David Manthey
Kitware Inc., Clifton Park, NY, USA
NuCLS: A scalable crowdsourcing, deep learning approach and dataset for nucleus classification, localization and segmentation
Feb 18, 2021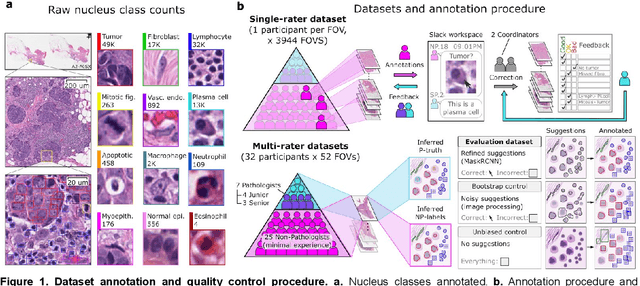
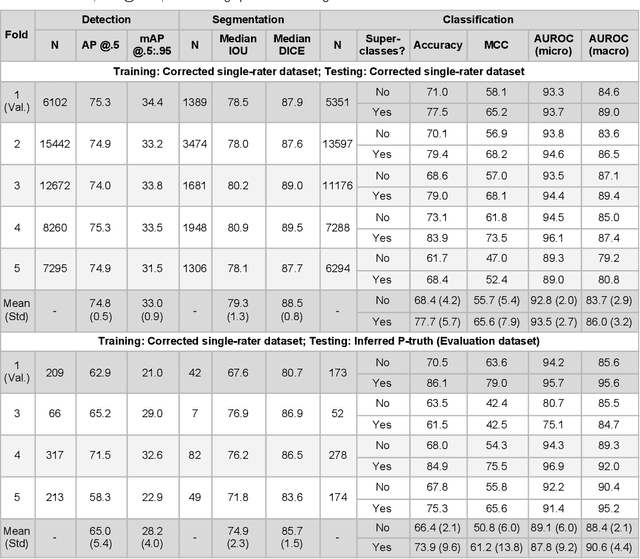
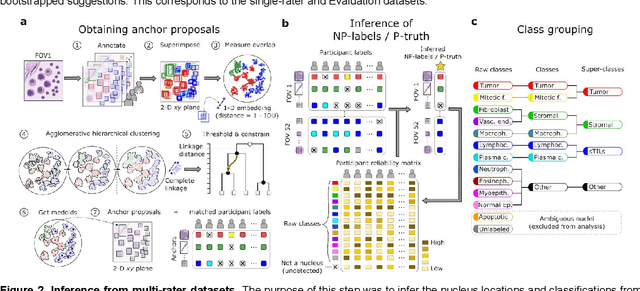
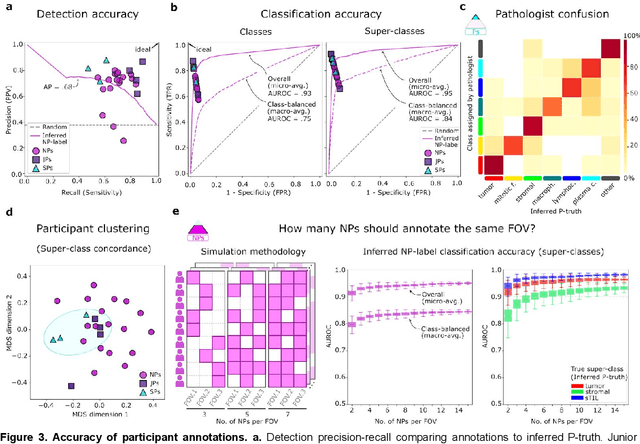
Abstract:High-resolution mapping of cells and tissue structures provides a foundation for developing interpretable machine-learning models for computational pathology. Deep learning algorithms can provide accurate mappings given large numbers of labeled instances for training and validation. Generating adequate volume of quality labels has emerged as a critical barrier in computational pathology given the time and effort required from pathologists. In this paper we describe an approach for engaging crowds of medical students and pathologists that was used to produce a dataset of over 220,000 annotations of cell nuclei in breast cancers. We show how suggested annotations generated by a weak algorithm can improve the accuracy of annotations generated by non-experts and can yield useful data for training segmentation algorithms without laborious manual tracing. We systematically examine interrater agreement and describe modifications to the MaskRCNN model to improve cell mapping. We also describe a technique we call Decision Tree Approximation of Learned Embeddings (DTALE) that leverages nucleus segmentations and morphologic features to improve the transparency of nucleus classification models. The annotation data produced in this study are freely available for algorithm development and benchmarking at: https://sites.google.com/view/nucls.
A tool for user friendly, cloud based, whole slide image segmentation
Jan 18, 2021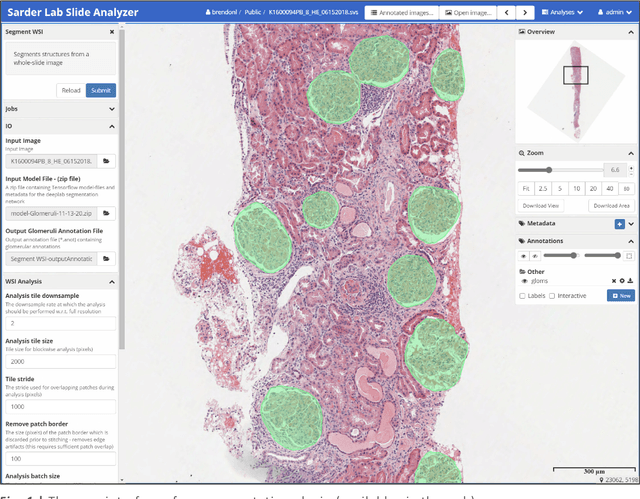
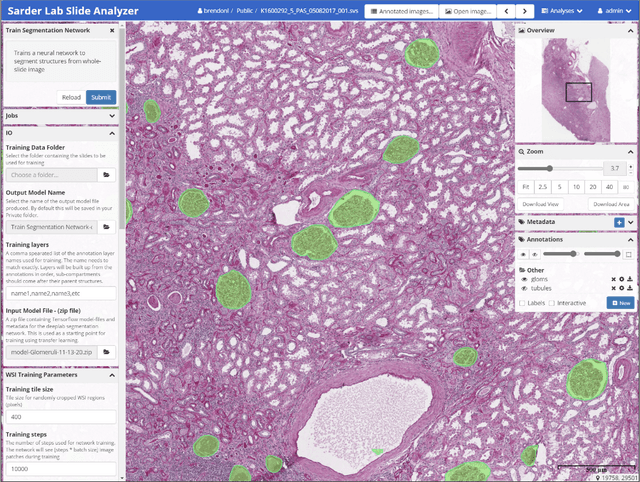
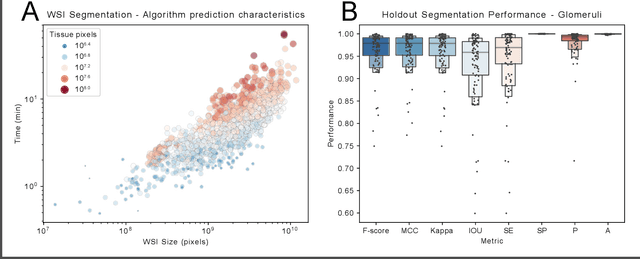
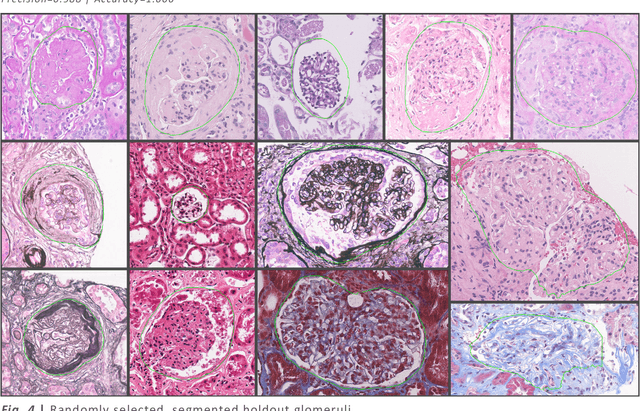
Abstract:Convolutional neural networks, the state of the art for image segmentation, have been successfully applied to histology images by many computational researchers. However, the translatability of this technology to clinicians and biological researchers is limited due to the complex and undeveloped user interface of the code, as well as the extensive computer setup required. As an extension of our previous work (arXiv:1812.07509), we have developed a tool for segmentation of whole slide images (WSIs) with an easy to use graphical user interface. Our tool runs a state-of-the-art convolutional neural network for segmentation of WSIs in the cloud. Our plugin is built on the open source tool HistomicsTK by Kitware Inc. (Clifton Park, NY), which provides remote data management and viewing abilities for WSI datasets. The ability to access this tool over the internet will facilitate widespread use by computational non-experts. Users can easily upload slides to a server where our plugin is installed and perform human in the loop segmentation analysis remotely. This tool is open source, and has the ability to be adapted to segment of any pathological structure. For a proof of concept, we have trained it to segment glomeruli from renal tissue images, achieving an F-score > 0.97 on holdout tissue slides.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge