Dinh-Viet-Toan Le
Evaluating Interval-based Tokenization for Pitch Representation in Symbolic Music Analysis
Jan 08, 2025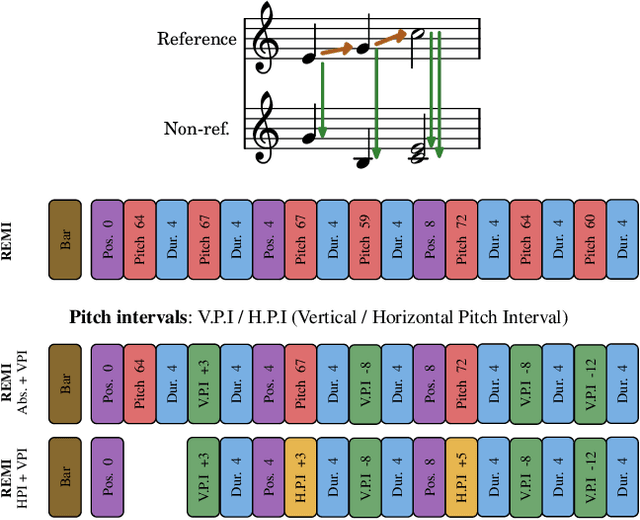
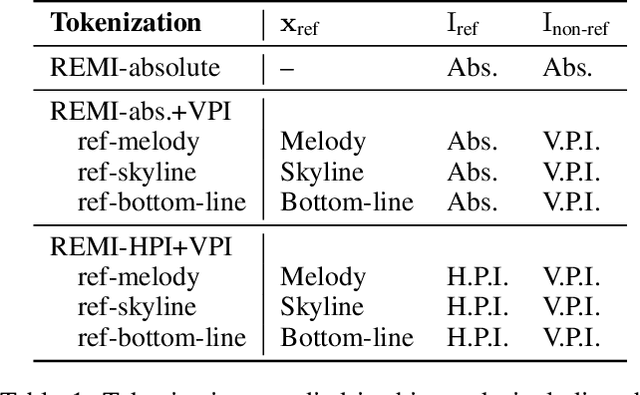
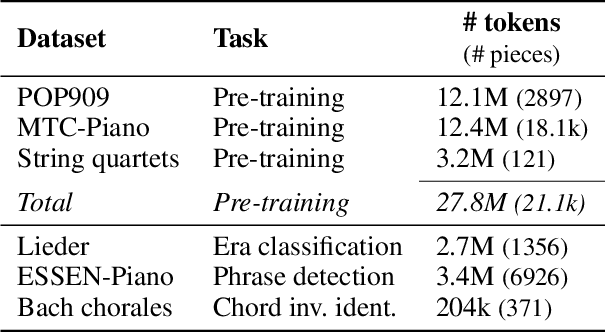
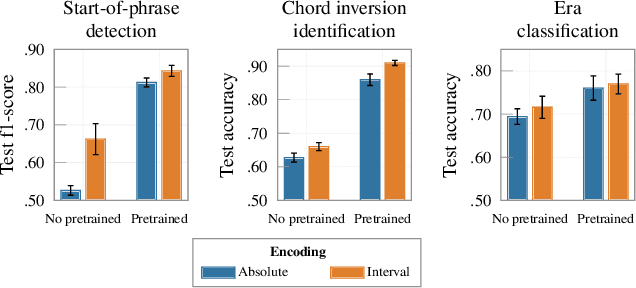
Abstract:Symbolic music analysis tasks are often performed by models originally developed for Natural Language Processing, such as Transformers. Such models require the input data to be represented as sequences, which is achieved through a process of tokenization. Tokenization strategies for symbolic music often rely on absolute MIDI values to represent pitch information. However, music research largely promotes the benefit of higher-level representations such as melodic contour and harmonic relations for which pitch intervals turn out to be more expressive than absolute pitches. In this work, we introduce a general framework for building interval-based tokenizations. By evaluating these tokenizations on three music analysis tasks, we show that such interval-based tokenizations improve model performances and facilitate their explainability.
Analyzing Byte-Pair Encoding on Monophonic and Polyphonic Symbolic Music: A Focus on Musical Phrase Segmentation
Oct 02, 2024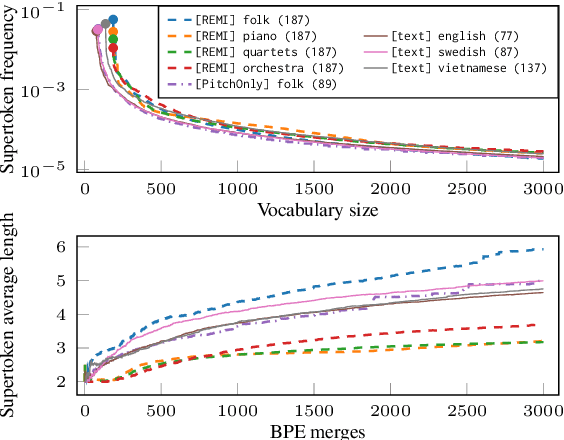
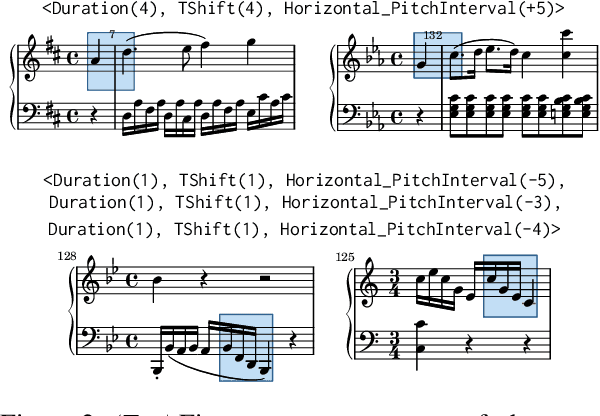
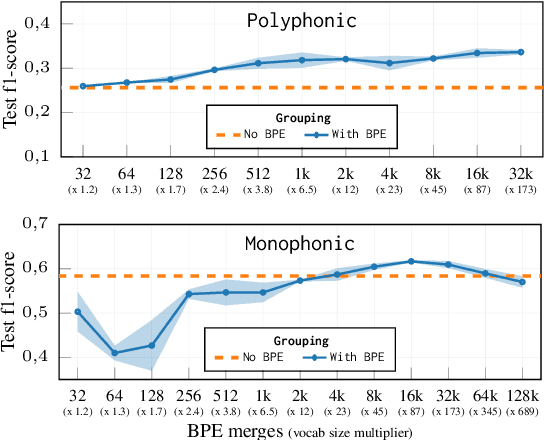
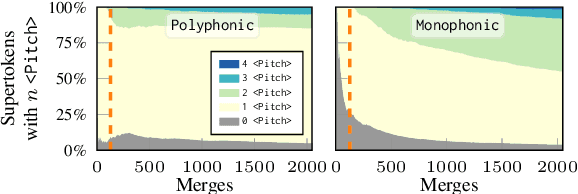
Abstract:Byte-Pair Encoding (BPE) is an algorithm commonly used in Natural Language Processing to build a vocabulary of subwords, which has been recently applied to symbolic music. Given that symbolic music can differ significantly from text, particularly with polyphony, we investigate how BPE behaves with different types of musical content. This study provides a qualitative analysis of BPE's behavior across various instrumentations and evaluates its impact on a musical phrase segmentation task for both monophonic and polyphonic music. Our findings show that the BPE training process is highly dependent on the instrumentation and that BPE "supertokens" succeed in capturing abstract musical content. In a musical phrase segmentation task, BPE notably improves performance in a polyphonic setting, but enhances performance in monophonic tunes only within a specific range of BPE merges.
METEOR: Melody-aware Texture-controllable Symbolic Orchestral Music Generation
Sep 18, 2024



Abstract:Western music is often characterized by a homophonic texture, in which the musical content can be organized into a melody and an accompaniment. In orchestral music, in particular, the composer can select specific characteristics for each instrument's part within the accompaniment, while also needing to adapt the melody to suit the capabilities of the instruments performing it. In this work, we propose METEOR, a model for Melody-aware Texture-controllable Orchestral music generation. This model performs symbolic multi-track music style transfer with a focus on melodic fidelity. We allow bar- and track-level controllability of the accompaniment with various textural attributes while keeping a homophonic texture. We show that the model can achieve controllability performances similar to strong baselines while greatly improve melodic fidelity.
Natural Language Processing Methods for Symbolic Music Generation and Information Retrieval: a Survey
Feb 27, 2024Abstract:Several adaptations of Transformers models have been developed in various domains since its breakthrough in Natural Language Processing (NLP). This trend has spread into the field of Music Information Retrieval (MIR), including studies processing music data. However, the practice of leveraging NLP tools for symbolic music data is not novel in MIR. Music has been frequently compared to language, as they share several similarities, including sequential representations of text and music. These analogies are also reflected through similar tasks in MIR and NLP. This survey reviews NLP methods applied to symbolic music generation and information retrieval studies following two axes. We first propose an overview of representations of symbolic music adapted from natural language sequential representations. Such representations are designed by considering the specificities of symbolic music. These representations are then processed by models. Such models, possibly originally developed for text and adapted for symbolic music, are trained on various tasks. We describe these models, in particular deep learning models, through different prisms, highlighting music-specialized mechanisms. We finally present a discussion surrounding the effective use of NLP tools for symbolic music data. This includes technical issues regarding NLP methods and fundamental differences between text and music, which may open several doors for further research into more effectively adapting NLP tools to symbolic MIR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge