Daniel M. Romero
Networks and Identity Drive Geographic Properties of the Diffusion of Linguistic Innovation
Feb 10, 2022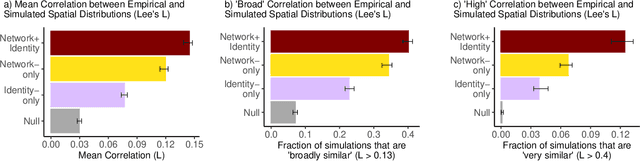
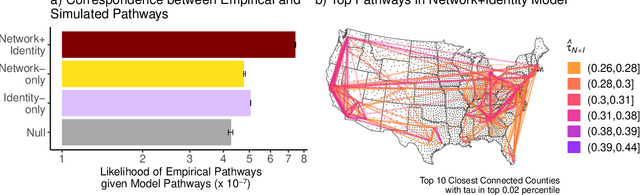
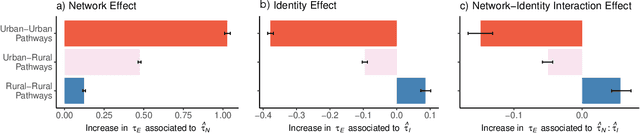
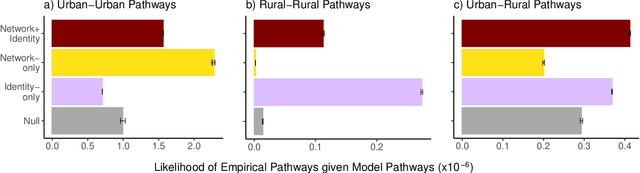
Abstract:Adoption of cultural innovation (e.g., music, beliefs, language) is often geographically correlated, with adopters largely residing within the boundaries of relatively few well-studied, socially significant areas. These cultural regions are often hypothesized to be the result of either (i) identity performance driving the adoption of cultural innovation, or (ii) homophily in the networks underlying diffusion. In this study, we show that demographic identity and network topology are both required to model the diffusion of innovation, as they play complementary roles in producing its spatial properties. We develop an agent-based model of cultural adoption, and validate geographic patterns of transmission in our model against a novel dataset of innovative words that we identify from a 10% sample of Twitter. Using our model, we are able to directly compare a combined network + identity model of diffusion to simulated network-only and identity-only counterfactuals -- allowing us to test the separate and combined roles of network and identity. While social scientists often treat either network or identity as the core social structure in modeling culture change, we show that key geographic properties of diffusion actually depend on both factors as each one influences different mechanisms of diffusion. Specifically, the network principally drives spread among urban counties via weak-tie diffusion, while identity plays a disproportionate role in transmission among rural counties via strong-tie diffusion. Diffusion between urban and rural areas, a key component in innovation diffusing nationally, requires both network and identity. Our work suggests that models must integrate both factors in order to understand and reproduce the adoption of innovation.
Mimicry Is Presidential: Linguistic Style Matching in Presidential Debates and Improved Polling Numbers
Aug 07, 2015
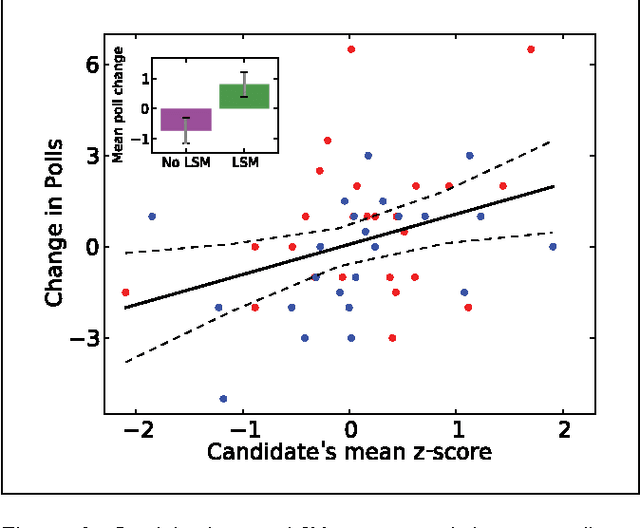
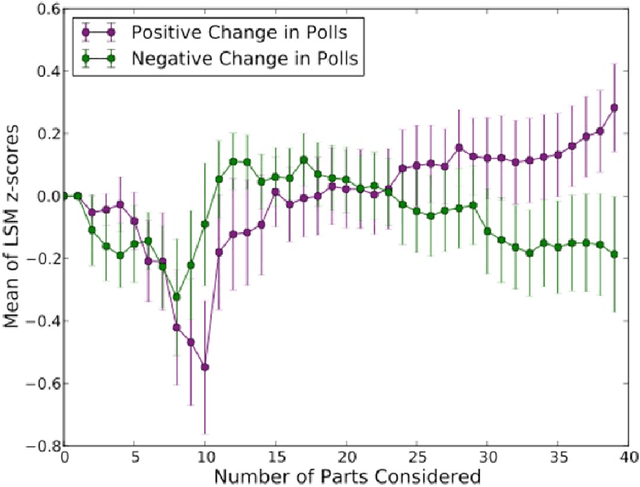
Abstract:The current research used the contexts of U.S. presidential debates and negotiations to examine whether matching the linguistic style of an opponent in a two-party exchange affects the reactions of third-party observers. Building off communication accommodation theory (CAT), interaction alignment theory (IAT), and processing fluency, we propose that language style matching (LSM) will improve subsequent third-party evaluations because matching an opponent's linguistic style reflects greater perspective taking and will make one's arguments easier to process. In contrast, research on status inferences predicts that LSM will negatively impact third-party evaluations because LSM implies followership. We conduct two studies to test these competing hypotheses. Study 1 analyzed transcripts of U.S. presidential debates between 1976 and 2012 and found that candidates who matched their opponent's linguistic style increased their standing in the polls. Study 2 demonstrated a causal relationship between LSM and third-party observer evaluations using negotiation transcripts.
The Directed Closure Process in Hybrid Social-Information Networks, with an Analysis of Link Formation on Twitter
Mar 12, 2010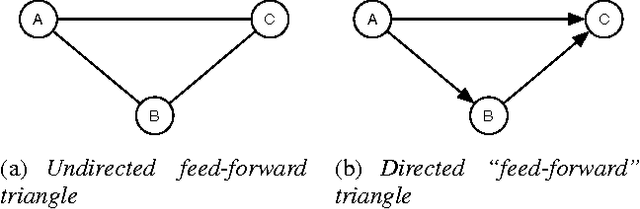
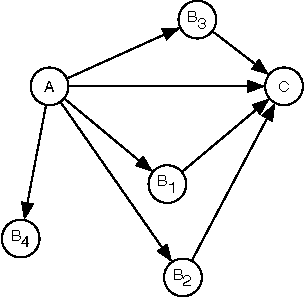
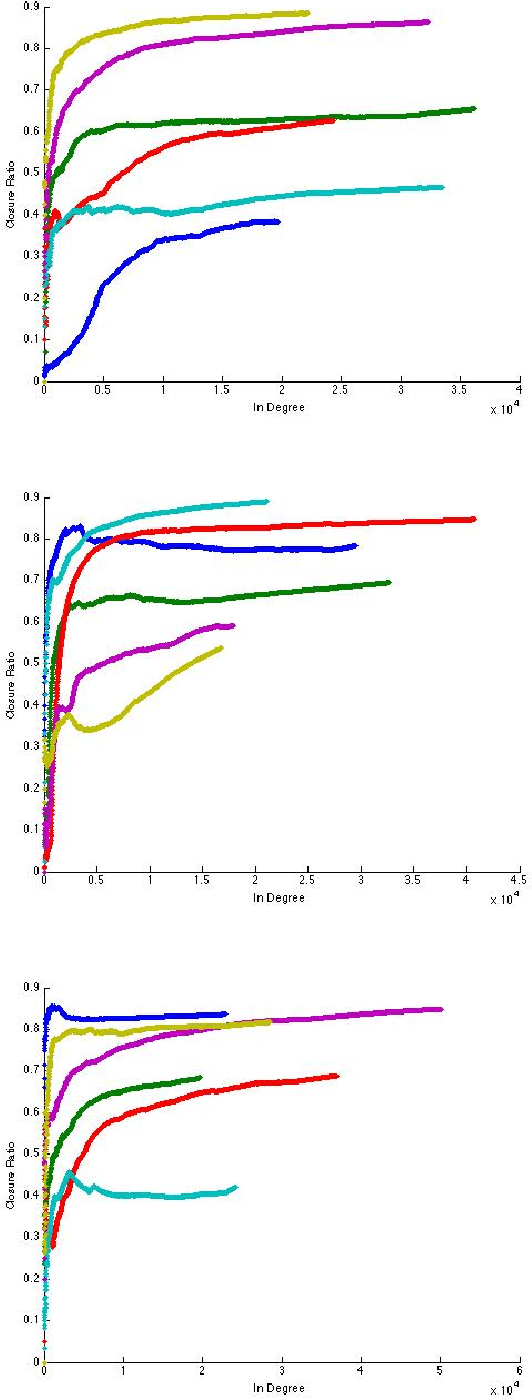
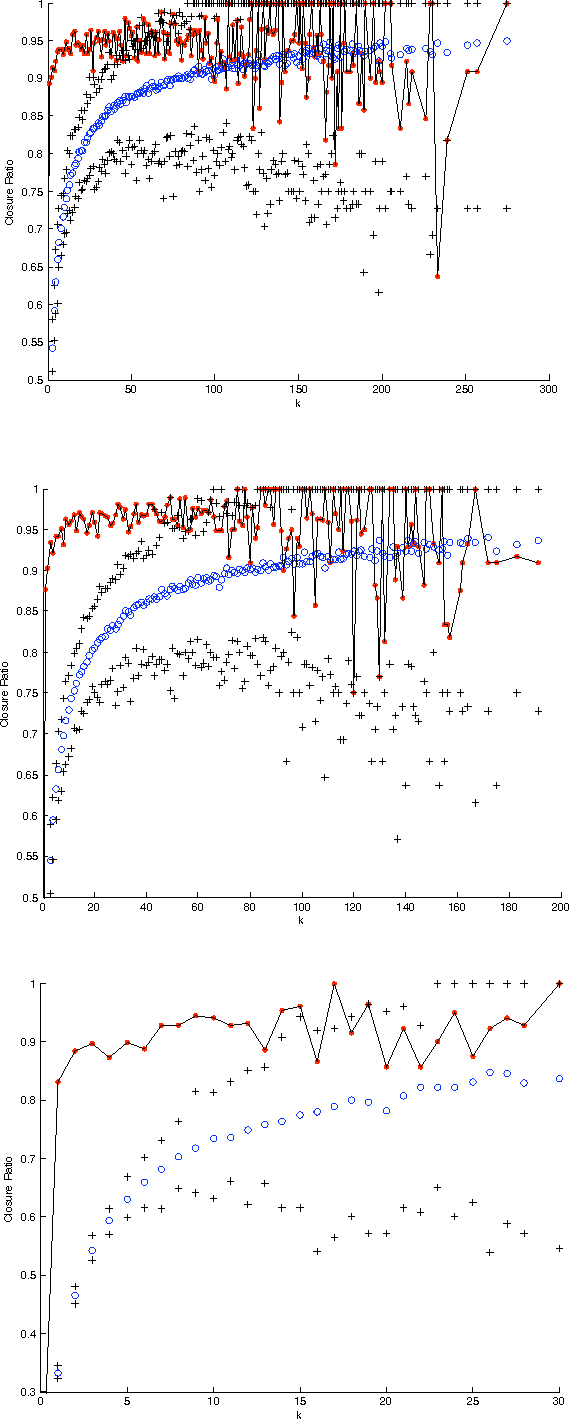
Abstract:It has often been taken as a working assumption that directed links in information networks are frequently formed by "short-cutting" a two-step path between the source and the destination -- a kind of implicit "link copying" analogous to the process of triadic closure in social networks. Despite the role of this assumption in theoretical models such as preferential attachment, it has received very little direct empirical investigation. Here we develop a formalization and methodology for studying this type of directed closure process, and we provide evidence for its important role in the formation of links on Twitter. We then analyze a sequence of models designed to capture the structural phenomena related to directed closure that we observe in the Twitter data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge