Cristina-Iulia Bucur
Nanopublication-Based Semantic Publishing and Reviewing: A Field Study with Formalization Papers
Mar 03, 2022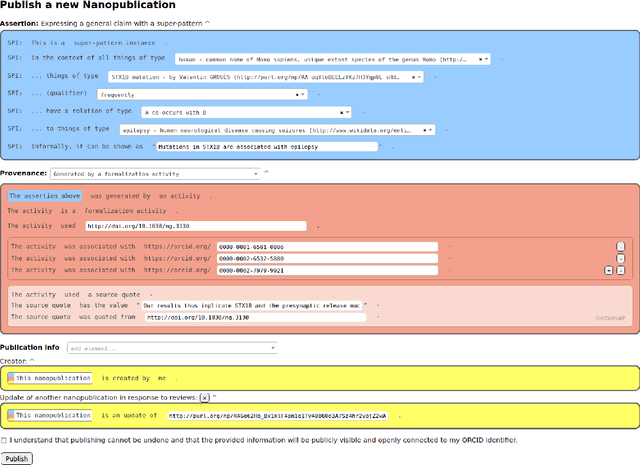
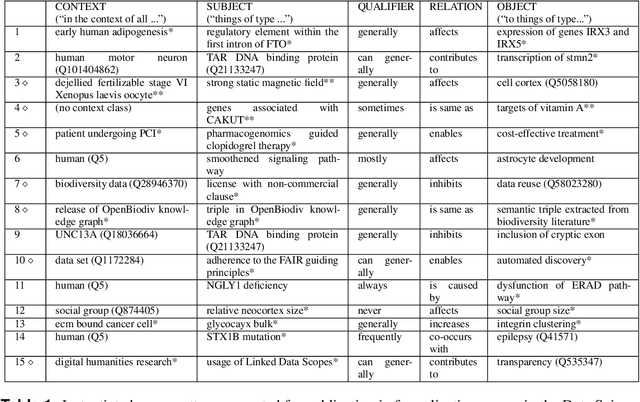
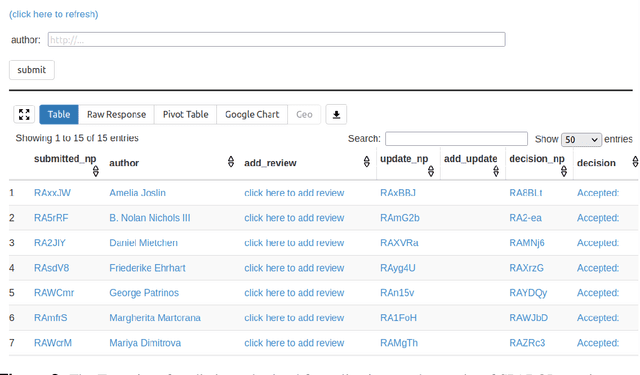
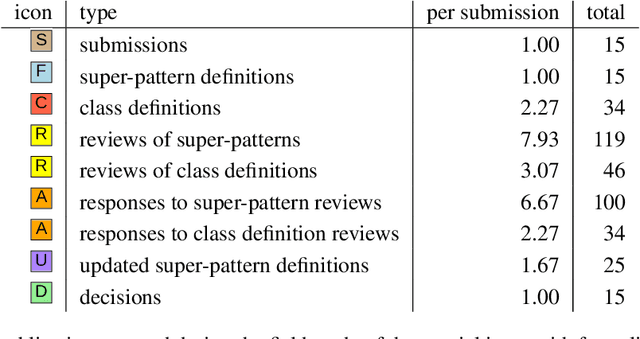
Abstract:With the rapidly increasing amount of scientific literature,it is getting continuously more difficult for researchers in different disciplines to be updated with the recent findings in their field of study.Processing scientific articles in an automated fashion has been proposed as a solution to this problem,but the accuracy of such processing remains very poor for extraction tasks beyond the basic ones.Few approaches have tried to change how we publish scientific results in the first place,by making articles machine-interpretable by expressing them with formal semantics from the start.In the work presented here,we set out to demonstrate that we can formally publish high-level scientific claims in formal logic,and publish the results in a special issue of an existing journal.We use the concept and technology of nanopublications for this endeavor,and represent not just the submissions and final papers in this RDF-based format,but also the whole process in between,including reviews,responses,and decisions.We do this by performing a field study with what we call formalization papers,which contribute a novel formalization of a previously published claim.We received 15 submissions from 18 authors,who then went through the whole publication process leading to the publication of their contributions in the special issue.Our evaluation shows the technical and practical feasibility of our approach.The participating authors mostly showed high levels of interest and confidence,and mostly experienced the process as not very difficult,despite the technical nature of the current user interfaces.We believe that these results indicate that it is possible to publish scientific results from different fields with machine-interpretable semantics from the start,which in turn opens countless possibilities to radically improve in the future the effectiveness and efficiency of the scientific endeavor as a whole.
Expressing High-Level Scientific Claims with Formal Semantics
Sep 27, 2021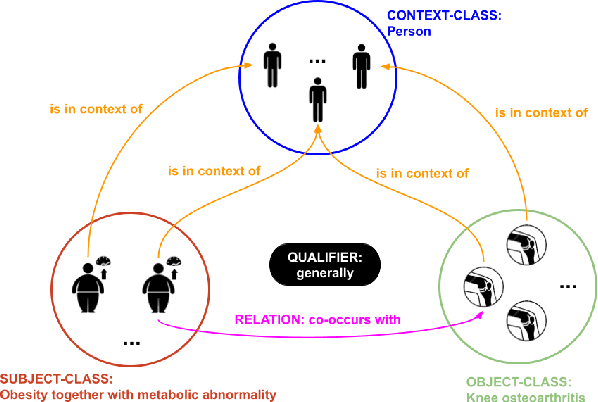
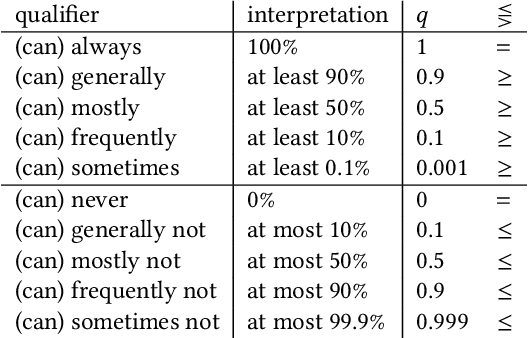
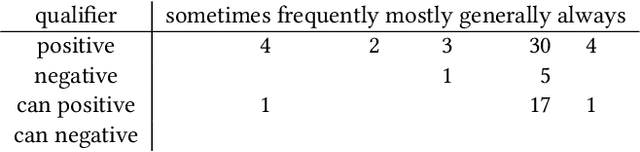
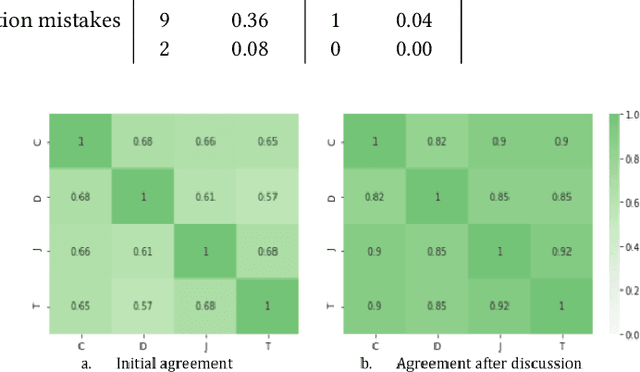
Abstract:The use of semantic technologies is gaining significant traction in science communication with a wide array of applications in disciplines including the Life Sciences, Computer Science, and the Social Sciences. Languages like RDF, OWL, and other formalisms based on formal logic are applied to make scientific knowledge accessible not only to human readers but also to automated systems. These approaches have mostly focused on the structure of scientific publications themselves, on the used scientific methods and equipment, or on the structure of the used datasets. The core claims or hypotheses of scientific work have only been covered in a shallow manner, such as by linking mentioned entities to established identifiers. In this research, we therefore want to find out whether we can use existing semantic formalisms to fully express the content of high-level scientific claims using formal semantics in a systematic way. Analyzing the main claims from a sample of scientific articles from all disciplines, we find that their semantics are more complex than what a straight-forward application of formalisms like RDF or OWL account for, but we managed to elicit a clear semantic pattern which we call the 'super-pattern'. We show here how the instantiation of the five slots of this super-pattern leads to a strictly defined statement in higher-order logic. We successfully applied this super-pattern to an enlarged sample of scientific claims. We show that knowledge representation experts, when instructed to independently instantiate the super-pattern with given scientific claims, show a high degree of consistency and convergence given the complexity of the task and the subject. These results therefore open the door for expressing high-level scientific findings in a manner they can be automatically interpreted, which on the longer run can allow us to do automated consistency checking, and much more.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge