Danupat Khamnuansin
THaLLE-ThaiLLM: Domain-Specialized Small LLMs for Finance and Thai -- Technical Report
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential across various domains, particularly in banking and finance, where they can automate complex tasks and enhance decision-making at scale. Due to privacy, security, and regulatory concerns, organizations often prefer on-premise deployment of LLMs. The ThaiLLM initiative aims to enhance Thai language capabilities in open-LLMs, enabling Thai industry to leverage advanced language models. However, organizations often face a trade-off between deploying multiple specialized models versus the prohibitive expense of training a single multi-capability model. To address this, we explore model merging as a resource-efficient alternative for developing high-performance, multi-capability LLMs. We present results from two key experiments: first, merging Qwen-8B with ThaiLLM-8B demonstrates how ThaiLLM-8B enhances Thai general capabilities, showing an uplift of M3 and M6 O-NET exams over the general instruction-following Qwen-8B. Second, we merge Qwen-8B with both ThaiLLM-8B and THaLLE-CFA-8B. This combination results in further improvements in performance across both general and financial domains, by demonstrating an uplift in both M3 and M6 O-NET, Flare-CFA, and Thai-IC benchmarks. The report showcases the viability of model merging for efficiently creating multi-capability LLMs.
Thai Financial Domain Adaptation of THaLLE -- Technical Report
Nov 27, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) excel in general tasks but struggle with domain-specific challenges, such as specialized terminology and localized regulations. Existing financial LLMs, like FinGPT and BloombergGPT, lack support for the Thai financial domain. We developed a Thai Financial LLM using the Investment Consultant (IC) exam dataset from the Stock Exchange of Thailand. To address dataset limitations, we applied data augmentation, ReLoRA for efficient training, Continued Pretraining (CPT) for domain knowledge, and Rank-Stabilized LoRA (rsLoRA) for fine-tuning. Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) simulated exam scenarios, while Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) refined the model using feedback. The model achieved scores of 72%, 72%, and 84% on IC exam levels P1, P2, and P3, respectively, demonstrating its effectiveness in Thai financial advisory tasks and its potential for specialized applications.
THaLLE: Text Hyperlocally Augmented Large Language Extension -- Technical Report
Jun 11, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have revealed new capabilities and opportunities across the technological landscape. However, the practicality of very large LLMs is challenged by their high compute cost, which does not justify the benefits given their limited capability compared to humans. While smaller, more practical LLMs have shown potential in financial analysis, though they are not yet fully proficient, as evidenced by their near-passing performance on the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) exam. In this work, we present Financial Analyst Extension to our Text Hyperlocally Augmented Large Language Extension (THaLLE), a series of 8B LLMs consistently achieving highest performance on mock CFA exams against models of comparable size. We thoroughly document the fine-tuning techniques used to facilitate future research. Additionally, we introduce the use of Flare CFA, a publicly available dataset for evaluating LLMs as a financial advisor.
MrRank: Improving Question Answering Retrieval System through Multi-Result Ranking Model
Jun 09, 2024
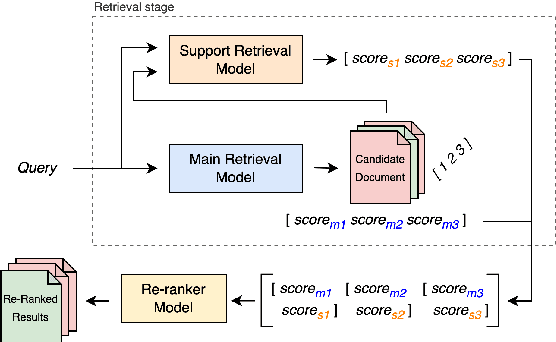

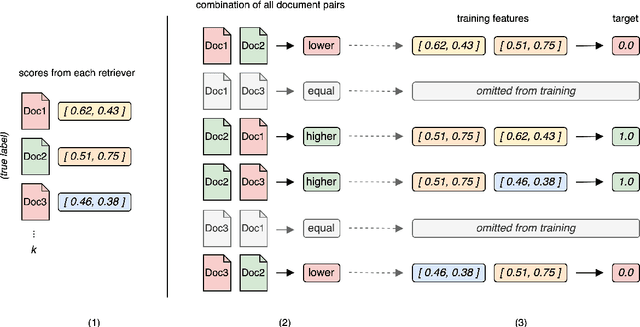
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle with hallucinations and outdated information. To address this, Information Retrieval (IR) systems can be employed to augment LLMs with up-to-date knowledge. However, existing IR techniques contain deficiencies, posing a performance bottleneck. Given the extensive array of IR systems, combining diverse approaches presents a viable strategy. Nevertheless, prior attempts have yielded restricted efficacy. In this work, we propose an approach that leverages learning-to-rank techniques to combine heterogeneous IR systems. We demonstrate the method on two Retrieval Question Answering (ReQA) tasks. Our empirical findings exhibit a significant performance enhancement, outperforming previous approaches and achieving state-of-the-art results on ReQA SQuAD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge