David Morris
Evaluation of Automated Image Descriptions for Visually Impaired Students
Jun 29, 2021
Abstract:Illustrations are widely used in education, and sometimes, alternatives are not available for visually impaired students. Therefore, those students would benefit greatly from an automatic illustration description system, but only if those descriptions were complete, correct, and easily understandable using a screenreader. In this paper, we report on a study for the assessment of automated image descriptions. We interviewed experts to establish evaluation criteria, which we then used to create an evaluation questionnaire for sighted non-expert raters, and description templates. We used this questionnaire to evaluate the quality of descriptions which could be generated with a template-based automatic image describer. We present evidence that these templates have the potential to generate useful descriptions, and that the questionnaire identifies problems with description templates.
* 6 pages, 12 references. Accepted for publication at the 22nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Education (AIED 2021), June 14-16 2021, Utrecht, The Netherlands
SlideImages: A Dataset for Educational Image Classification
Jan 19, 2020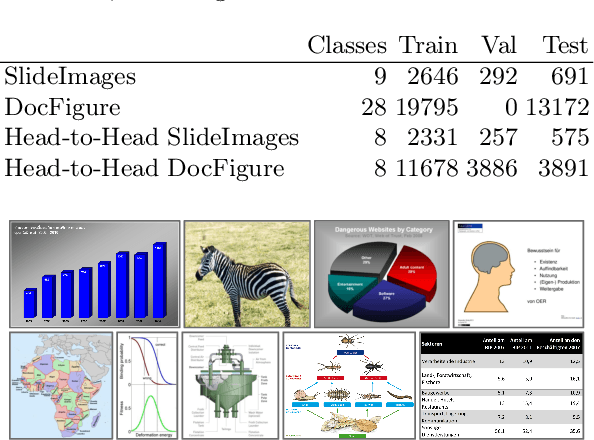
Abstract:In the past few years, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have achieved impressive results in computer vision tasks, which however mainly focus on photos with natural scene content. Besides, non-sensor derived images such as illustrations, data visualizations, figures, etc. are typically used to convey complex information or to explore large datasets. However, this kind of images has received little attention in computer vision. CNNs and similar techniques use large volumes of training data. Currently, many document analysis systems are trained in part on scene images due to the lack of large datasets of educational image data. In this paper, we address this issue and present SlideImages, a dataset for the task of classifying educational illustrations. SlideImages contains training data collected from various sources, e.g., Wikimedia Commons and the AI2D dataset, and test data collected from educational slides. We have reserved all the actual educational images as a test dataset in order to ensure that the approaches using this dataset generalize well to new educational images, and potentially other domains. Furthermore, we present a baseline system using a standard deep neural architecture and discuss dealing with the challenge of limited training data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge