Clara Barbanson
$\textit{A Contrario}$ Paradigm for YOLO-based Infrared Small Target Detection
Feb 03, 2024



Abstract:Detecting small to tiny targets in infrared images is a challenging task in computer vision, especially when it comes to differentiating these targets from noisy or textured backgrounds. Traditional object detection methods such as YOLO struggle to detect tiny objects compared to segmentation neural networks, resulting in weaker performance when detecting small targets. To reduce the number of false alarms while maintaining a high detection rate, we introduce an $\textit{a contrario}$ decision criterion into the training of a YOLO detector. The latter takes advantage of the $\textit{unexpectedness}$ of small targets to discriminate them from complex backgrounds. Adding this statistical criterion to a YOLOv7-tiny bridges the performance gap between state-of-the-art segmentation methods for infrared small target detection and object detection networks. It also significantly increases the robustness of YOLO towards few-shot settings.
Détection de petites cibles par apprentissage profond et critère a contrario
Oct 03, 2022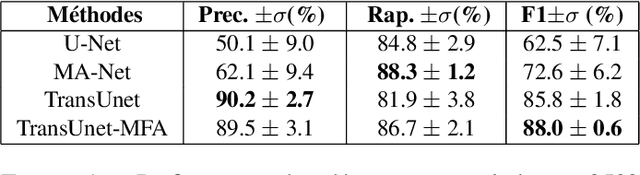
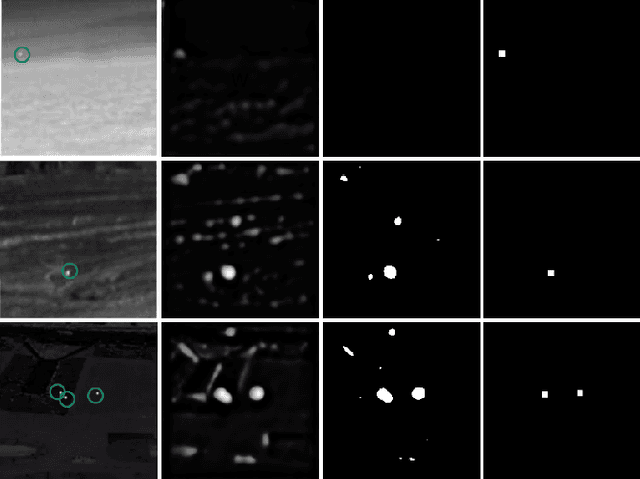
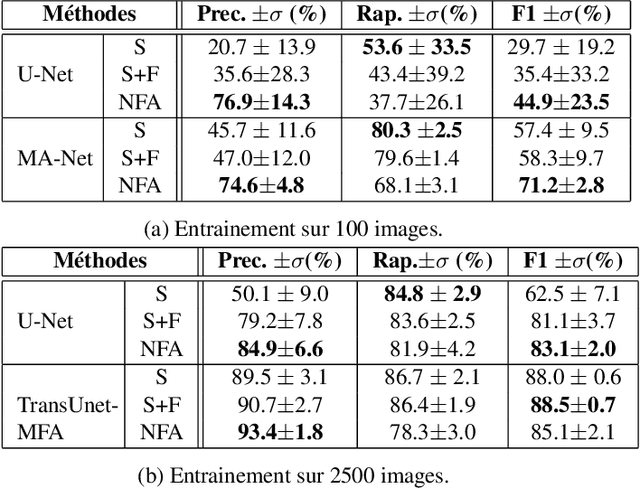
Abstract:Small target detection is an essential yet challenging task in defense applications, since differentiating low-contrast targets from natural textured and noisy environment remains difficult. To better take into account the contextual information, we propose to explore deep learning approaches based on attention mechanisms. Specifically, we propose a customized version of TransUnet including channel attention, which has shown a significant improvement in performance. Moreover, the lack of annotated data induces weak detection precision, leading to many false alarms. We thus explore a contrario methods in order to select meaningful potential targets detected by a weak deep learning training. -- La d\'etection de petites cibles est une probl\'ematique d\'elicate mais essentielle dans le domaine de la d\'efense, notamment lorsqu'il s'agit de diff\'erencier ces cibles d'un fond bruit\'e ou textur\'e, ou lorsqu'elles sont de faible contraste. Pour mieux prendre en compte les informations contextuelles, nous proposons d'explorer diff\'erentes approches de segmentation par apprentissage profond, dont certaines bas\'ees sur les m\'ecanismes d'attention. Nous proposons \'egalement d'inclure un module d'attention par canal au TransUnet, r\'eseau \`a l'\'etat de l'art, ce qui permet d'am\'eliorer significativement les performances. Par ailleurs, le manque de donn\'ees annot\'ees induit une perte en pr\'ecision lors des d\'etections, conduisant \`a de nombreuses fausses alarmes non pertinentes. Nous explorons donc des m\'ethodes a contrario afin de s\'electionner les cibles les plus significatives d\'etect\'ees par un r\'eseau entra\^in\'e avec peu de donn\'ees.
* 4 pages, in French
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge