Curtiss B. Cook
LLM-Forest for Health Tabular Data Imputation
Oct 28, 2024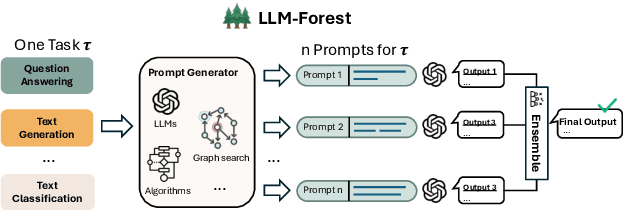
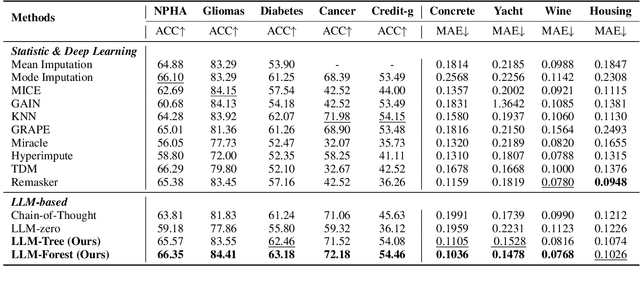
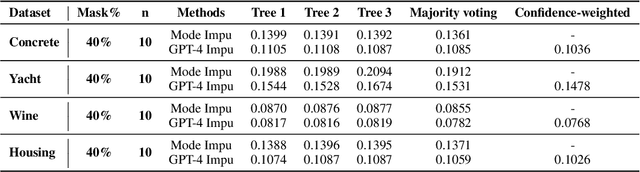
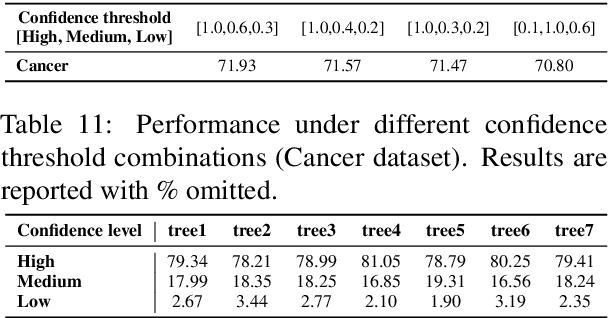
Abstract:Missing data imputation is a critical challenge in tabular datasets, especially in healthcare, where data completeness is vital for accurate analysis. Large language models (LLMs), trained on vast corpora, have shown strong potential in data generation, making them a promising tool for tabular data imputation. However, challenges persist in designing effective prompts for a finetuning-free process and in mitigating the risk of LLM hallucinations. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework, LLM-Forest, which introduces a "forest" of few-shot learning LLM "trees" with confidence-based weighted voting. This framework is established on a new concept of bipartite information graphs to identify high-quality relevant neighboring entries with both feature and value granularity. Extensive experiments on four real-world healthcare datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of LLM-Forest.
Multi-facet Contextual Bandits: A Neural Network Perspective
Jun 13, 2021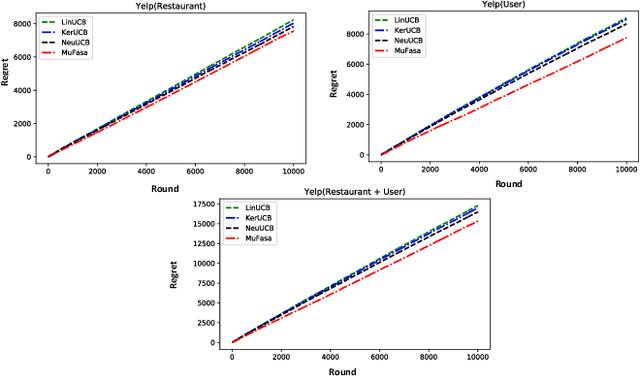
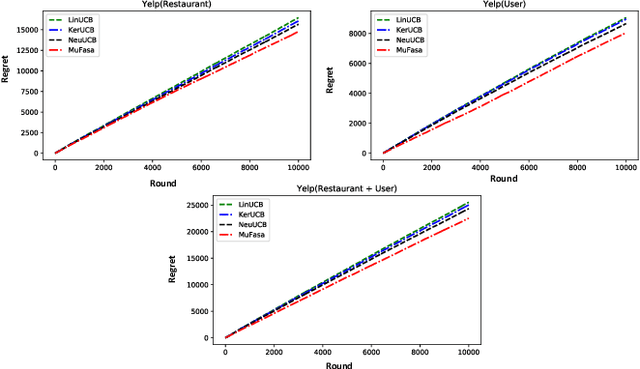
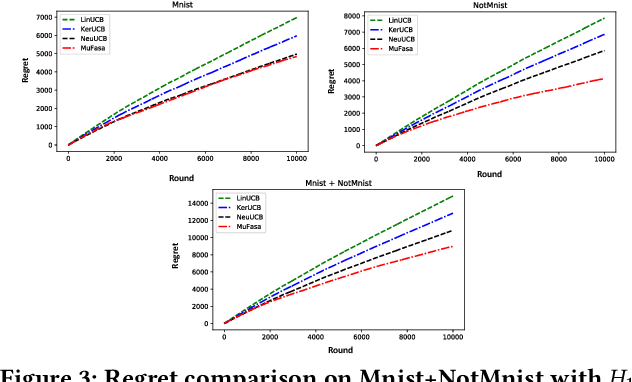
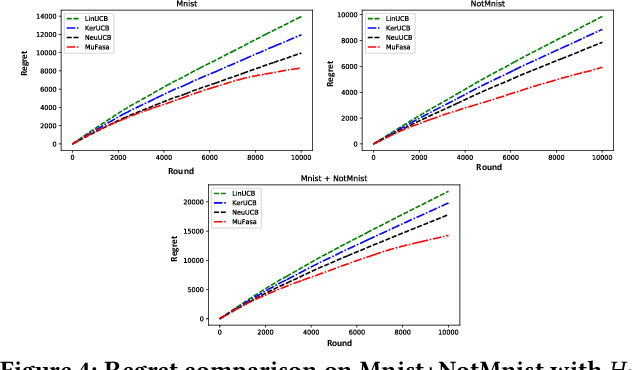
Abstract:Contextual multi-armed bandit has shown to be an effective tool in recommender systems. In this paper, we study a novel problem of multi-facet bandits involving a group of bandits, each characterizing the users' needs from one unique aspect. In each round, for the given user, we need to select one arm from each bandit, such that the combination of all arms maximizes the final reward. This problem can find immediate applications in E-commerce, healthcare, etc. To address this problem, we propose a novel algorithm, named MuFasa, which utilizes an assembled neural network to jointly learn the underlying reward functions of multiple bandits. It estimates an Upper Confidence Bound (UCB) linked with the expected reward to balance between exploitation and exploration. Under mild assumptions, we provide the regret analysis of MuFasa. It can achieve the near-optimal $\widetilde{ \mathcal{O}}((K+1)\sqrt{T})$ regret bound where $K$ is the number of bandits and $T$ is the number of played rounds. Furthermore, we conduct extensive experiments to show that MuFasa outperforms strong baselines on real-world data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge