David Brellmann
Improving Semantic Uncertainty Quantification in LVLMs with Semantic Gaussian Processes
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) often produce plausible but unreliable outputs, making robust uncertainty estimation essential. Recent work on semantic uncertainty estimates relies on external models to cluster multiple sampled responses and measure their semantic consistency. However, these clustering methods are often fragile, highly sensitive to minor phrasing variations, and can incorrectly group or separate semantically similar answers, leading to unreliable uncertainty estimates. We propose Semantic Gaussian Process Uncertainty (SGPU), a Bayesian framework that quantifies semantic uncertainty by analyzing the geometric structure of answer embeddings, avoiding brittle clustering. SGPU maps generated answers into a dense semantic space, computes the Gram matrix of their embeddings, and summarizes their semantic configuration via the eigenspectrum. This spectral representation is then fed into a Gaussian Process Classifier that learns to map patterns of semantic consistency to predictive uncertainty, and that can be applied in both black-box and white-box settings. Across six LLMs and LVLMs on eight datasets spanning VQA, image classification, and textual QA, SGPU consistently achieves state-of-the-art calibration (ECE) and discriminative (AUROC, AUARC) performance. We further show that SGPU transfers across models and modalities, indicating that its spectral representation captures general patterns of semantic uncertainty.
Double Descent Meets Out-of-Distribution Detection: Theoretical Insights and Empirical Analysis on the role of model complexity
Nov 04, 2024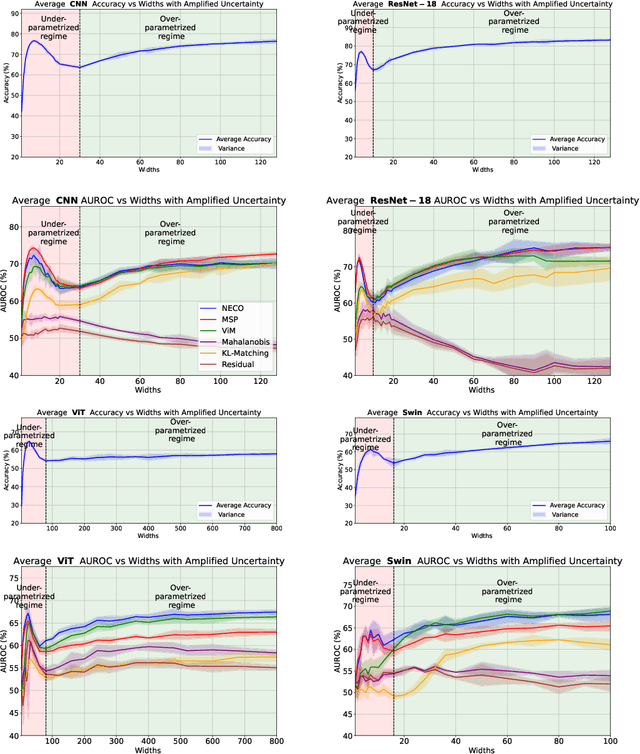
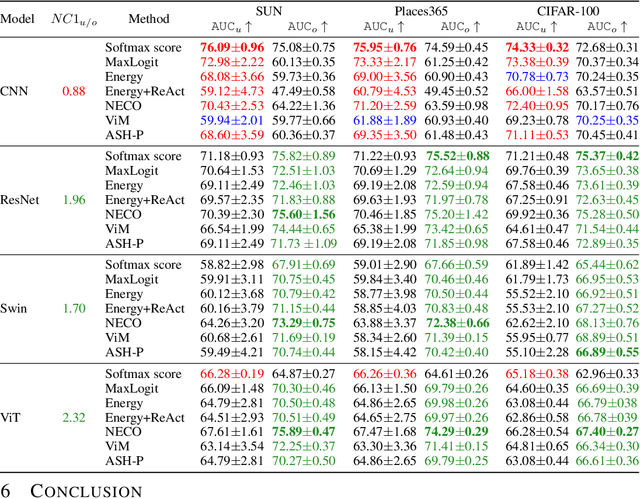
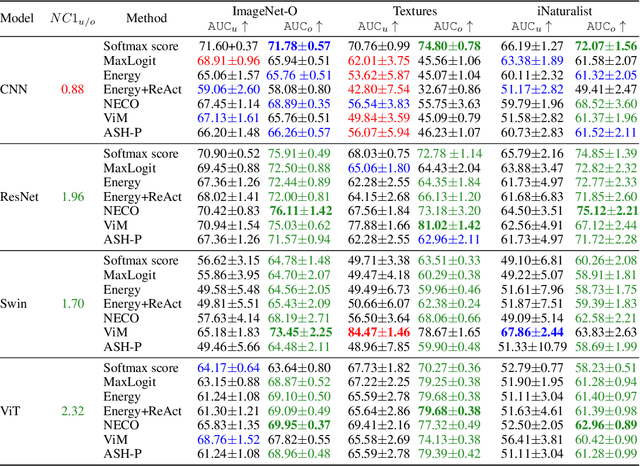
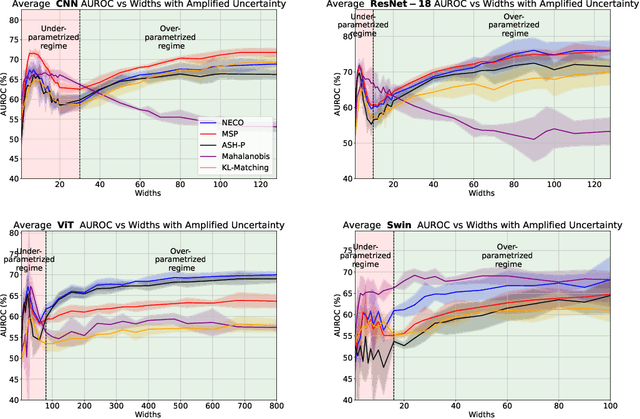
Abstract:While overparameterization is known to benefit generalization, its impact on Out-Of-Distribution (OOD) detection is less understood. This paper investigates the influence of model complexity in OOD detection. We propose an expected OOD risk metric to evaluate classifiers confidence on both training and OOD samples. Leveraging Random Matrix Theory, we derive bounds for the expected OOD risk of binary least-squares classifiers applied to Gaussian data. We show that the OOD risk depicts an infinite peak, when the number of parameters is equal to the number of samples, which we associate with the double descent phenomenon. Our experimental study on different OOD detection methods across multiple neural architectures extends our theoretical insights and highlights a double descent curve. Our observations suggest that overparameterization does not necessarily lead to better OOD detection. Using the Neural Collapse framework, we provide insights to better understand this behavior. To facilitate reproducibility, our code will be made publicly available upon publication.
On Double Descent in Reinforcement Learning with LSTD and Random Features
Oct 20, 2023



Abstract:Temporal Difference (TD) algorithms are widely used in Deep Reinforcement Learning (RL). Their performance is heavily influenced by the size of the neural network. While in supervised learning, the regime of over-parameterization and its benefits are well understood, the situation in RL is much less clear. In this paper, we present a theoretical analysis of the influence of network size and $l_2$-regularization on performance. We identify the ratio between the number of parameters and the number of visited states as a crucial factor and define over-parameterization as the regime when it is larger than one. Furthermore, we observe a double descent phenomenon, i.e., a sudden drop in performance around the parameter/state ratio of one. Leveraging random features and the lazy training regime, we study the regularized Least-Square Temporal Difference (LSTD) algorithm in an asymptotic regime, as both the number of parameters and states go to infinity, maintaining a constant ratio. We derive deterministic limits of both the empirical and the true Mean-Square Bellman Error (MSBE) that feature correction terms responsible for the double-descent. Correction terms vanish when the $l_2$-regularization is increased or the number of unvisited states goes to zero. Numerical experiments with synthetic and small real-world environments closely match the theoretical predictions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge