Daniele Caradonna
Model-based Optimal Control for Rigid-Soft Underactuated Systems
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Continuum soft robots are inherently underactuated and subject to intrinsic input constraints, making dynamic control particularly challenging, especially in hybrid rigid-soft robots. While most existing methods focus on quasi-static behaviors, dynamic tasks such as swing-up require accurate exploitation of continuum dynamics. This has led to studies on simple low-order template systems that often fail to capture the complexity of real continuum deformations. Model-based optimal control offers a systematic solution; however, its application to rigid-soft robots is often limited by the computational cost and inaccuracy of numerical differentiation for high-dimensional models. Building on recent advances in the Geometric Variable Strain model that enable analytical derivatives, this work investigates three optimal control strategies for underactuated soft systems-Direct Collocation, Differential Dynamic Programming, and Nonlinear Model Predictive Control-to perform dynamic swing-up tasks. To address stiff continuum dynamics and constrained actuation, implicit integration schemes and warm-start strategies are employed to improve numerical robustness and computational efficiency. The methods are evaluated in simulation on three Rigid-Soft and high-order soft benchmark systems-the Soft Cart-Pole, the Soft Pendubot, and the Soft Furuta Pendulum- highlighting their performance and computational trade-offs.
Collision Detection with Analytical Derivatives of Contact Kinematics
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Differentiable contact kinematics are essential for gradient-based methods in robotics, yet the mapping from robot state to contact distance, location, and normal becomes non-smooth in degenerate configurations of shapes with zero or undefined curvature. We address this inherent limitation by selectively regularizing such geometries into strictly convex implicit representations, restoring uniqueness and smoothness of the contact map. Leveraging this geometric regularization, we develop iDCOL, an implicit differentiable collision detection and contact kinematics framework. iDCOL represents colliding bodies using strictly convex implicit surfaces and computes collision detection and contact kinematics by solving a fixed-size nonlinear system derived from a geometric scaling-based convex optimization formulation. By applying the Implicit Function Theorem to the resulting system residual, we derive analytical derivatives of the contact kinematic quantities. We develop a fast Newton-based solver for iDCOL and provide an open-source C++ implementation of the framework. The robustness of the approach is evaluated through extensive collision simulations and benchmarking, and applicability is demonstrated in gradient-based kinematic path planning and differentiable contact physics, including multi-body rigid collisions and a soft-robot interaction example.
SoFFT: Spatial Fourier Transform for Modeling Continuum Soft Robots
Feb 24, 2025



Abstract:Continuum soft robots, composed of flexible materials, exhibit theoretically infinite degrees of freedom, enabling notable adaptability in unstructured environments. Cosserat Rod Theory has emerged as a prominent framework for modeling these robots efficiently, representing continuum soft robots as time-varying curves, known as backbones. In this work, we propose viewing the robot's backbone as a signal in space and time, applying the Fourier transform to describe its deformation compactly. This approach unifies existing modeling strategies within the Cosserat Rod Theory framework, offering insights into commonly used heuristic methods. Moreover, the Fourier transform enables the development of a data-driven methodology to experimentally capture the robot's deformation. The proposed approach is validated through numerical simulations and experiments on a real-world prototype, demonstrating a reduction in the degrees of freedom while preserving the accuracy of the deformation representation.
Rod models in continuum and soft robot control: a review
Jul 08, 2024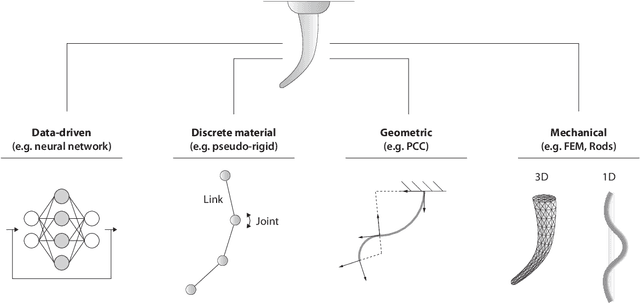
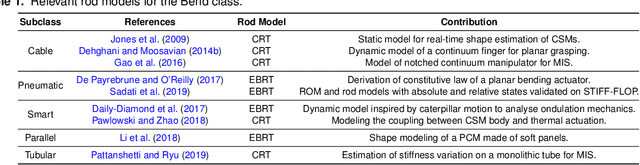
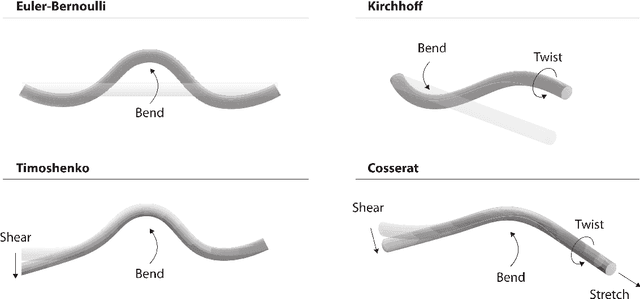
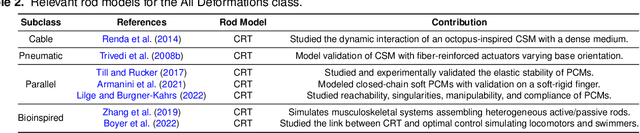
Abstract:Continuum and soft robots can positively impact diverse sectors, from biomedical applications to marine and space exploration, thanks to their potential to adaptively interact with unstructured environments. However, the complex mechanics exhibited by these robots pose diverse challenges in modeling and control. Reduced order continuum mechanical models based on rod theories have emerged as a promising framework, striking a balance between accurately capturing deformations of slender bodies and computational efficiency. This review paper explores rod-based models and control strategies for continuum and soft robots. In particular, it summarizes the mathematical background underlying the four main rod theories applied in soft robotics. Then, it categorizes the literature on rod models applied to continuum and soft robots based on deformation classes, actuation technology, or robot type. Finally, it reviews recent model-based and learning-based control strategies leveraging rod models. The comprehensive review includes a critical discussion of the trends, advantages, limits, and possible future developments of rod models. This paper could guide researchers intending to simulate and control new soft robots and provide feedback to the design and manufacturing community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge