Corrado Santoro
Robotics Laboratory - Department of Mathematics and Computer Science - University of Catania - Italy
Image-based Navigation in Real-World Environments via Multiple Mid-level Representations: Fusion Models, Benchmark and Efficient Evaluation
Feb 02, 2022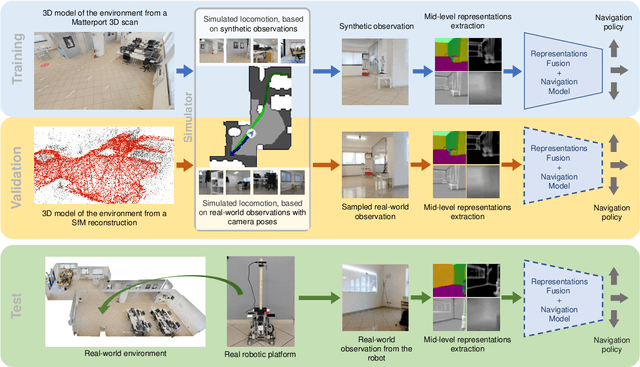
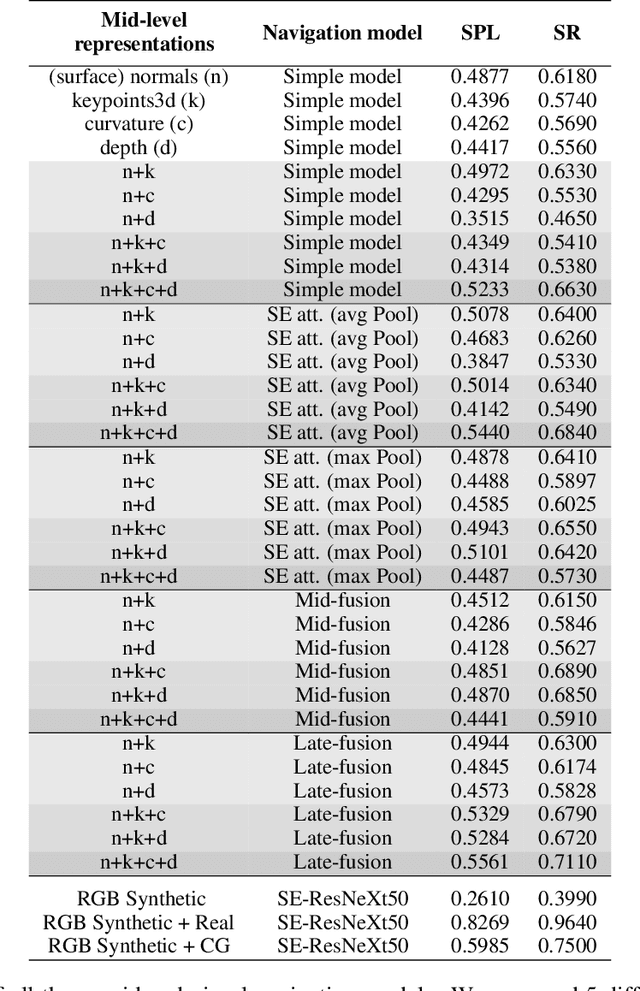
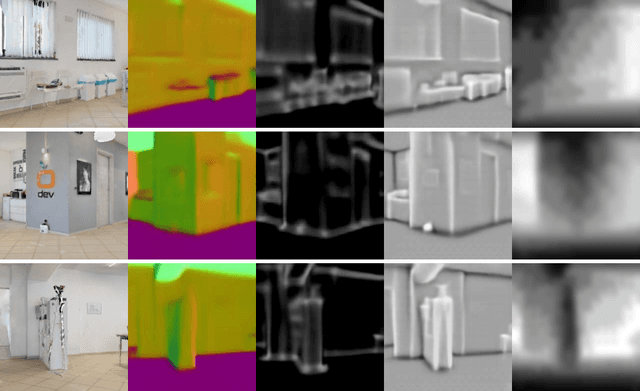
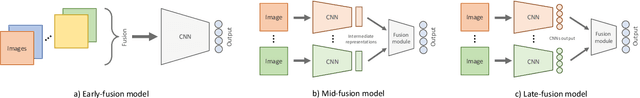
Abstract:Navigating complex indoor environments requires a deep understanding of the space the robotic agent is acting into to correctly inform the navigation process of the agent towards the goal location. In recent learning-based navigation approaches, the scene understanding and navigation abilities of the agent are achieved simultaneously by collecting the required experience in simulation. Unfortunately, even if simulators represent an efficient tool to train navigation policies, the resulting models often fail when transferred into the real world. One possible solution is to provide the navigation model with mid-level visual representations containing important domain-invariant properties of the scene. But, what are the best representations that facilitate the transfer of a model to the real-world? How can they be combined? In this work we address these issues by proposing a benchmark of Deep Learning architectures to combine a range of mid-level visual representations, to perform a PointGoal navigation task following a Reinforcement Learning setup. All the proposed navigation models have been trained with the Habitat simulator on a synthetic office environment and have been tested on the same real-world environment using a real robotic platform. To efficiently assess their performance in a real context, a validation tool has been proposed to generate realistic navigation episodes inside the simulator. Our experiments showed that navigation models can benefit from the multi-modal input and that our validation tool can provide good estimation of the expected navigation performance in the real world, while saving time and resources. The acquired synthetic and real 3D models of the environment, together with the code of our validation tool built on top of Habitat, are publicly available at the following link: https://iplab.dmi.unict.it/EmbodiedVN/
Ontological Smart Contracts in OASIS: Ontology for Agents, Systems, and Integration of Services
Dec 02, 2020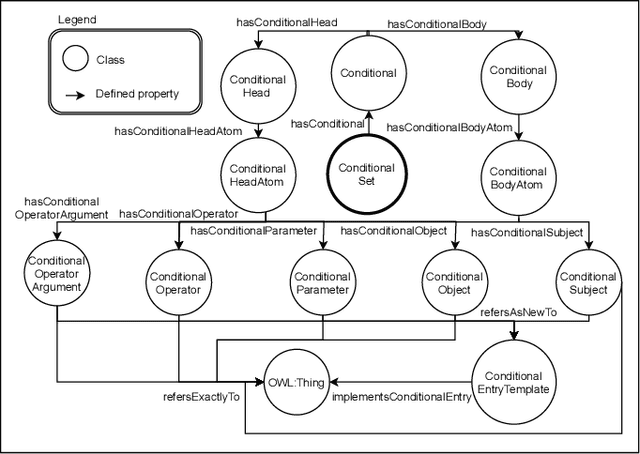
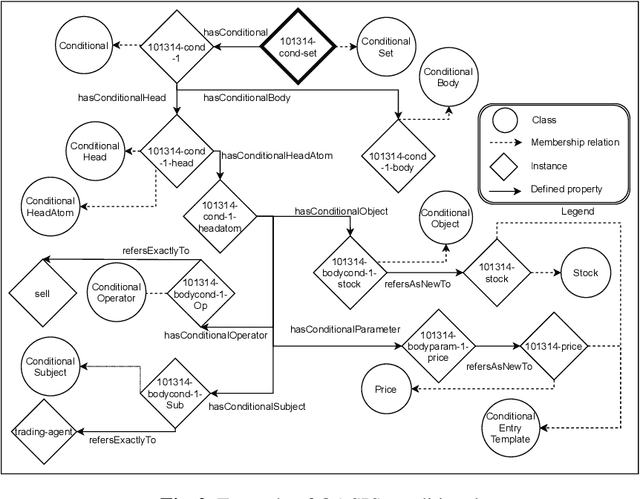
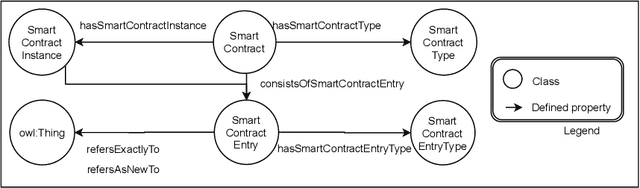
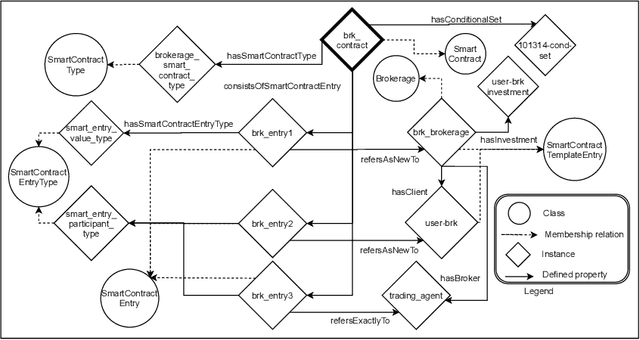
Abstract:In this contribution we extend an ontology for modelling agents and their interactions, called Ontology for Agents, Systems, and Integration of Services (in short, OASIS), with conditionals and ontological smart contracts (in short, OSCs). OSCs are ontological representations of smart contracts that allow to establish responsibilities and authorizations among agents and set agreements, whereas conditionals allow one to restrict and limit agent interactions, define activation mechanisms that trigger agent actions, and define constraints and contract terms on OSCs. Conditionals and OSCs, as defined in OASIS, are applied to extend with ontological capabilities digital public ledgers such as the blockchain and smart contracts implemented on it. We will also sketch the architecture of a framework based on the OASIS definition of OSCs that exploits the Ethereum platform and the Interplanetary File System.
* This work has been accepted for publication at The 14th International Symposium on Intelligent Distributed Computing, 21--23 September 2020, Scilla, Reggio Calabria, Italy. Proceedings and conference have been postponed to September 2021. Paper accepted on 8 September 2020
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge