David Leake
Case-Enhanced Vision Transformer: Improving Explanations of Image Similarity with a ViT-based Similarity Metric
Jul 24, 2024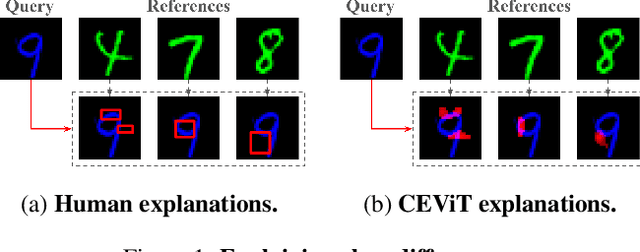



Abstract:This short paper presents preliminary research on the Case-Enhanced Vision Transformer (CEViT), a similarity measurement method aimed at improving the explainability of similarity assessments for image data. Initial experimental results suggest that integrating CEViT into k-Nearest Neighbor (k-NN) classification yields classification accuracy comparable to state-of-the-art computer vision models, while adding capabilities for illustrating differences between classes. CEViT explanations can be influenced by prior cases, to illustrate aspects of similarity relevant to those cases.
Applying the Case Difference Heuristic to Learn Adaptations from Deep Network Features
Jul 15, 2021


Abstract:The case difference heuristic (CDH) approach is a knowledge-light method for learning case adaptation knowledge from the case base of a case-based reasoning system. Given a pair of cases, the CDH approach attributes the difference in their solutions to the difference in the problems they solve, and generates adaptation rules to adjust solutions accordingly when a retrieved case and new query have similar problem differences. As an alternative to learning adaptation rules, several researchers have applied neural networks to learn to predict solution differences from problem differences. Previous work on such approaches has assumed that the feature set describing problems is predefined. This paper investigates a two-phase process combining deep learning for feature extraction and neural network based adaptation learning from extracted features. Its performance is demonstrated in a regression task on an image data: predicting age given the image of a face. Results show that the combined process can successfully learn adaptation knowledge applicable to nonsymbolic differences in cases. The CBR system achieves slightly lower performance overall than a baseline deep network regressor, but better performance than the baseline on novel queries.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge