Dekel Galor
A prescriptive theory for brain-like inference
Oct 25, 2024



Abstract:The Evidence Lower Bound (ELBO) is a widely used objective for training deep generative models, such as Variational Autoencoders (VAEs). In the neuroscience literature, an identical objective is known as the variational free energy, hinting at a potential unified framework for brain function and machine learning. Despite its utility in interpreting generative models, including diffusion models, ELBO maximization is often seen as too broad to offer prescriptive guidance for specific architectures in neuroscience or machine learning. In this work, we show that maximizing ELBO under Poisson assumptions for general sequence data leads to a spiking neural network that performs Bayesian posterior inference through its membrane potential dynamics. The resulting model, the iterative Poisson VAE (iP-VAE), has a closer connection to biological neurons than previous brain-inspired predictive coding models based on Gaussian assumptions. Compared to amortized and iterative VAEs, iP-VAElearns sparser representations and exhibits superior generalization to out-of-distribution samples. These findings suggest that optimizing ELBO, combined with Poisson assumptions, provides a solid foundation for developing prescriptive theories in NeuroAI.
Poisson Variational Autoencoder
May 23, 2024


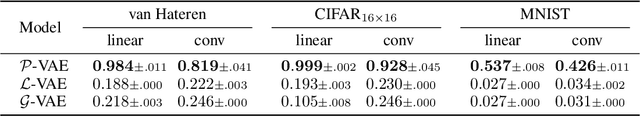
Abstract:Variational autoencoders (VAE) employ Bayesian inference to interpret sensory inputs, mirroring processes that occur in primate vision across both ventral (Higgins et al., 2021) and dorsal (Vafaii et al., 2023) pathways. Despite their success, traditional VAEs rely on continuous latent variables, which deviates sharply from the discrete nature of biological neurons. Here, we developed the Poisson VAE (P-VAE), a novel architecture that combines principles of predictive coding with a VAE that encodes inputs into discrete spike counts. Combining Poisson-distributed latent variables with predictive coding introduces a metabolic cost term in the model loss function, suggesting a relationship with sparse coding which we verify empirically. Additionally, we analyze the geometry of learned representations, contrasting the P-VAE to alternative VAE models. We find that the P-VAEencodes its inputs in relatively higher dimensions, facilitating linear separability of categories in a downstream classification task with a much better (5x) sample efficiency. Our work provides an interpretable computational framework to study brain-like sensory processing and paves the way for a deeper understanding of perception as an inferential process.
Noise2Image: Noise-Enabled Static Scene Recovery for Event Cameras
Apr 01, 2024Abstract:Event cameras capture changes of intensity over time as a stream of 'events' and generally cannot measure intensity itself; hence, they are only used for imaging dynamic scenes. However, fluctuations due to random photon arrival inevitably trigger noise events, even for static scenes. While previous efforts have been focused on filtering out these undesirable noise events to improve signal quality, we find that, in the photon-noise regime, these noise events are correlated with the static scene intensity. We analyze the noise event generation and model its relationship to illuminance. Based on this understanding, we propose a method, called Noise2Image, to leverage the illuminance-dependent noise characteristics to recover the static parts of a scene, which are otherwise invisible to event cameras. We experimentally collect a dataset of noise events on static scenes to train and validate Noise2Image. Our results show that Noise2Image can robustly recover intensity images solely from noise events, providing a novel approach for capturing static scenes in event cameras, without additional hardware.
BiPMAP: A Toolbox for Predictions of Perceived Motion Artifacts on Modern Displays
Dec 07, 2022Abstract:Presenting dynamic scenes without incurring motion artifacts visible to observers requires sustained effort from the display industry. A tool that predicts motion artifacts and simulates artifact elimination through optimizing the display configuration is highly desired to guide the design and manufacture of modern displays. Despite the popular demands, there is no such tool available in the market. In this study, we deliver an interactive toolkit, Binocular Perceived Motion Artifact Predictor (BiPMAP), as an executable file with GPU acceleration. BiPMAP accounts for an extensive collection of user-defined parameters and directly visualizes a variety of motion artifacts by presenting the perceived continuous and sampled moving stimuli side-by-side. For accurate artifact predictions, BiPMAP utilizes a novel model of the human contrast sensitivity function to effectively imitate the frequency modulation of the human visual system. In addition, BiPMAP is capable of deriving various in-plane motion artifacts for 2D displays and depth distortion in 3D stereoscopic displays.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge