Cosmin Badea
Can a Machine be Conscious? Towards Universal Criteria for Machine Consciousness
Apr 30, 2024Abstract:As artificially intelligent systems become more anthropomorphic and pervasive, and their potential impact on humanity more urgent, discussions about the possibility of machine consciousness have significantly intensified, and it is sometimes seen as 'the holy grail'. Many concerns have been voiced about the ramifications of creating an artificial conscious entity. This is compounded by a marked lack of consensus around what constitutes consciousness and by an absence of a universal set of criteria for determining consciousness. By going into depth on the foundations and characteristics of consciousness, we propose five criteria for determining whether a machine is conscious, which can also be applied more generally to any entity. This paper aims to serve as a primer and stepping stone for researchers of consciousness, be they in philosophy, computer science, medicine, or any other field, to further pursue this holy grail of philosophy, neuroscience and artificial intelligence.
If our aim is to build morality into an artificial agent, how might we begin to go about doing so?
Oct 12, 2023Abstract:As Artificial Intelligence (AI) becomes pervasive in most fields, from healthcare to autonomous driving, it is essential that we find successful ways of building morality into our machines, especially for decision-making. However, the question of what it means to be moral is still debated, particularly in the context of AI. In this paper, we highlight the different aspects that should be considered when building moral agents, including the most relevant moral paradigms and challenges. We also discuss the top-down and bottom-up approaches to design and the role of emotion and sentience in morality. We then propose solutions including a hybrid approach to design and a hierarchical approach to combining moral paradigms. We emphasize how governance and policy are becoming ever more critical in AI Ethics and in ensuring that the tasks we set for moral agents are attainable, that ethical behavior is achieved, and that we obtain good AI.
* 12 pages, 1 figure,
Minimum Levels of Interpretability for Artificial Moral Agents
Jul 02, 2023Abstract:As artificial intelligence (AI) models continue to scale up, they are becoming more capable and integrated into various forms of decision-making systems. For models involved in moral decision-making, also known as artificial moral agents (AMA), interpretability provides a way to trust and understand the agent's internal reasoning mechanisms for effective use and error correction. In this paper, we provide an overview of this rapidly-evolving sub-field of AI interpretability, introduce the concept of the Minimum Level of Interpretability (MLI) and recommend an MLI for various types of agents, to aid their safe deployment in real-world settings.
Establishing Meta-Decision-Making for AI: An Ontology of Relevance, Representation and Reasoning
Oct 02, 2022Abstract:We propose an ontology of building decision-making systems, with the aim of establishing Meta-Decision-Making for Artificial Intelligence (AI), improving autonomy, and creating a framework to build metrics and benchmarks upon. To this end, we propose the three parts of Relevance, Representation, and Reasoning, and discuss their value in ensuring safety and mitigating risk in the context of third wave cognitive systems. Our nomenclature reflects the literature on decision-making, and our ontology allows researchers that adopt it to frame their work in relation to one or more of these parts.
Developing moral AI to support antimicrobial decision making
Aug 12, 2022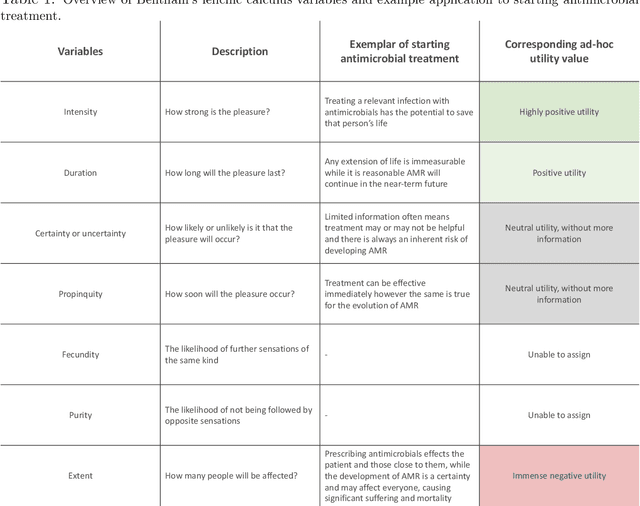
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) assisting with antimicrobial prescribing raises significant moral questions. Utilising ethical frameworks alongside AI-driven systems, while considering infection specific complexities, can support moral decision making to tackle antimicrobial resistance.
Breaking Bad News in the Era of Artificial Intelligence and Algorithmic Medicine: An Exploration of Disclosure and its Ethical Justification using the Hedonic Calculus
Jun 23, 2022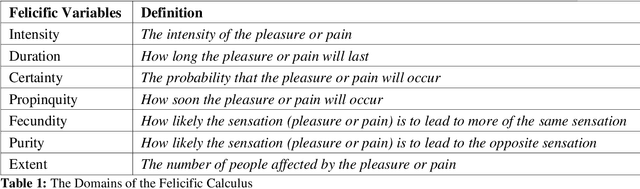
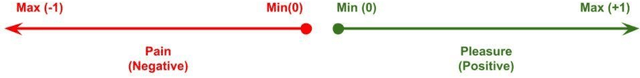
Abstract:An appropriate ethical framework around the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare has become a key desirable with the increasingly widespread deployment of this technology. Advances in AI hold the promise of improving the precision of outcome prediction at the level of the individual. However, the addition of these technologies to patient-clinician interactions, as with any complex human interaction, has potential pitfalls. While physicians have always had to carefully consider the ethical background and implications of their actions, detailed deliberations around fast-moving technological progress may not have kept up. We use a common but key challenge in healthcare interactions, the disclosure of bad news (likely imminent death), to illustrate how the philosophical framework of the 'Felicific Calculus' developed in the 18th century by Jeremy Bentham, may have a timely quasi-quantitative application in the age of AI. We show how this ethical algorithm can be used to assess, across seven mutually exclusive and exhaustive domains, whether an AI-supported action can be morally justified.
Have a break from making decisions, have a MARS: The Multi-valued Action Reasoning System
Sep 07, 2021Abstract:The Multi-valued Action Reasoning System (MARS) is an automated value-based ethical decision-making model for artificial agents (AI). Given a set of available actions and an underlying moral paradigm, by employing MARS one can identify the ethically preferred action. It can be used to implement and model different ethical theories, different moral paradigms, as well as combinations of such, in the context of automated practical reasoning and normative decision analysis. It can also be used to model moral dilemmas and discover the moral paradigms that result in the desired outcomes therein. In this paper, we give a condensed description of MARS, explain its uses, and comparatively place it in the existing literature.
Morality, Machines and the Interpretation Problem: A value-based, Wittgensteinian approach to building Moral Agents
Mar 03, 2021Abstract:We argue that the attempt to build morality into machines is subject to what we call the Interpretation problem, whereby any rule we give the machine is open to infinite interpretation in ways that we might morally disapprove of, and that the interpretation problem in Artificial Intelligence is an illustration of Wittgenstein's general claim that no rule can contain the criteria for its own application. Using games as an example, we attempt to define the structure of normative spaces and argue that any rule-following within a normative space is guided by values that are external to that space and which cannot themselves be represented as rules. In light of this problem, we analyse the types of mistakes an artificial moral agent could make and we make suggestions about how to build morality into machines by getting them to interpret the rules we give in accordance with these external values, through explicit moral reasoning and the presence of structured values, the adjustment of causal power assigned to the agent and interaction with human agents, such that the machine develops a virtuous character and the impact of the interpretation problem is minimised.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge