Colin Daniels
On the geometry and topology of representations: the manifolds of modular addition
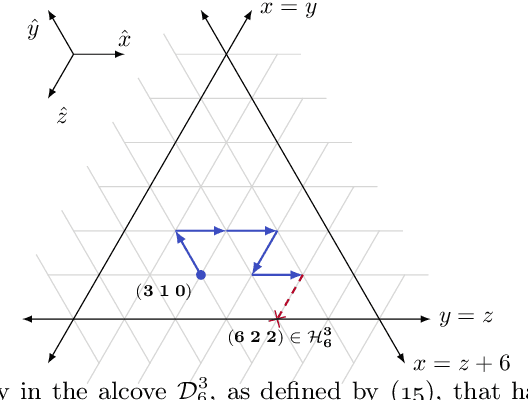
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:The Clock and Pizza interpretations, associated with architectures differing in either uniform or learnable attention, were introduced to argue that different architectural designs can yield distinct circuits for modular addition. In this work, we show that this is not the case, and that both uniform attention and trainable attention architectures implement the same algorithm via topologically and geometrically equivalent representations. Our methodology goes beyond the interpretation of individual neurons and weights. Instead, we identify all of the neurons corresponding to each learned representation and then study the collective group of neurons as one entity. This method reveals that each learned representation is a manifold that we can study utilizing tools from topology. Based on this insight, we can statistically analyze the learned representations across hundreds of circuits to demonstrate the similarity between learned modular addition circuits that arise naturally from common deep learning paradigms.
A Study of Policy Gradient on a Class of Exactly Solvable Models
Nov 03, 2020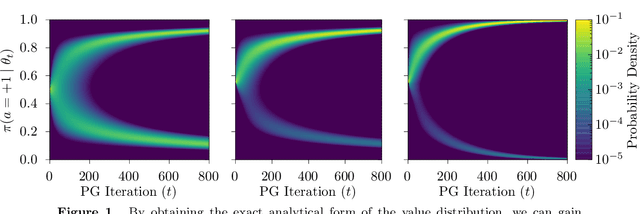
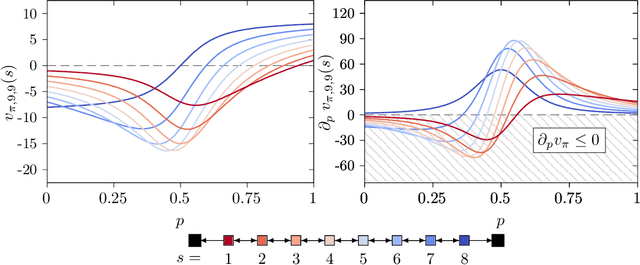
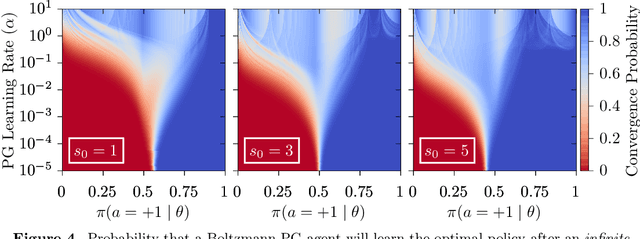
Abstract:Policy gradient methods are extensively used in reinforcement learning as a way to optimize expected return. In this paper, we explore the evolution of the policy parameters, for a special class of exactly solvable POMDPs, as a continuous-state Markov chain, whose transition probabilities are determined by the gradient of the distribution of the policy's value. Our approach relies heavily on random walk theory, specifically on affine Weyl groups. We construct a class of novel partially observable environments with controllable exploration difficulty, in which the value distribution, and hence the policy parameter evolution, can be derived analytically. Using these environments, we analyze the probabilistic convergence of policy gradient to different local maxima of the value function. To our knowledge, this is the first approach developed to analytically compute the landscape of policy gradient in POMDPs for a class of such environments, leading to interesting insights into the difficulty of this problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge