Denis Sedov
Stochastic Cluster Embedding
Aug 18, 2021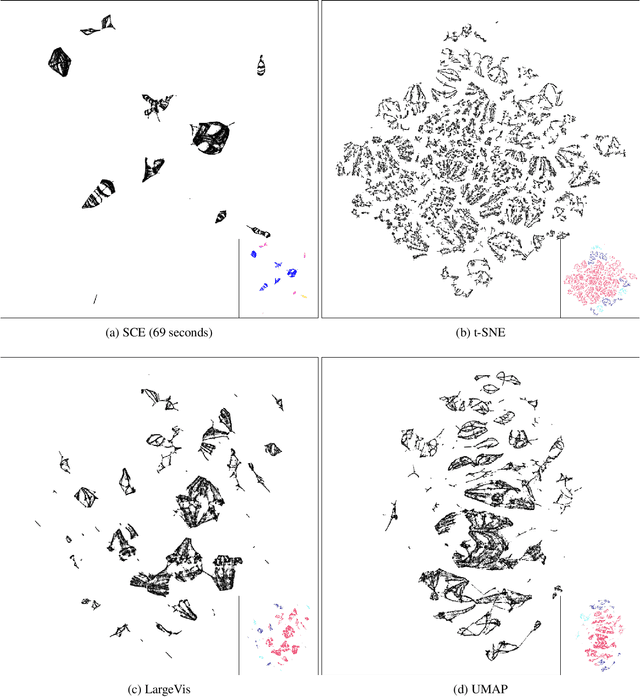

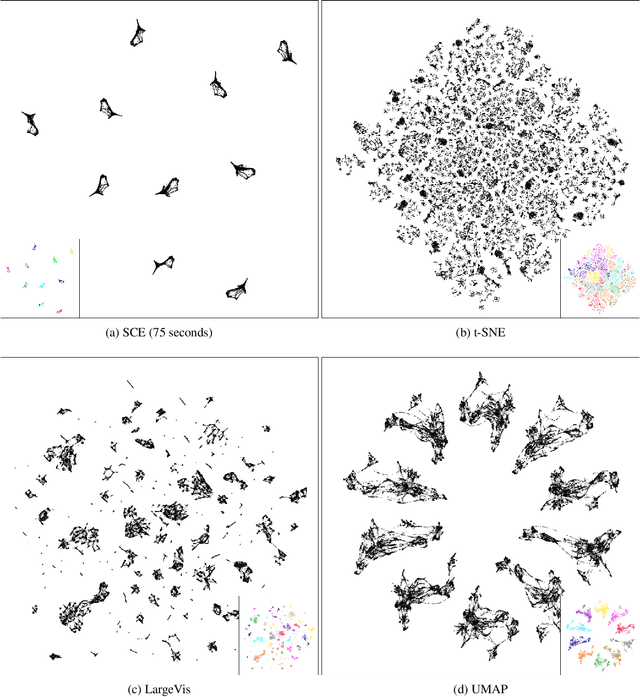
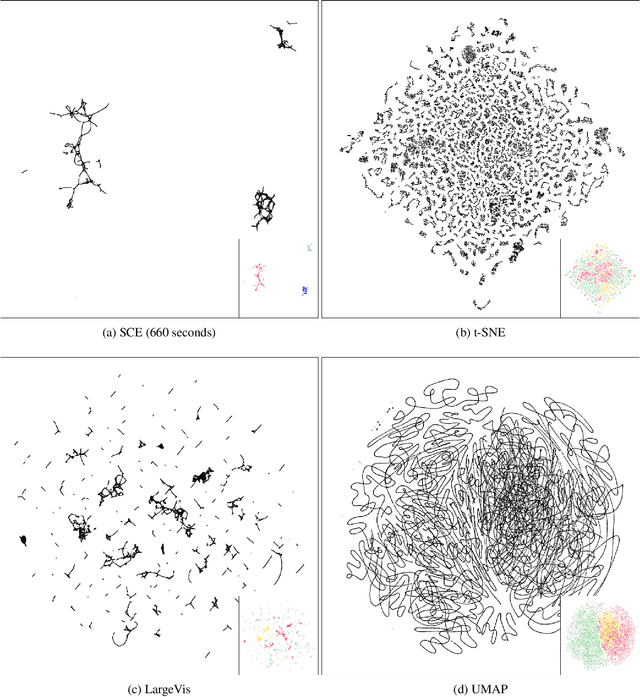
Abstract:Neighbor Embedding (NE) that aims to preserve pairwise similarities between data items has been shown to yield an effective principle for data visualization. However, even the currently best NE methods such as Stochastic Neighbor Embedding (SNE) may leave large-scale patterns such as clusters hidden despite of strong signals being present in the data. To address this, we propose a new cluster visualization method based on Neighbor Embedding. We first present a family of Neighbor Embedding methods which generalizes SNE by using non-normalized Kullback-Leibler divergence with a scale parameter. In this family, much better cluster visualizations often appear with a parameter value different from the one corresponding to SNE. We also develop an efficient software which employs asynchronous stochastic block coordinate descent to optimize the new family of objective functions. The experimental results demonstrate that our method consistently and substantially improves visualization of data clusters compared with the state-of-the-art NE approaches.
Word Embedding based on Low-Rank Doubly Stochastic Matrix Decomposition
Dec 12, 2018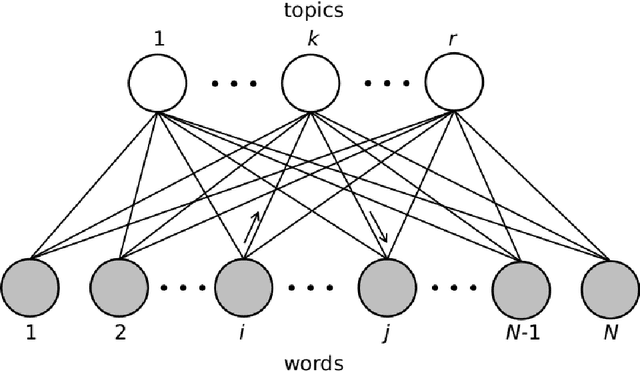
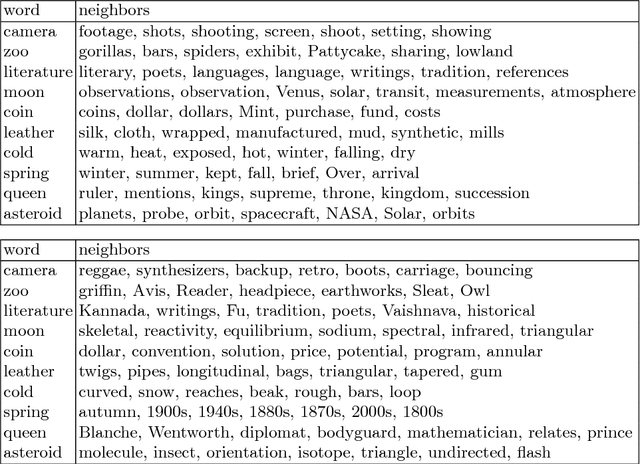

Abstract:Word embedding, which encodes words into vectors, is an important starting point in natural language processing and commonly used in many text-based machine learning tasks. However, in most current word embedding approaches, the similarity in embedding space is not optimized in the learning. In this paper we propose a novel neighbor embedding method which directly learns an embedding simplex where the similarities between the mapped words are optimal in terms of minimal discrepancy to the input neighborhoods. Our method is built upon two-step random walks between words via topics and thus able to better reveal the topics among the words. Experiment results indicate that our method, compared with another existing word embedding approach, is more favorable for various queries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge