Chunxin Qiu
Terrain Inclination Aided Three Dimensional Localization and Mapping for an Outdoor Mobile Robot
May 03, 2019
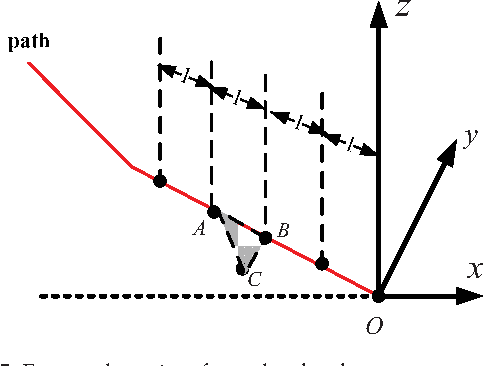

Abstract:A new 3D localization and mapping techinque with terrain inclination assistance is proposed in this paper to allow a robot to identify its location and build a global map in an outdoor environment. The Iterative Closest Points (ICP) algorithm and terrain inclination-based localization are combined together to achieve accurate and fast localization and mapping. Inclinations of the terrains the robot navigates are used to achieve local localization during the interval between two laser scans. Using the results of the above localization as the initial condition, the ICP algorithm is then applied to align the overlapped laser scan maps to update the overhanging obstacles for building a global map of the surrounding area. Comprehensive experiments were carried out for the validation of the proposed 3D localization and mapping technique. The experimental results show that the proposed technique could reduce time consumption and improve the accuracy of the performance.
Vision-based Unscented FastSLAM for Mobile Robot
May 03, 2019



Abstract:This paper presents a vision-based Unscented FastSLAM (UFastSLAM) algorithm combing the Rao-Blackwellized particle filter and Unscented Kalman filte(UKF). The landmarks are detected by a binocular vision to integrate localization and mapping. Since such binocular vision system generally inherits larger measurement errors, it is suitable to adopt Unscented FastSLAM to improve the performance of localization and mapping. Unscented FastSLAM takes advantage of UKF instead of the linear approximations of the nonlinear function where the effective number of particles is used as the criteria to reduce the particle degeneration. Simulations and experiments are carried out to demonstrate that the Unscented FastSLAM algorithm can achieve much better performance in the vision-based system than FastSLAM2.0 algorithm on the accuracy and robustness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge