Dhruv Mittal
Two-stage Early Prediction Framework of Remaining Useful Life for Lithium-ion Batteries
Aug 07, 2023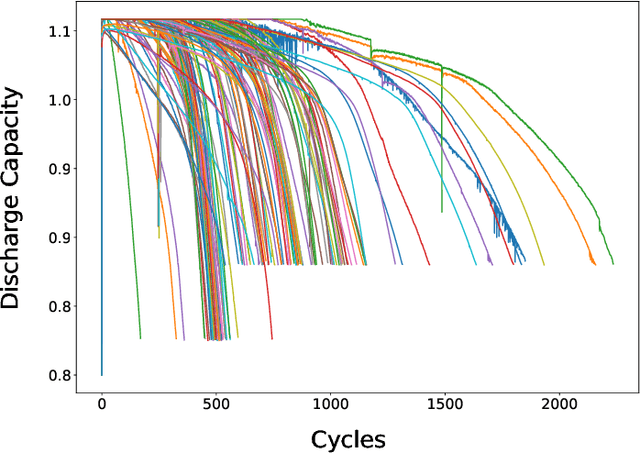
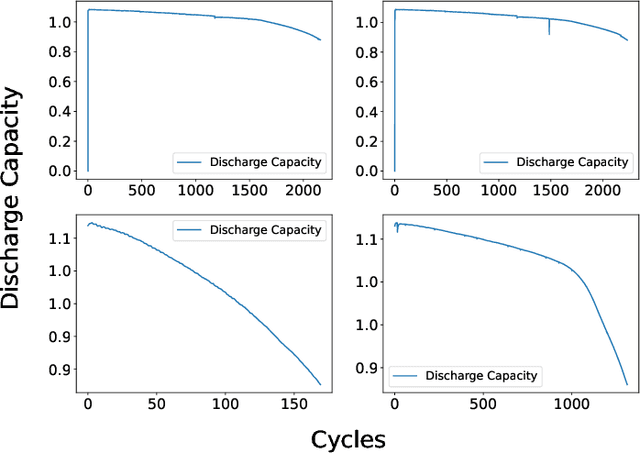

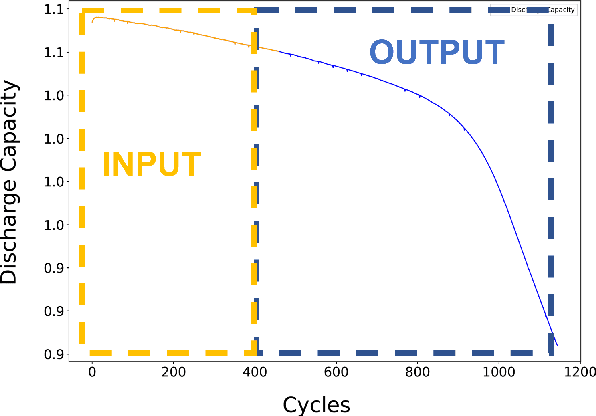
Abstract:Early prediction of remaining useful life (RUL) is crucial for effective battery management across various industries, ranging from household appliances to large-scale applications. Accurate RUL prediction improves the reliability and maintainability of battery technology. However, existing methods have limitations, including assumptions of data from the same sensors or distribution, foreknowledge of the end of life (EOL), and neglect to determine the first prediction cycle (FPC) to identify the start of the unhealthy stage. This paper proposes a novel method for RUL prediction of Lithium-ion batteries. The proposed framework comprises two stages: determining the FPC using a neural network-based model to divide the degradation data into distinct health states and predicting the degradation pattern after the FPC to estimate the remaining useful life as a percentage. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms conventional approaches in terms of RUL prediction. Furthermore, the proposed method shows promise for real-world scenarios, providing improved accuracy and applicability for battery management.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge