Domenico Cantone
The Ontology for Agents, Systems and Integration of Services: OASIS version 2
Jun 14, 2023



Abstract:Semantic representation is a key enabler for several application domains, and the multi-agent systems realm makes no exception. Among the methods for semantically representing agents, one has been essentially achieved by taking a behaviouristic vision, through which one can describe how they operate and engage with their peers. The approach essentially aims at defining the operational capabilities of agents through the mental states related with the achievement of tasks. The OASIS ontology -- An Ontology for Agent, Systems, and Integration of Services, presented in 2019 -- pursues the behaviouristic approach to deliver a semantic representation system and a communication protocol for agents and their commitments. This paper reports on the main modeling choices concerning the representation of agents in OASIS 2, the latest major upgrade of OASIS, and the achievement reached by the ontology since it was first introduced, in particular in the context of ontologies for blockchains.
* Already published on Intelligenza Artificiale, Vol. 17, no 1, pp. 51-62, 2023. DOI 10.3233/IA-230002
Complexity assessments for decidable fragments of Set Theory. III: A quadratic reduction of constraints over nested sets to Boolean formulae
Dec 09, 2021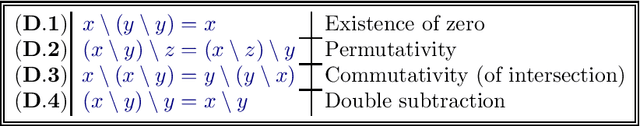
Abstract:As a contribution to quantitative set-theoretic inferencing, a translation is proposed of conjunctions of literals of the forms $x=y\setminus z$, $x \neq y\setminus z$, and $z =\{x\}$, where $x,y,z$ stand for variables ranging over the von Neumann universe of sets, into unquantified Boolean formulae of a rather simple conjunctive normal form. The formulae in the target language involve variables ranging over a Boolean ring of sets, along with a difference operator and relators designating equality, non-disjointness and inclusion. Moreover, the result of each translation is a conjunction of literals of the forms $x=y\setminus z$, $x\neq y\setminus z$ and of implications whose antecedents are isolated literals and whose consequents are either inclusions (strict or non-strict) between variables, or equalities between variables. Besides reflecting a simple and natural semantics, which ensures satisfiability-preservation, the proposed translation has quadratic algorithmic time-complexity, and bridges two languages both of which are known to have an NP-complete satisfiability problem.
Blockchains through ontologies: the case study of the Ethereum ERC721 standard in OASIS (Extended Version)
Sep 18, 2021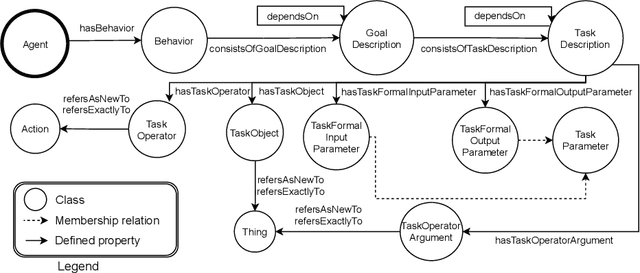
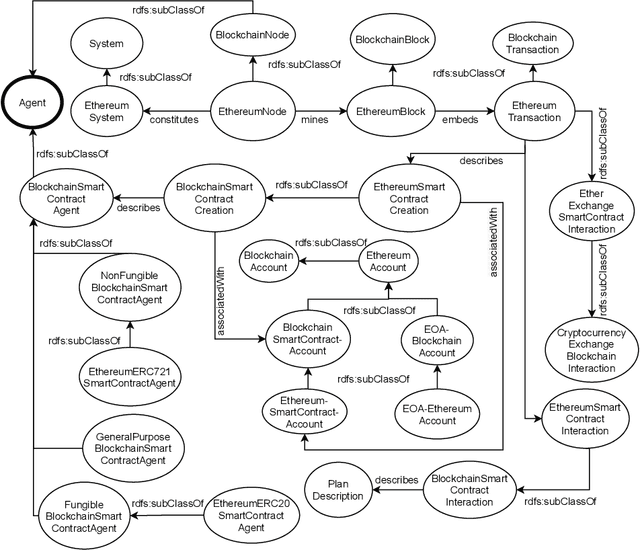
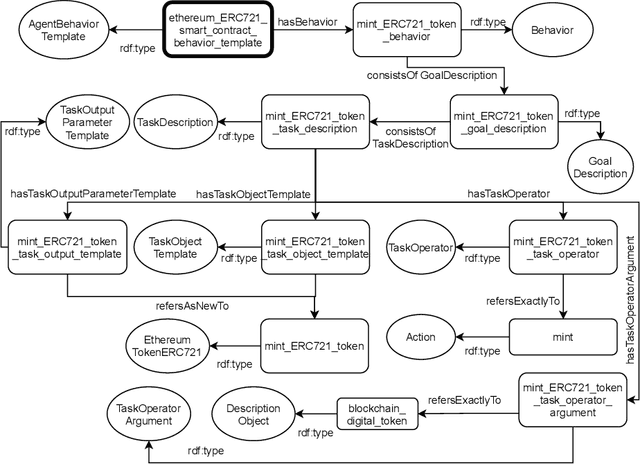
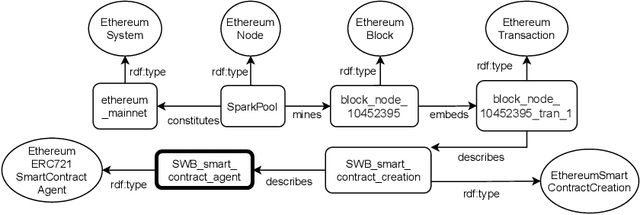
Abstract:Blockchains are gaining momentum due to the interest of industries and people in \emph{decentralized applications} (Dapps), particularly in those for trading assets through digital certificates secured on blockchain, called tokens. As a consequence, providing a clear unambiguous description of any activities carried out on blockchains has become crucial, and we feel the urgency to achieve that description at least for trading. This paper reports on how to leverage the \emph{Ontology for Agents, Systems, and Integration of Services} ("\ONT{}") as a general means for the semantic representation of smart contracts stored on blockchain as software agents. Special attention is paid to non-fungible tokens (NFTs), whose management through the ERC721 standard is presented as a case study.
Ontological Smart Contracts in OASIS: Ontology for Agents, Systems, and Integration of Services
Dec 02, 2020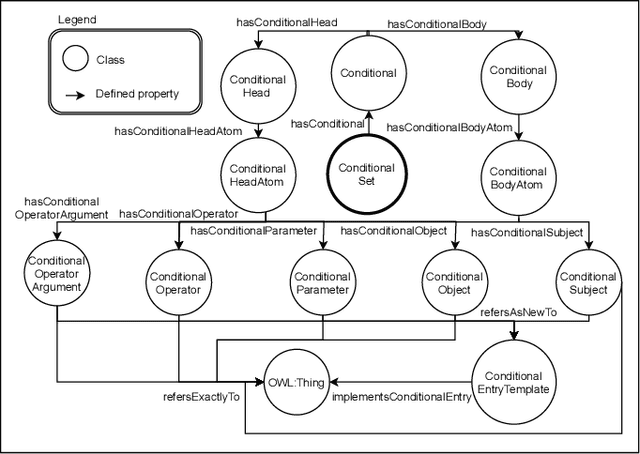
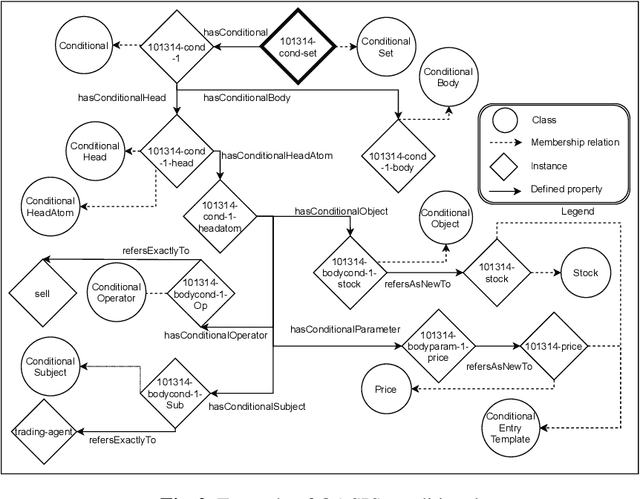
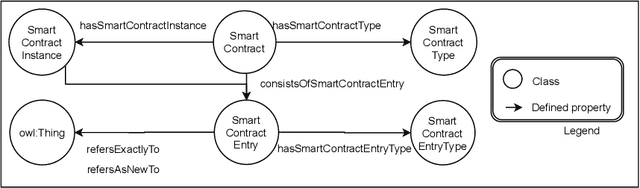
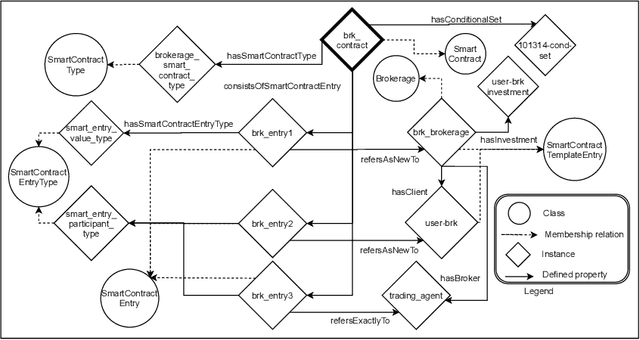
Abstract:In this contribution we extend an ontology for modelling agents and their interactions, called Ontology for Agents, Systems, and Integration of Services (in short, OASIS), with conditionals and ontological smart contracts (in short, OSCs). OSCs are ontological representations of smart contracts that allow to establish responsibilities and authorizations among agents and set agreements, whereas conditionals allow one to restrict and limit agent interactions, define activation mechanisms that trigger agent actions, and define constraints and contract terms on OSCs. Conditionals and OSCs, as defined in OASIS, are applied to extend with ontological capabilities digital public ledgers such as the blockchain and smart contracts implemented on it. We will also sketch the architecture of a framework based on the OASIS definition of OSCs that exploits the Ethereum platform and the Interplanetary File System.
* This work has been accepted for publication at The 14th International Symposium on Intelligent Distributed Computing, 21--23 September 2020, Scilla, Reggio Calabria, Italy. Proceedings and conference have been postponed to September 2021. Paper accepted on 8 September 2020
The Shape of a Benedictine Monastery: The SaintGall Ontology
Jun 29, 2018
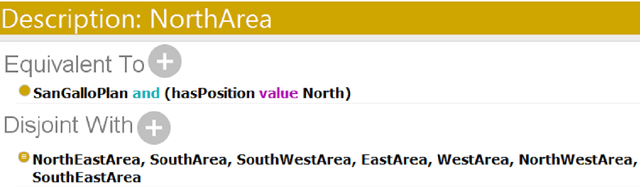


Abstract:We present an OWL 2 ontology representing the Saint Gall plan, one of the most ancient documents arrived intact to us, which describes the ideal model of a Benedictine monastic complex that inspired the design of many European monasteries.
An Experiment on the Connection between the DLs' Family DL<ForAllPiZero> and the Real World
Nov 23, 2012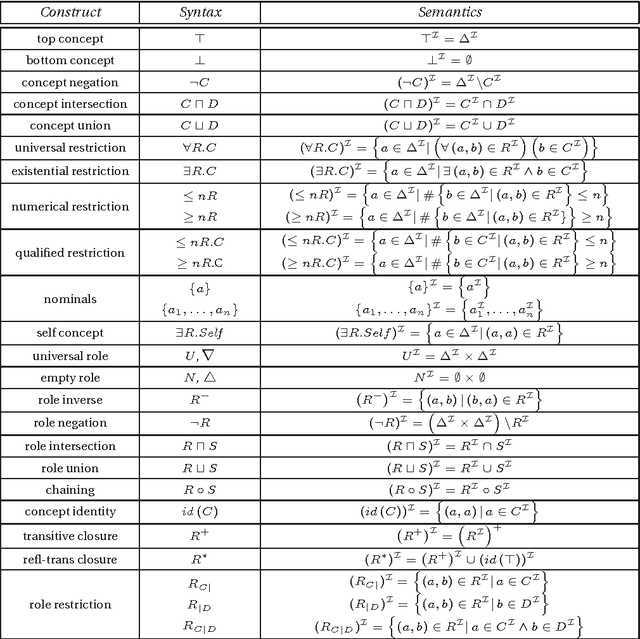
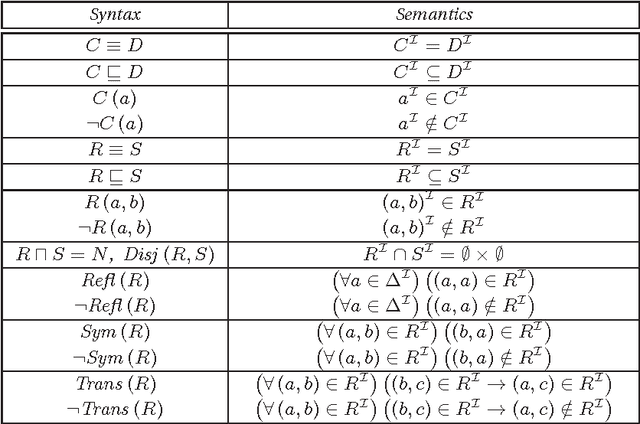
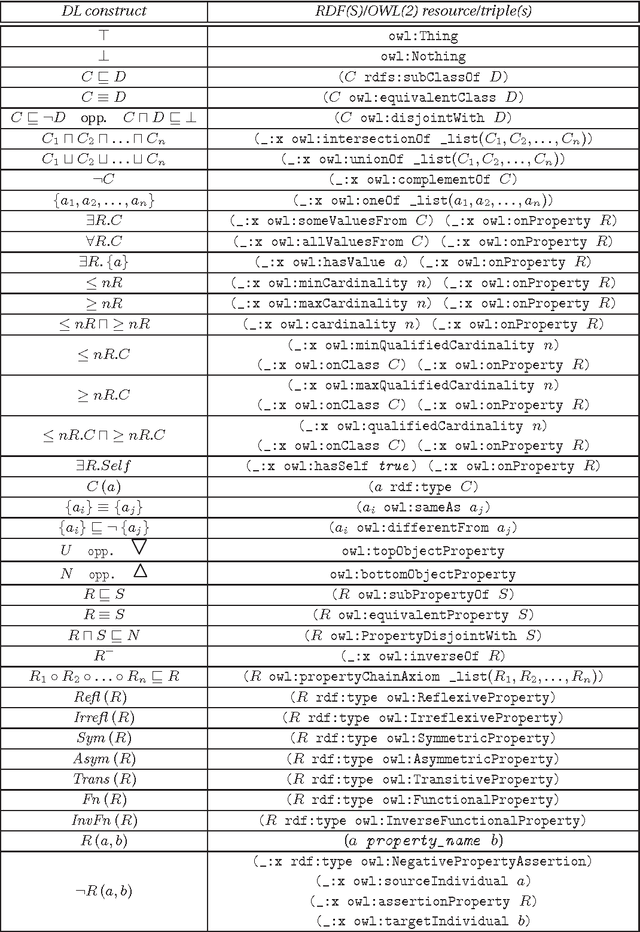
Abstract:This paper describes the analysis of a selected testbed of Semantic Web ontologies, by a SPARQL query, which determines those ontologies that can be related to the description logic DL<ForAllPiZero>, introduced in [4] and studied in [9]. We will see that a reasonable number of them is expressible within such computationally efficient language. We expect that, in a long-term view, a temporalization of description logics, and consequently, of OWL(2), can open new perspectives for the inclusion in this language of a greater number of ontologies of the testbed and, hopefully, of the "real world".
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge