Christy Doran
University of Pennsylvania
Status of the XTAG System
Nov 03, 1994Abstract:XTAG is an ongoing project to develop a wide-coverage grammar for English, based on the Feature-based Lexicalized Tree Adjoining Grammar (FB-LTAG) formalism. The XTAG system integrates a morphological analyzer, an N-best part-of-speech tagger, an Early-style parser and an X-window interface, along with a wide-coverage grammar for English developed using the system. This system serves as a linguist's workbench for developing FB-LTAG specifications. This paper presents a description of and recent improvements to the various components of the XTAG system. It also presents the recent performance of the wide-coverage grammar on various corpora and compares it against the performance of other wide-coverage and domain-specific grammars.
* uuencoded compressed ps file. 4 pages
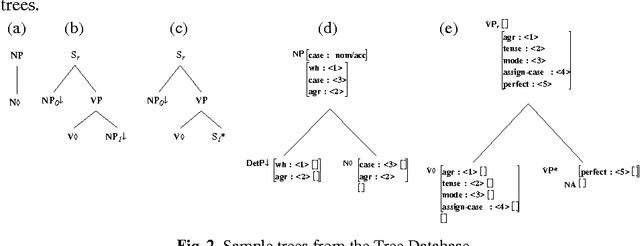
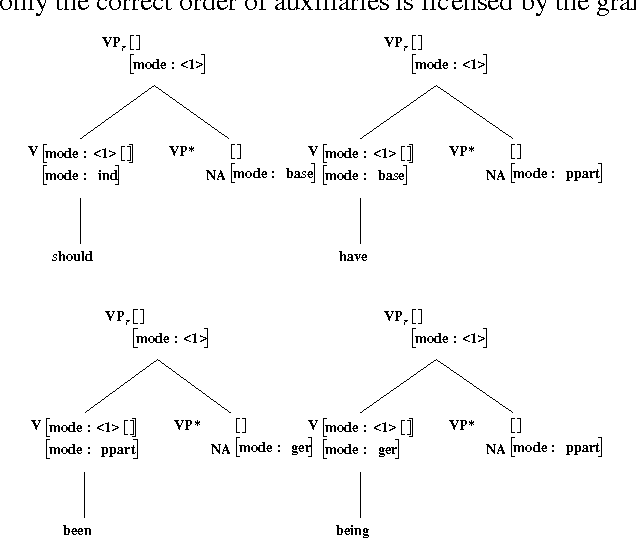
Lexicalization and Grammar Development
Oct 21, 1994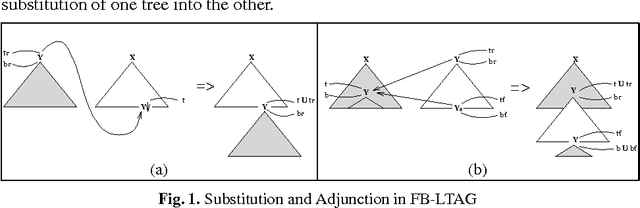

Abstract:In this paper we present a fully lexicalized grammar formalism as a particularly attractive framework for the specification of natural language grammars. We discuss in detail Feature-based, Lexicalized Tree Adjoining Grammars (FB-LTAGs), a representative of the class of lexicalized grammars. We illustrate the advantages of lexicalized grammars in various contexts of natural language processing, ranging from wide-coverage grammar development to parsing and machine translation. We also present a method for compact and efficient representation of lexicalized trees.
* ps file. English w/ German abstract. 10 pages
XTAG system - A Wide Coverage Grammar for English
Oct 20, 1994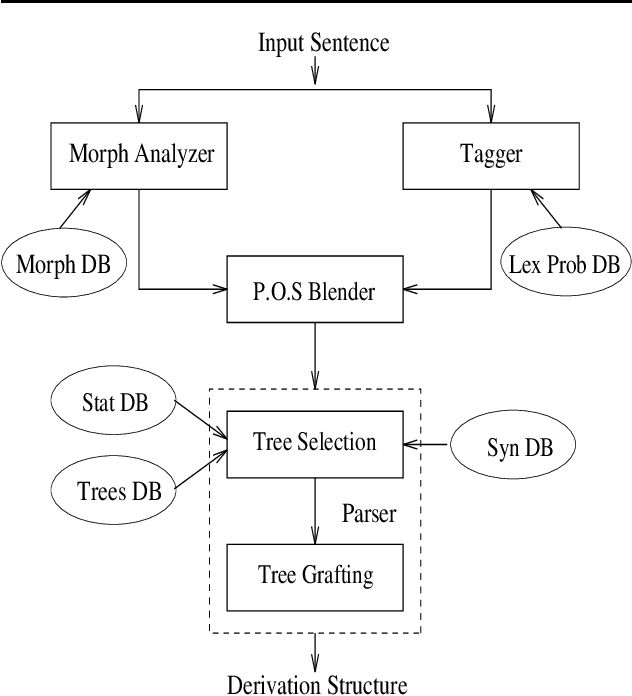

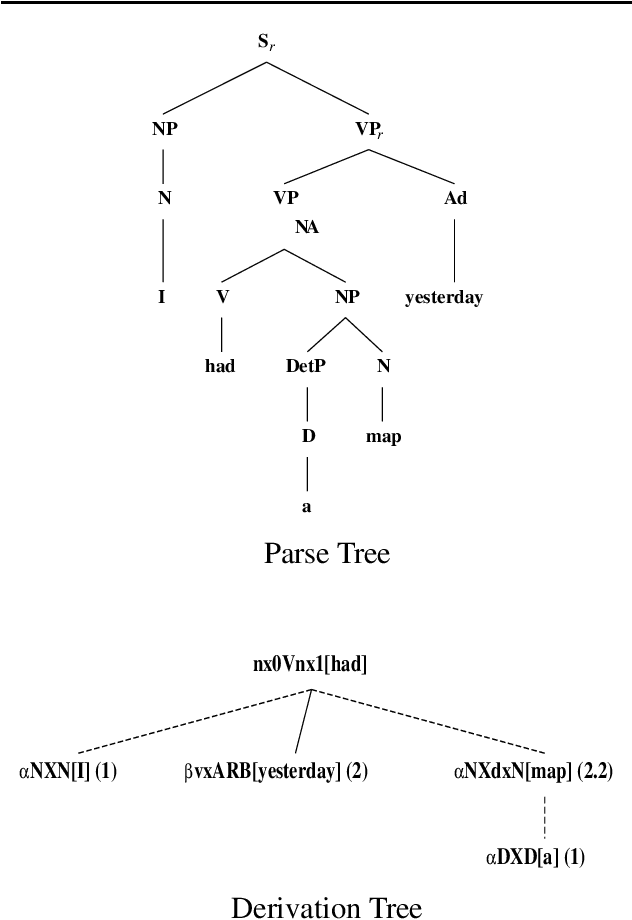
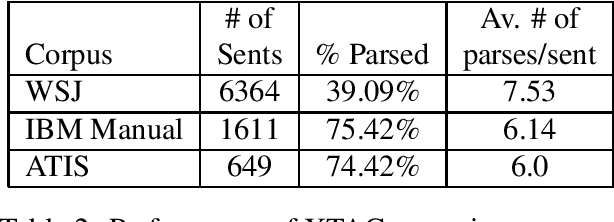
Abstract:This paper presents the XTAG system, a grammar development tool based on the Tree Adjoining Grammar (TAG) formalism that includes a wide-coverage syntactic grammar for English. The various components of the system are discussed and preliminary evaluation results from the parsing of various corpora are given. Results from the comparison of XTAG against the IBM statistical parser and the Alvey Natural Language Tool parser are also given.
* ps file. 7 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge