Neuromorphic Circuits with Spiking Astrocytes for Increased Energy Efficiency, Fault Tolerance, and Memory Capacitance
Paper and Code
Feb 27, 2025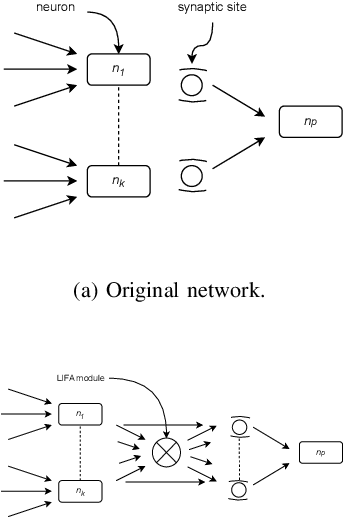
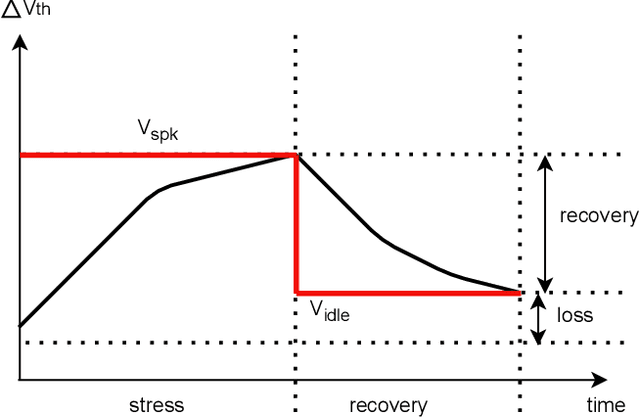
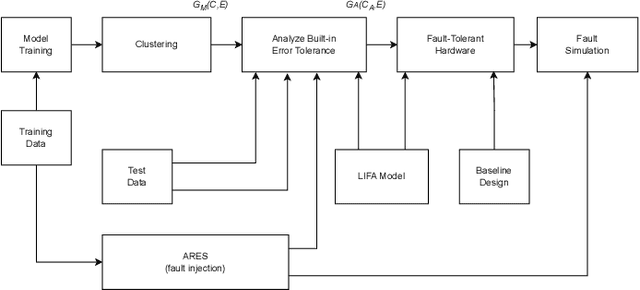
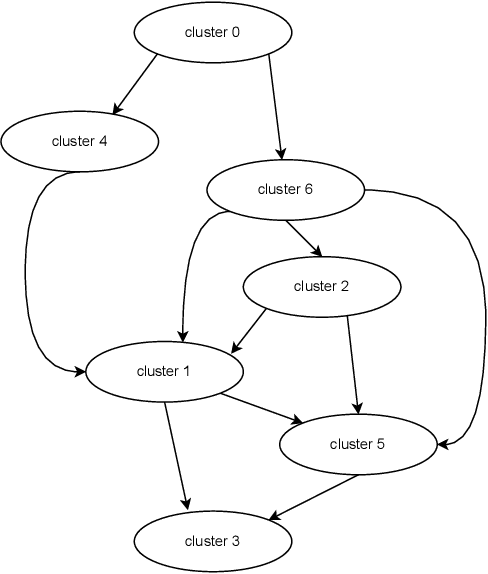
In the rapidly advancing field of neuromorphic computing, integrating biologically-inspired models like the Leaky Integrate-and-Fire Astrocyte (LIFA) into spiking neural networks (SNNs) enhances system robustness and performance. This paper introduces the LIFA model in SNNs, addressing energy efficiency, memory management, routing mechanisms, and fault tolerance. Our core architecture consists of neurons, synapses, and astrocyte circuits, with each astrocyte supporting multiple neurons for self-repair. This clustered model improves fault tolerance and operational efficiency, especially under adverse conditions. We developed a routing methodology to map the LIFA model onto a fault-tolerant, many-core design, optimizing network functionality and efficiency. Our model features a fault tolerance rate of 81.10\% and a resilience improvement rate of 18.90\%, significantly surpassing other implementations. The results validate our approach in memory management, highlighting its potential as a robust solution for advanced neuromorphic computing applications. The integration of astrocytes represents a significant advancement, setting the stage for more resilient and adaptable neuromorphic systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge