Dexter Le
Neuromorphic Circuits with Spiking Astrocytes for Increased Energy Efficiency, Fault Tolerance, and Memory Capacitance
Feb 27, 2025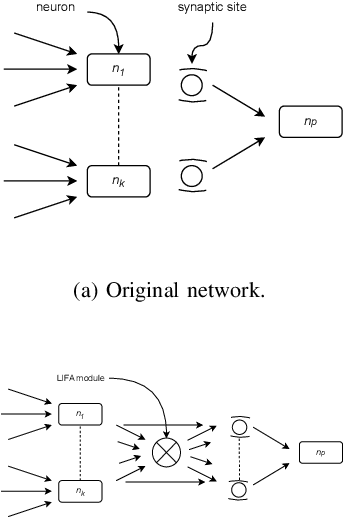
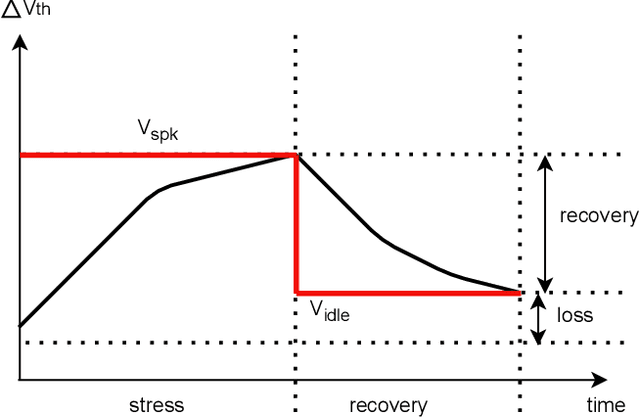
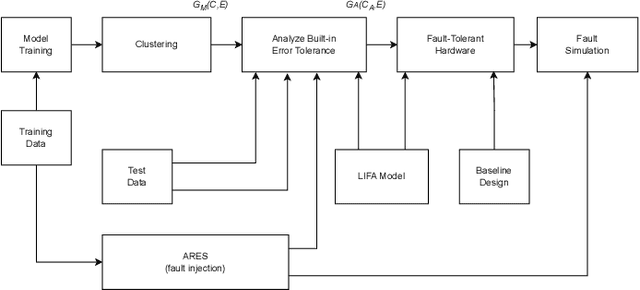
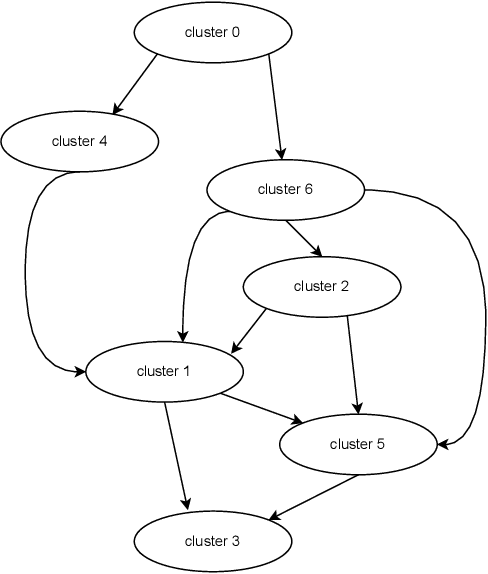
Abstract:In the rapidly advancing field of neuromorphic computing, integrating biologically-inspired models like the Leaky Integrate-and-Fire Astrocyte (LIFA) into spiking neural networks (SNNs) enhances system robustness and performance. This paper introduces the LIFA model in SNNs, addressing energy efficiency, memory management, routing mechanisms, and fault tolerance. Our core architecture consists of neurons, synapses, and astrocyte circuits, with each astrocyte supporting multiple neurons for self-repair. This clustered model improves fault tolerance and operational efficiency, especially under adverse conditions. We developed a routing methodology to map the LIFA model onto a fault-tolerant, many-core design, optimizing network functionality and efficiency. Our model features a fault tolerance rate of 81.10\% and a resilience improvement rate of 18.90\%, significantly surpassing other implementations. The results validate our approach in memory management, highlighting its potential as a robust solution for advanced neuromorphic computing applications. The integration of astrocytes represents a significant advancement, setting the stage for more resilient and adaptable neuromorphic systems.
Battery State of Health Estimation Using LLM Framework
Jan 30, 2025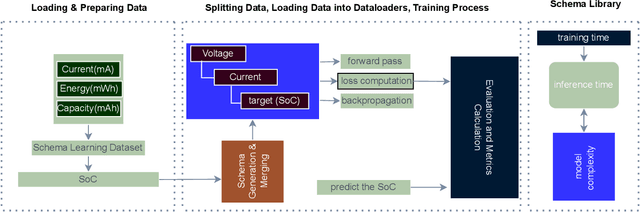
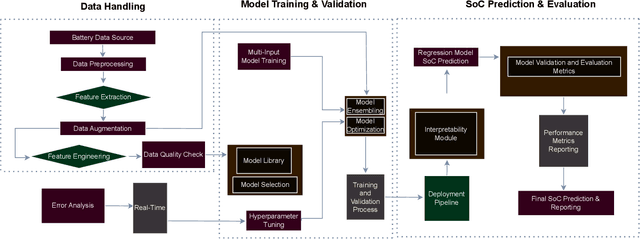
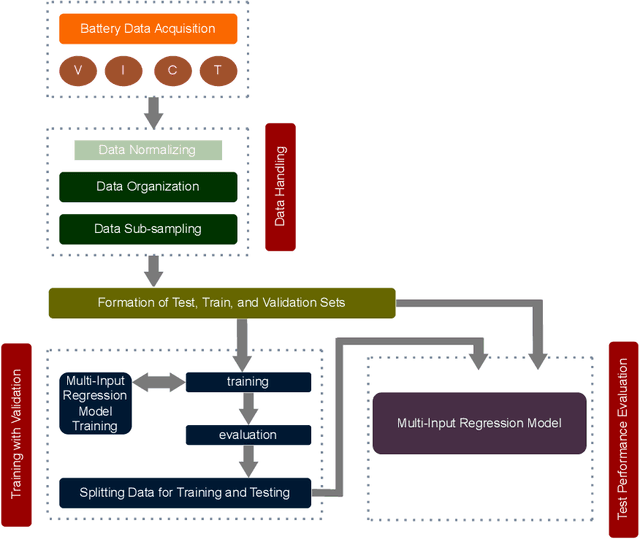
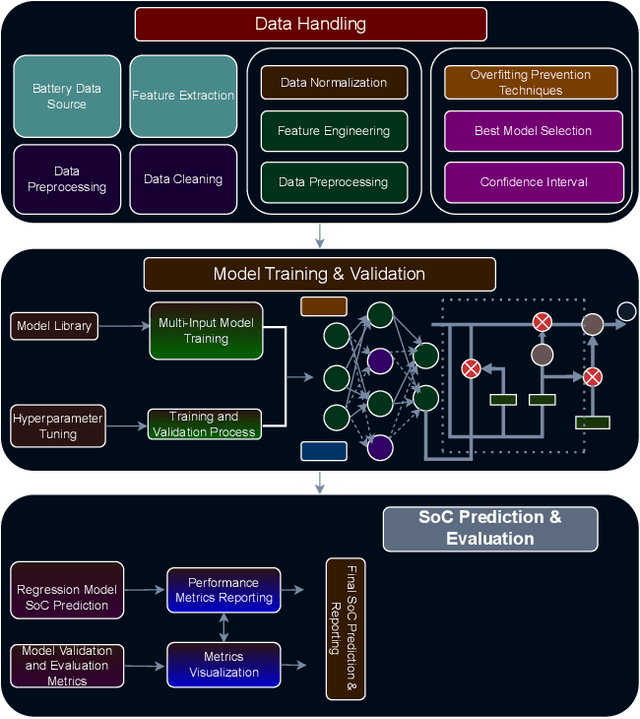
Abstract:Battery health monitoring is critical for the efficient and reliable operation of electric vehicles (EVs). This study introduces a transformer-based framework for estimating the State of Health (SoH) and predicting the Remaining Useful Life (RUL) of lithium titanate (LTO) battery cells by utilizing both cycle-based and instantaneous discharge data. Testing on eight LTO cells under various cycling conditions over 500 cycles, we demonstrate the impact of charge durations on energy storage trends and apply Differential Voltage Analysis (DVA) to monitor capacity changes (dQ/dV) across voltage ranges. Our LLM model achieves superior performance, with a Mean Absolute Error (MAE) as low as 0.87\% and varied latency metrics that support efficient processing, demonstrating its strong potential for real-time integration into EVs. The framework effectively identifies early signs of degradation through anomaly detection in high-resolution data, facilitating predictive maintenance to prevent sudden battery failures and enhance energy efficiency.
Multimodal LLM for Intelligent Transportation Systems
Dec 16, 2024



Abstract:In the evolving landscape of transportation systems, integrating Large Language Models (LLMs) offers a promising frontier for advancing intelligent decision-making across various applications. This paper introduces a novel 3-dimensional framework that encapsulates the intersection of applications, machine learning methodologies, and hardware devices, particularly emphasizing the role of LLMs. Instead of using multiple machine learning algorithms, our framework uses a single, data-centric LLM architecture that can analyze time series, images, and videos. We explore how LLMs can enhance data interpretation and decision-making in transportation. We apply this LLM framework to different sensor datasets, including time-series data and visual data from sources like Oxford Radar RobotCar, D-Behavior (D-Set), nuScenes by Motional, and Comma2k19. The goal is to streamline data processing workflows, reduce the complexity of deploying multiple models, and make intelligent transportation systems more efficient and accurate. The study was conducted using state-of-the-art hardware, leveraging the computational power of AMD RTX 3060 GPUs and Intel i9-12900 processors. The experimental results demonstrate that our framework achieves an average accuracy of 91.33\% across these datasets, with the highest accuracy observed in time-series data (92.7\%), showcasing the model's proficiency in handling sequential information essential for tasks such as motion planning and predictive maintenance. Through our exploration, we demonstrate the versatility and efficacy of LLMs in handling multimodal data within the transportation sector, ultimately providing insights into their application in real-world scenarios. Our findings align with the broader conference themes, highlighting the transformative potential of LLMs in advancing transportation technologies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge