Dharshana Kasthurirathna
GADS: A Super Lightweight Model for Head Pose Estimation
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:In human-computer interaction, head pose estimation profoundly influences application functionality. Although utilizing facial landmarks is valuable for this purpose, existing landmark-based methods prioritize precision over simplicity and model size, limiting their deployment on edge devices and in compute-poor environments. To bridge this gap, we propose \textbf{Grouped Attention Deep Sets (GADS)}, a novel architecture based on the Deep Set framework. By grouping landmarks into regions and employing small Deep Set layers, we reduce computational complexity. Our multihead attention mechanism extracts and combines inter-group information, resulting in a model that is $7.5\times$ smaller and executes $25\times$ faster than the current lightest state-of-the-art model. Notably, our method achieves an impressive reduction, being $4321\times$ smaller than the best-performing model. We introduce vanilla GADS and Hybrid-GADS (landmarks + RGB) and evaluate our models on three benchmark datasets -- AFLW2000, BIWI, and 300W-LP. We envision our architecture as a robust baseline for resource-constrained head pose estimation methods.
Enhancing Multilingual Sentiment Analysis with Explainability for Sinhala, English, and Code-Mixed Content
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:Sentiment analysis is crucial for brand reputation management in the banking sector, where customer feedback spans English, Sinhala, Singlish, and code-mixed text. Existing models struggle with low-resource languages like Sinhala and lack interpretability for practical use. This research develops a hybrid aspect-based sentiment analysis framework that enhances multilingual capabilities with explainable outputs. Using cleaned banking customer reviews, we fine-tune XLM-RoBERTa for Sinhala and code-mixed text, integrate domain-specific lexicon correction, and employ BERT-base-uncased for English. The system classifies sentiment (positive, neutral, negative) with confidence scores, while SHAP and LIME improve interpretability by providing real-time sentiment explanations. Experimental results show that our approaches outperform traditional transformer-based classifiers, achieving 92.3 percent accuracy and an F1-score of 0.89 in English and 88.4 percent in Sinhala and code-mixed content. An explainability analysis reveals key sentiment drivers, improving trust and transparency. A user-friendly interface delivers aspect-wise sentiment insights, ensuring accessibility for businesses. This research contributes to robust, transparent sentiment analysis for financial applications by bridging gaps in multilingual, low-resource NLP and explainability.
Keyword Extraction, and Aspect Classification in Sinhala, English, and Code-Mixed Content
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Brand reputation in the banking sector is maintained through insightful analysis of customer opinion on code-mixed and multilingual content. Conventional NLP models misclassify or ignore code-mixed text, when mix with low resource languages such as Sinhala-English and fail to capture domain-specific knowledge. This study introduces a hybrid NLP method to improve keyword extraction, content filtering, and aspect-based classification of banking content. Keyword extraction in English is performed with a hybrid approach comprising a fine-tuned SpaCy NER model, FinBERT-based KeyBERT embeddings, YAKE, and EmbedRank, which results in a combined accuracy of 91.2%. Code-mixed and Sinhala keywords are extracted using a fine-tuned XLM-RoBERTa model integrated with a domain-specific Sinhala financial vocabulary, and it results in an accuracy of 87.4%. To ensure data quality, irrelevant comment filtering was performed using several models, with the BERT-base-uncased model achieving 85.2% for English and XLM-RoBERTa 88.1% for Sinhala, which was better than GPT-4o, SVM, and keyword-based filtering. Aspect classification followed the same pattern, with the BERT-base-uncased model achieving 87.4% for English and XLM-RoBERTa 85.9% for Sinhala, both exceeding GPT-4 and keyword-based approaches. These findings confirm that fine-tuned transformer models outperform traditional methods in multilingual financial text analysis. The present framework offers an accurate and scalable solution for brand reputation monitoring in code-mixed and low-resource banking environments.
2D Pose Estimation based Child Action Recognition
Dec 18, 2022Abstract:We present a graph convolutional network with 2D pose estimation for the first time on child action recognition task achieving on par results with an RGB modality based model on a novel benchmark dataset containing unconstrained environment based videos.
Graph Neural Network based Child Activity Recognition
Dec 18, 2022Abstract:This paper presents an implementation on child activity recognition (CAR) with a graph convolution network (GCN) based deep learning model since prior implementations in this domain have been dominated by CNN, LSTM and other methods despite the superior performance of GCN. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to use a GCN model in child activity recognition domain. In overcoming the challenges of having small size publicly available child action datasets, several learning methods such as feature extraction, fine-tuning and curriculum learning were implemented to improve the model performance. Inspired by the contradicting claims made on the use of transfer learning in CAR, we conducted a detailed implementation and analysis on transfer learning together with a study on negative transfer learning effect on CAR as it hasn't been addressed previously. As the principal contribution, we were able to develop a ST-GCN based CAR model which, despite the small size of the dataset, obtained around 50% accuracy on vanilla implementations. With feature extraction and fine-tuning methods, accuracy was improved by 20%-30% with the highest accuracy being 82.24%. Furthermore, the results provided on activity datasets empirically demonstrate that with careful selection of pre-train model datasets through methods such as curriculum learning could enhance the accuracy levels. Finally, we provide preliminary evidence on possible frame rate effect on the accuracy of CAR models, a direction future research can explore.
MNet-Sim: A Multi-layered Semantic Similarity Network to Evaluate Sentence Similarity
Nov 09, 2021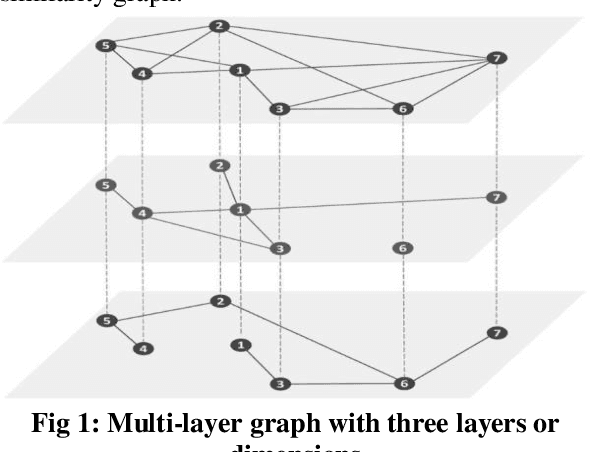
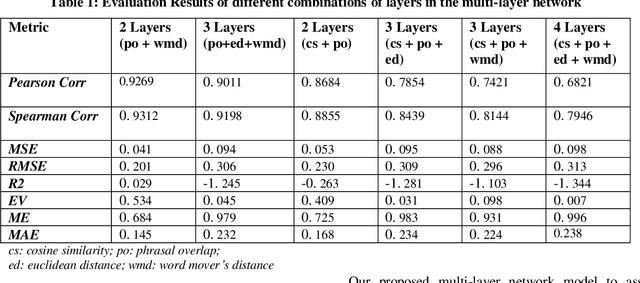

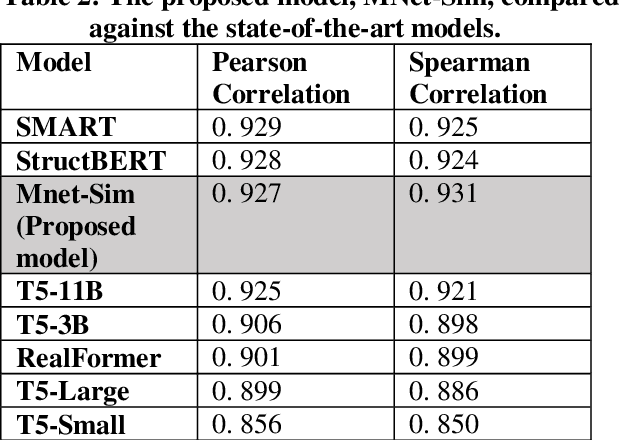
Abstract:Similarity is a comparative-subjective measure that varies with the domain within which it is considered. In several NLP applications such as document classification, pattern recognition, chatbot question-answering, sentiment analysis, etc., identifying an accurate similarity score for sentence pairs has become a crucial area of research. In the existing models that assess similarity, the limitation of effectively computing this similarity based on contextual comparisons, the localization due to the centering theory, and the lack of non-semantic textual comparisons have proven to be drawbacks. Hence, this paper presents a multi-layered semantic similarity network model built upon multiple similarity measures that render an overall sentence similarity score based on the principles of Network Science, neighboring weighted relational edges, and a proposed extended node similarity computation formula. The proposed multi-layered network model was evaluated and tested against established state-of-the-art models and is shown to have demonstrated better performance scores in assessing sentence similarity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge