Dimitris Pados
Kernel Regression of Multi-Way Data via Tensor Trains with Hadamard Overparametrization: The Dynamic Graph Flow Case
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:A regression-based framework for interpretable multi-way data imputation, termed Kernel Regression via Tensor Trains with Hadamard overparametrization (KReTTaH), is introduced. KReTTaH adopts a nonparametric formulation by casting imputation as regression via reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces. Parameter efficiency is achieved through tensors of fixed tensor-train (TT) rank, which reside on low-dimensional Riemannian manifolds, and is further enhanced via Hadamard overparametrization, which promotes sparsity within the TT parameter space. Learning is accomplished by solving a smooth inverse problem posed on the Riemannian manifold of fixed TT-rank tensors. As a representative application, the estimation of dynamic graph flows is considered. In this setting, KReTTaH exhibits flexibility by seamlessly incorporating graph-based (topological) priors via its inverse problem formulation. Numerical tests on real-world graph datasets demonstrate that KReTTaH consistently outperforms state-of-the-art alternatives-including a nonparametric tensor- and a neural-network-based methods-for imputing missing, time-varying edge flows.
Imputation of Time-varying Edge Flows in Graphs by Multilinear Kernel Regression and Manifold Learning
Sep 08, 2024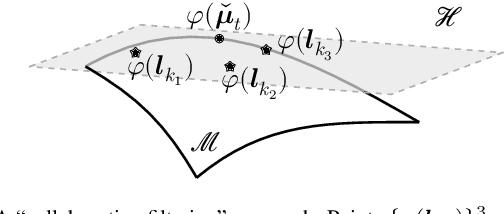
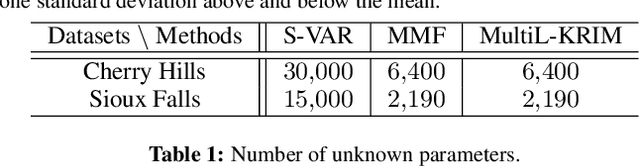
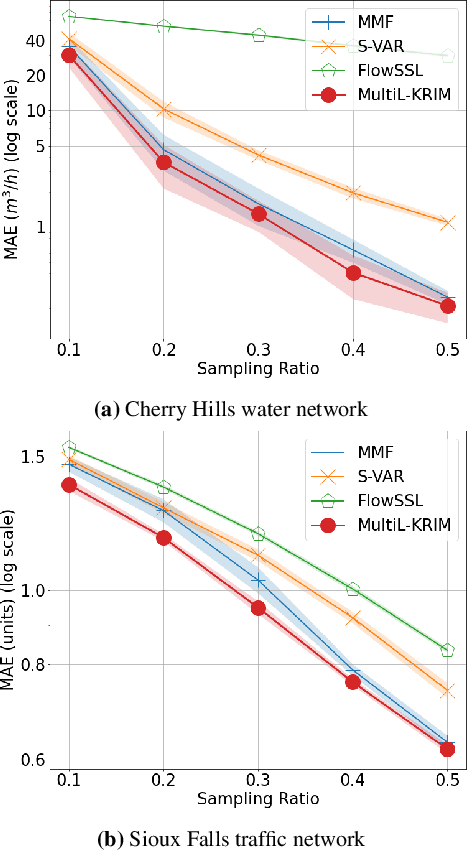
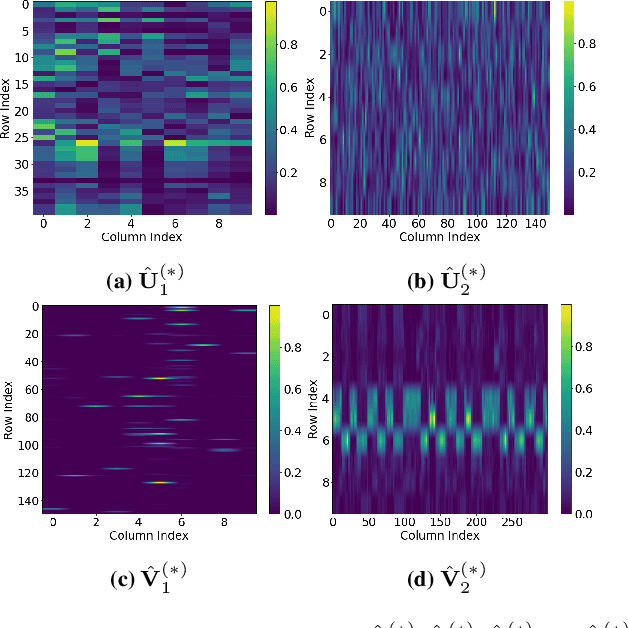
Abstract:This paper extends the recently developed framework of multilinear kernel regression and imputation via manifold learning (MultiL-KRIM) to impute time-varying edge flows in a graph. MultiL-KRIM uses simplicial-complex arguments and Hodge Laplacians to incorporate the graph topology, and exploits manifold-learning arguments to identify latent geometries within features which are modeled as a point-cloud around a smooth manifold embedded in a reproducing kernel Hilbert space (RKHS). Following the concept of tangent spaces to smooth manifolds, linear approximating patches are used to add a collaborative-filtering flavor to the point-cloud approximations. Together with matrix factorizations, MultiL-KRIM effects dimensionality reduction, and enables efficient computations, without any training data or additional information. Numerical tests on real-network time-varying edge flows demonstrate noticeable improvements of MultiL-KRIM over several state-of-the-art schemes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge