Daniele Mazzei
Towards a Taxonomy of Industrial Challenges and Enabling Technologies in Industry 4.0
Nov 29, 2022



Abstract:Today, one of the biggest challenges for digital transformation in the Industry 4.0 paradigm is the lack of mutual understanding between the academic and the industrial world. On the one hand, the industry fails to apply new technologies and innovations from scientific research. At the same time, academics struggle to find and focus on real-world applications for their developing technological solutions. Moreover, the increasing complexity of industrial challenges and technologies is widening this hiatus. To reduce this knowledge and communication gap, this article proposes a mixed approach of humanistic and engineering techniques applied to the technological and enterprise fields. The study's results are represented by a taxonomy in which industrial challenges and I4.0-focused technologies are categorized and connected through academic and grey literature analysis. This taxonomy also formed the basis for creating a public web platform where industrial practitioners can identify candidate solutions for an industrial challenge. At the same time, from the educational perspective, the learning procedure can be supported since, through this tool, academics can identify real-world scenarios to integrate digital technologies' teaching process.
TEACHING -- Trustworthy autonomous cyber-physical applications through human-centred intelligence
Jul 14, 2021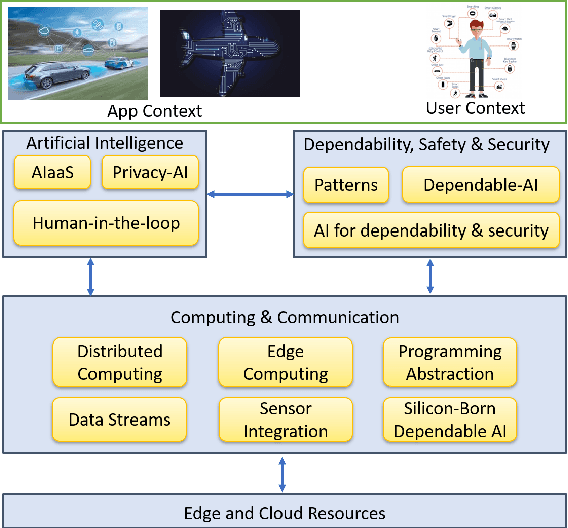
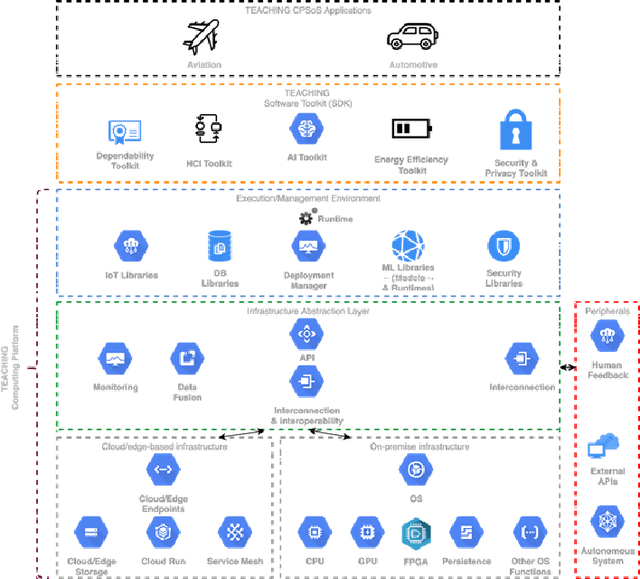
Abstract:This paper discusses the perspective of the H2020 TEACHING project on the next generation of autonomous applications running in a distributed and highly heterogeneous environment comprising both virtual and physical resources spanning the edge-cloud continuum. TEACHING puts forward a human-centred vision leveraging the physiological, emotional, and cognitive state of the users as a driver for the adaptation and optimization of the autonomous applications. It does so by building a distributed, embedded and federated learning system complemented by methods and tools to enforce its dependability, security and privacy preservation. The paper discusses the main concepts of the TEACHING approach and singles out the main AI-related research challenges associated with it. Further, we provide a discussion of the design choices for the TEACHING system to tackle the aforementioned challenges
Towards Automatic building of Human-Machine Conversational System to support Maintenance Processes
May 13, 2020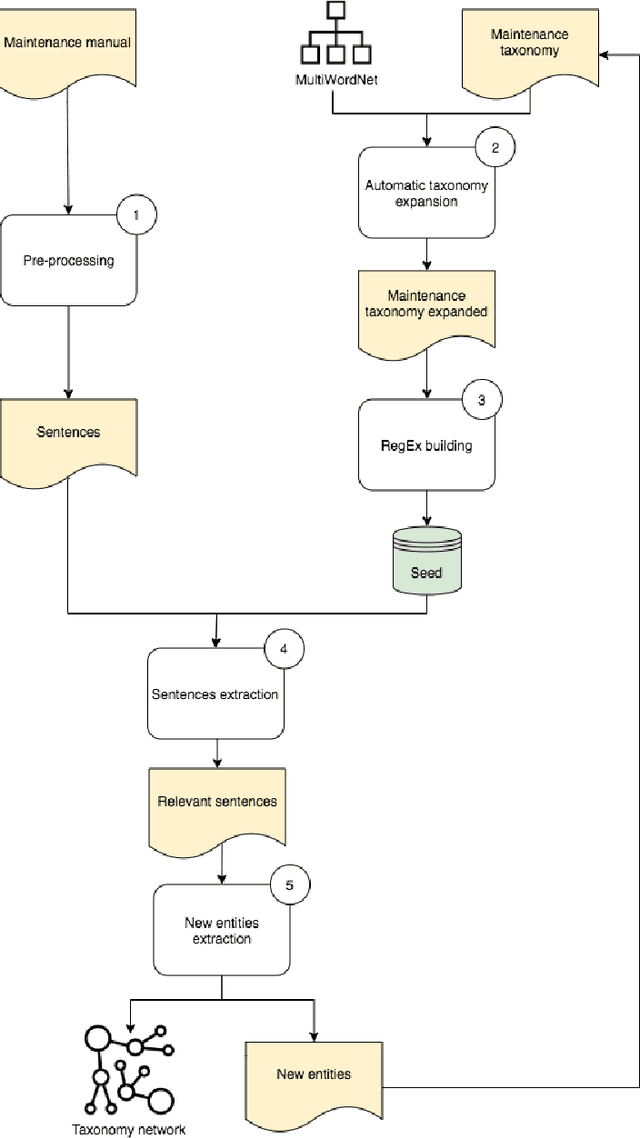
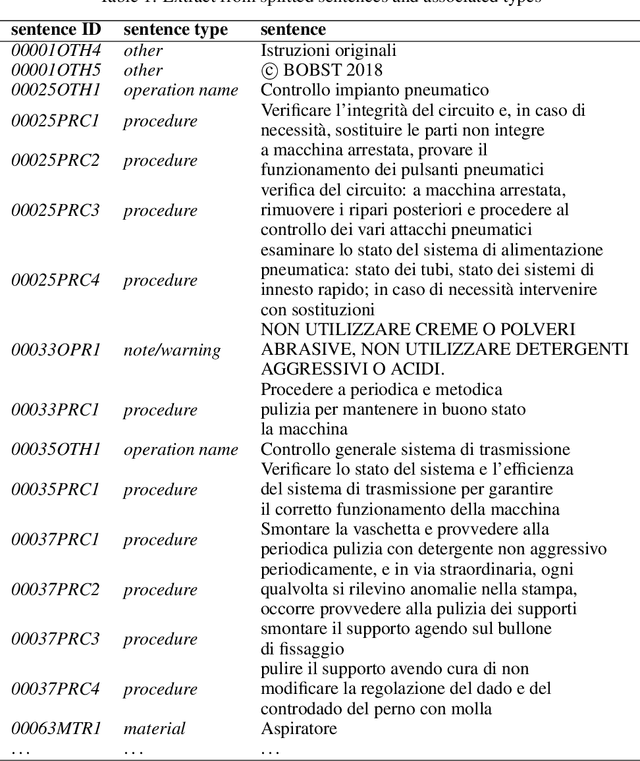

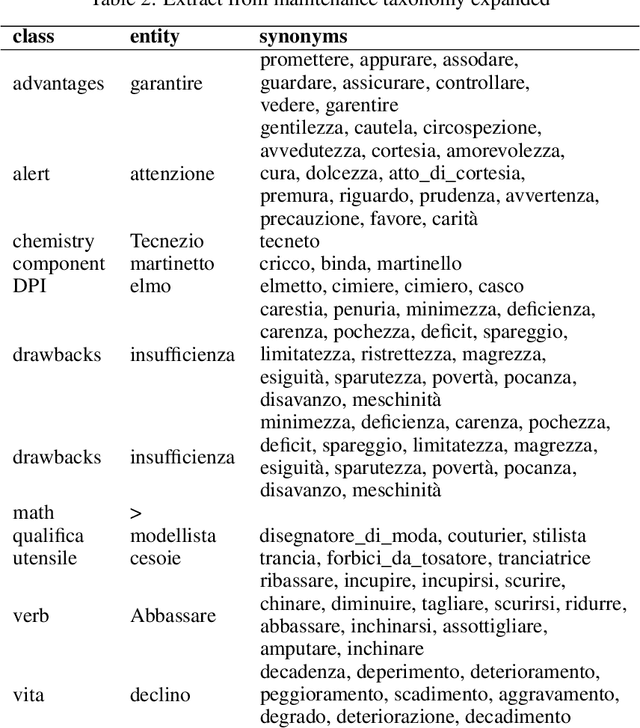
Abstract:Companies are dealing with many cognitive changes with the introduction of the Industry 4.0 paradigm. In this constantly changing environment, knowledge management is a key factor. Dialog systems, being able to hold a conversation with humans, could support the knowledge management in business environment. Although, these systems are currently hand-coded and need the intervention of a human being in writing all the possible questions and answers, and then planning the interactions. This process, besides being time-consuming, is not scalable. Conversely, a dialog system, also referred to as chatbot, can be built from scratch by simply extracting rules from technical documentation. So, the goal of this research is designing a methodology for automatic building of human-machine conversational system, able to interact in an industrial environment. An initial taxonomy, containing entities expected to be found in maintenance manuals, is used to identify the relevant sentences of a manual provided by the company BOBST SA and applying text mining techniques, it is automatically expanded. The final result is a taxonomy network representing the entities and their relation, that will be used in future works for managing the interactions of a maintenance chatbot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge