Chuhui Qiu
Maternal and Fetal Health Status Assessment by Using Machine Learning on Optical 3D Body Scans
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Monitoring maternal and fetal health during pregnancy is crucial for preventing adverse outcomes. While tests such as ultrasound scans offer high accuracy, they can be costly and inconvenient. Telehealth and more accessible body shape information provide pregnant women with a convenient way to monitor their health. This study explores the potential of 3D body scan data, captured during the 18-24 gestational weeks, to predict adverse pregnancy outcomes and estimate clinical parameters. We developed a novel algorithm with two parallel streams which are used for extract body shape features: one for supervised learning to extract sequential abdominal circumference information, and another for unsupervised learning to extract global shape descriptors, alongside a branch for demographic data. Our results indicate that 3D body shape can assist in predicting preterm labor, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), gestational hypertension (GH), and in estimating fetal weight. Compared to other machine learning models, our algorithm achieved the best performance, with prediction accuracies exceeding 88% and fetal weight estimation accuracy of 76.74% within a 10% error margin, outperforming conventional anthropometric methods by 22.22%.
Integrating HCI Datasets in Project-Based Machine Learning Courses: A College-Level Review and Case Study
Aug 06, 2024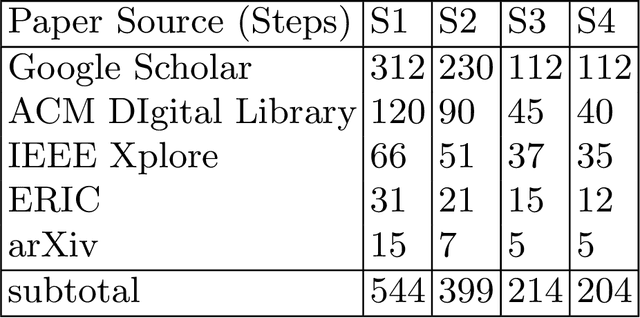

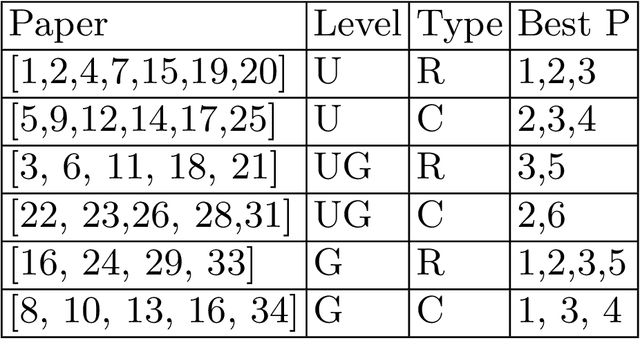
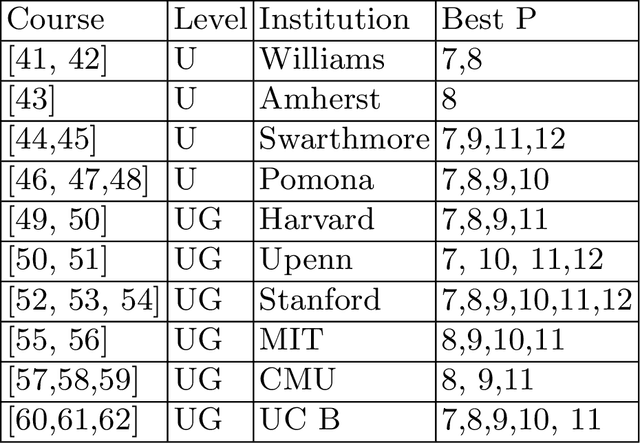
Abstract:This study explores the integration of real-world machine learning (ML) projects using human-computer interfaces (HCI) datasets in college-level courses to enhance both teaching and learning experiences. Employing a comprehensive literature review, course websites analysis, and a detailed case study, the research identifies best practices for incorporating HCI datasets into project-based ML education. Key f indings demonstrate increased student engagement, motivation, and skill development through hands-on projects, while instructors benefit from effective tools for teaching complex concepts. The study also addresses challenges such as data complexity and resource allocation, offering recommendations for future improvements. These insights provide a valuable framework for educators aiming to bridge the gap between
Effect of Kernel Size on CNN-Vision-Transformer-Based Gaze Prediction Using Electroencephalography Data
Aug 06, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we present an algorithm of gaze prediction from Electroencephalography (EEG) data. EEG-based gaze prediction is a new research topic that can serve as an alternative to traditional video-based eye-tracking. Compared to the existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) method, we improved the root mean-squared-error of EEG-based gaze prediction to 53.06 millimeters, while reducing the training time to less than 33% of its original duration. Our source code can be found at https://github.com/AmCh-Q/CSCI6907Project
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge