Dante Mantini
Edge Sparse Basis Network: A Deep Learning Framework for EEG Source Localization
Feb 28, 2021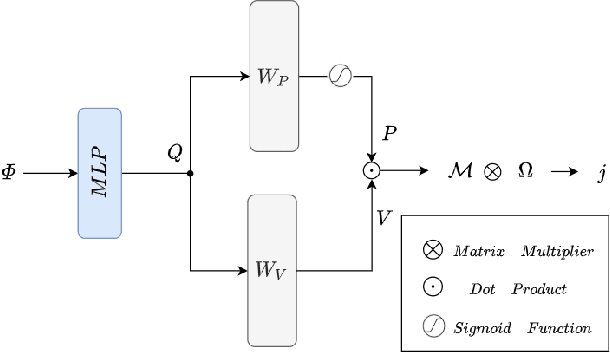
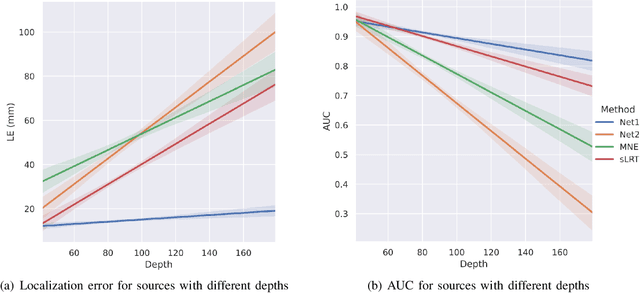
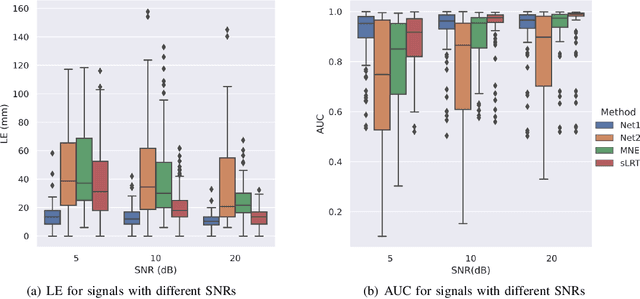
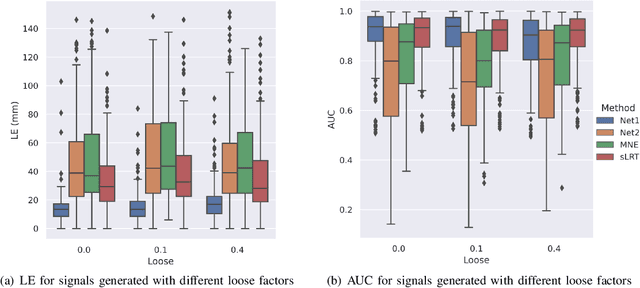
Abstract:EEG source localization is an important technical issue in EEG analysis. Despite many numerical methods existed for EEG source localization, they all rely on strong priors and the deep sources are intractable. Here we propose a deep learning framework using spatial basis function decomposition for EEG source localization. This framework combines the edge sparsity prior and Gaussian source basis, called Edge Sparse Basis Network (ESBN). The performance of ESBN is validated by both synthetic data and real EEG data during motor tasks. The results suggest that the supervised ESBN outperforms the traditional numerical methods in synthetic data and the unsupervised fine-tuning provides more focal and accurate localizations in real data. Our proposed deep learning framework can be extended to account for other source priors, and the real-time property of ESBN can facilitate the applications of EEG in brain-computer interfaces and clinics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge