Ranking (HBPR) for optimization. Recognizing the need for scalability, our approach integrates a specialized multi-behavior sub-graph sampling technique. Moreover, the adaptability of HMGN allows for the seamless inclusion of knowledge metadata and time-series data. Empirical results attest to our model's prowess, registering a notable performance boost of up to 64\% in NDCG@100 metrics over conventional graph neural network methods.
Framework for 2D Ad placements in LinearTV
Dec 05, 2022



Abstract:Virtual Product placement(VPP) is the advertising technique of digitally placing a branded object into the scene of a movie or TV show. This type of advertising provides the ability for brands to reach consumers without interrupting the viewing experience with a commercial break, as the products are seen in the background or as props. Despite this being a billion-dollar industry, ad rendering technique is currently executed at post production stage, manually either with the help of VFx artists or through semi-automated solutions. In this paper, we demonstrate a fully automated framework to digitally place 2-D ads in linear TV cooking shows captured using single-view camera with small camera movements. Without access to full video or production camera configuration, this framework performs the following tasks (i) identifying empty space for 2-D ad placement (ii) kitchen scene understanding (iii) occlusion handling (iv) ambient lighting and (v) ad tracking.
Knock, knock. Who's there? -- Identifying football player jersey numbers with synthetic data
Apr 04, 2022
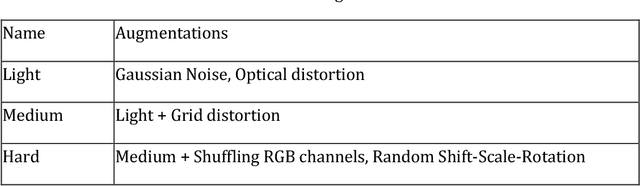

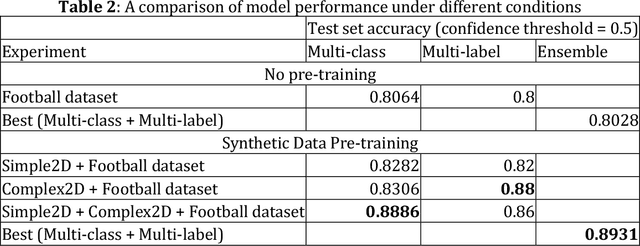
Abstract:Automatic player identification is an essential and complex task in sports video analysis. Different strategies have been devised over the years, but identification based on jersey numbers is one of the most common approaches given its versatility and relative simplicity. However, automatic detection of jersey numbers is still challenging due to changing camera angles, low video resolution, small object size in wide-range shots and transient changes in the player's posture and movement. In this paper we present a novel approach for jersey number identification in a small, highly imbalanced dataset from the Seattle Seahawks practice videos. Our results indicate that simple models can achieve an acceptable performance on the jersey number detection task and that synthetic data can improve the performance dramatically (accuracy increase of ~9% overall, ~18% on low frequency numbers) making our approach achieve state of the art results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge