Deepak Akkil
AEGIS: An Agent for Extraction and Geographic Identification in Scholarly Proceedings
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Keeping pace with the rapid growth of academia literature presents a significant challenge for researchers, funding bodies, and academic societies. To address the time-consuming manual effort required for scholarly discovery, we present a novel, fully automated system that transitions from data discovery to direct action. Our pipeline demonstrates how a specialized AI agent, 'Agent-E', can be tasked with identifying papers from specific geographic regions within conference proceedings and then executing a Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to complete a predefined action, such as submitting a nomination form. We validated our system on 586 papers from five different conferences, where it successfully identified every target paper with a recall of 100% and a near perfect accuracy of 99.4%. This demonstration highlights the potential of task-oriented AI agents to not only filter information but also to actively participate in and accelerate the workflows of the academic community.
MathViz-E: A Case-study in Domain-Specialized Tool-Using Agents
Jul 24, 2024


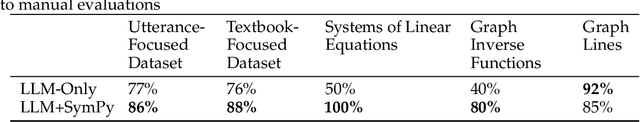
Abstract:There has been significant recent interest in harnessing LLMs to control software systems through multi-step reasoning, planning and tool-usage. While some promising results have been obtained, application to specific domains raises several general issues including the control of specialized domain tools, the lack of existing datasets for training and evaluation, and the non-triviality of automated system evaluation and improvement. In this paper, we present a case-study where we examine these issues in the context of a specific domain. Specifically, we present an automated math visualizer and solver system for mathematical pedagogy. The system orchestrates mathematical solvers and math graphing tools to produce accurate visualizations from simple natural language commands. We describe the creation of specialized data-sets, and also develop an auto-evaluator to easily evaluate the outputs of our system by comparing them to ground-truth expressions. We have open sourced the data-sets and code for the proposed system.
Agent-E: From Autonomous Web Navigation to Foundational Design Principles in Agentic Systems
Jul 17, 2024



Abstract:AI Agents are changing the way work gets done, both in consumer and enterprise domains. However, the design patterns and architectures to build highly capable agents or multi-agent systems are still developing, and the understanding of the implication of various design choices and algorithms is still evolving. In this paper, we present our work on building a novel web agent, Agent-E \footnote{Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/EmergenceAI/Agent-E}}. Agent-E introduces numerous architectural improvements over prior state-of-the-art web agents such as hierarchical architecture, flexible DOM distillation and denoising method, and the concept of \textit{change observation} to guide the agent towards more accurate performance. We first present the results of an evaluation of Agent-E on WebVoyager benchmark dataset and show that Agent-E beats other SOTA text and multi-modal web agents on this benchmark in most categories by 10-30\%. We then synthesize our learnings from the development of Agent-E into general design principles for developing agentic systems. These include the use of domain-specific primitive skills, the importance of distillation and de-noising of environmental observations, the advantages of a hierarchical architecture, and the role of agentic self-improvement to enhance agent efficiency and efficacy as the agent gathers experience.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge