Denys Katerenchuk
Traits of a Leader: User Influence Level Prediction through Sociolinguistic Modeling
Jan 05, 2025Abstract:Recognition of a user's influence level has attracted much attention as human interactions move online. Influential users have the ability to sway others' opinions to achieve some goals. As a result, predicting users' level of influence can help to understand social networks, forecast trends, prevent misinformation, etc. However, predicting user influence is a challenging problem because the concept of influence is specific to a situation or a domain, and user communications are limited to text. In this work, we define user influence level as a function of community endorsement and develop a model that significantly outperforms the baseline by leveraging demographic and personality data. This approach consistently improves RankDCG scores across eight different domains.
''You should probably read this'': Hedge Detection in Text
May 22, 2024Abstract:Humans express ideas, beliefs, and statements through language. The manner of expression can carry information indicating the author's degree of confidence in their statement. Understanding the certainty level of a claim is crucial in areas such as medicine, finance, engineering, and many others where errors can lead to disastrous results. In this work, we apply a joint model that leverages words and part-of-speech tags to improve hedge detection in text and achieve a new top score on the CoNLL-2010 Wikipedia corpus.
A Survey of Hierarchy Identification in Social Networks
Dec 20, 2018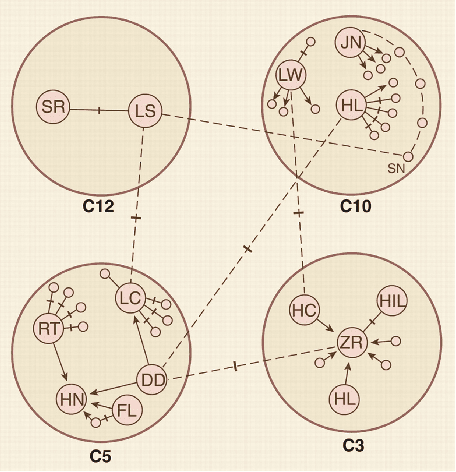
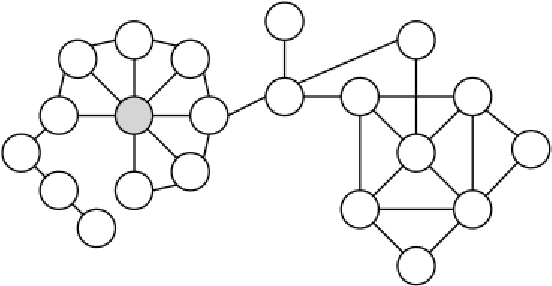

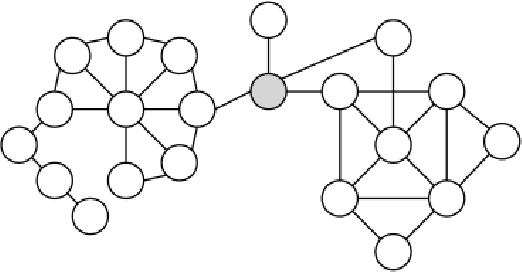
Abstract:Humans are social by nature. Throughout history, people have formed communities and built relationships. Most relationships with coworkers, friends, and family are developed during face-to-face interactions. These relationships are established through explicit means of communications such as words and implicit such as intonation, body language, etc. By analyzing human interactions we can derive information about the relationships and influence among conversation participants. However, with the development of the Internet, people started to communicate through text in online social networks. Interestingly, they brought their communicational habits to the Internet. Many social network users form relationships with each other and establish communities with leaders and followers. Recognizing these hierarchical relationships is an important task because it will help to understand social networks and predict future trends, improve recommendations, better target advertisement, and improve national security by identifying leaders of anonymous terror groups. In this work, I provide an overview of current research in this area and present the state-of-the-art approaches to deal with the problem of identifying hierarchical relationships in social networks.
Learning Joint Gaussian Representations for Movies, Actors, and Literary Characters
Apr 06, 2018
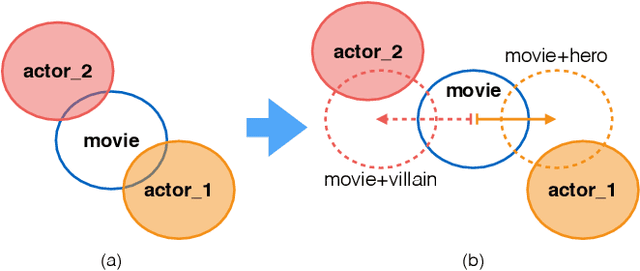

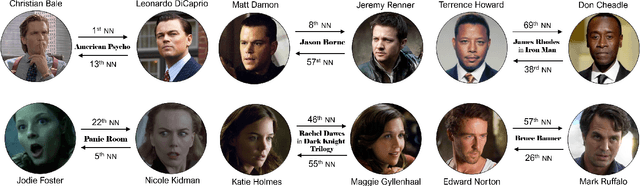
Abstract:Understanding of narrative content has become an increasingly popular topic. However, narrative semantics pose difficult challenges as the effects of multiple narrative facets, such as the text, events, character types, and genres, are tightly intertwined. We present a joint representation learning framework for embedding actors, literary characters, movies, genres, and descriptive keywords as Gaussian distributions and translation vectors on the Gaussian means. The Gaussian variance naturally corresponds to actors' versatility, a central concept in acting. Our estimate of actors' versatility agree with domain experts' rankings 65.95% of the time. This is, to our knowledge, the first computational technique for estimating this semantic concept. Additionally, the model substantially outperforms a TransE baseline in prediction of actor casting choices.
Age Group Classification with Speech and Metadata Multimodality Fusion
Mar 02, 2018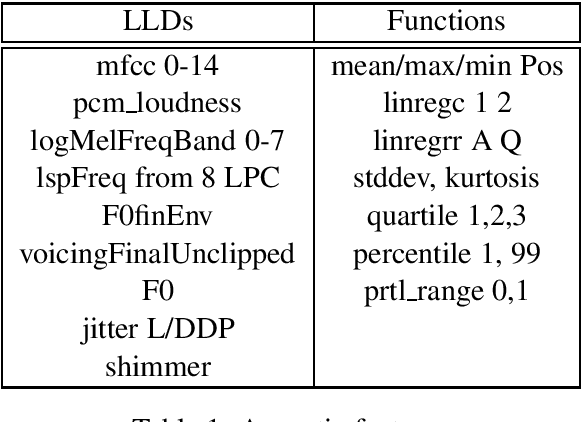

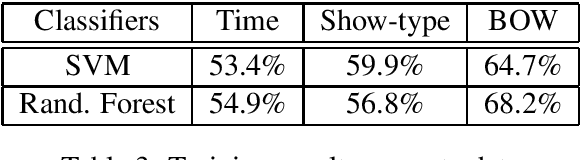

Abstract:Children comprise a significant proportion of TV viewers and it is worthwhile to customize the experience for them. However, identifying who is a child in the audience can be a challenging task. Identifying gender and age from audio commands is a well-studied problem but is still very challenging to get good accuracy when the utterances are typically only a couple of seconds long. We present initial studies of a novel method which combines utterances with user metadata. In particular, we develop an ensemble of different machine learning techniques on different subsets of data to improve child detection. Our initial results show a 9.2\% absolute improvement over the baseline, leading to a state-of-the-art performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge