Christos Koutlis
Composite Data Augmentations for Synthetic Image Detection Against Real-World Perturbations
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:The advent of accessible Generative AI tools enables anyone to create and spread synthetic images on social media, often with the intention to mislead, thus posing a significant threat to online information integrity. Most existing Synthetic Image Detection (SID) solutions struggle on generated images sourced from the Internet, as these are often altered by compression and other operations. To address this, our research enhances SID by exploring data augmentation combinations, leveraging a genetic algorithm for optimal augmentation selection, and introducing a dual-criteria optimization approach. These methods significantly improve model performance under real-world perturbations. Our findings provide valuable insights for developing detection models capable of identifying synthetic images across varying qualities and transformations, with the best-performing model achieving a mean average precision increase of +22.53% compared to models without augmentations. The implementation is available at github.com/efthimia145/sid-composite-data-augmentation.
Latent Multimodal Reconstruction for Misinformation Detection
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Multimodal misinformation, such as miscaptioned images, where captions misrepresent an image's origin, context, or meaning, poses a growing challenge in the digital age. To support fact-checkers, researchers have been focusing on creating datasets and developing methods for multimodal misinformation detection (MMD). Due to the scarcity of large-scale annotated MMD datasets, recent studies leverage synthetic training data via out-of-context image-caption pairs or named entity manipulations; altering names, dates, and locations. However, these approaches often produce simplistic misinformation that fails to reflect real-world complexity, limiting the robustness of detection models trained on them. Meanwhile, despite recent advancements, Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) remain underutilized for generating diverse, realistic synthetic training data for MMD. To address this gap, we introduce "MisCaption This!", a training dataset comprising LVLM-generated miscaptioned images. Additionally, we introduce "Latent Multimodal Reconstruction" (LAMAR), a network trained to reconstruct the embeddings of truthful captions, providing a strong auxiliary signal to the detection process. To optimize LAMAR, we explore different training strategies (end-to-end training and large-scale pre-training) and integration approaches (direct, mask, gate, and attention). Extensive experiments show that models trained on "MisCaption This!" generalize better on real-world misinformation, while LAMAR sets new state-of-the-art on both NewsCLIPpings and VERITE benchmarks; highlighting the potential of LVLM-generated data and reconstruction-based approaches for advancing MMD. We release our code at: https://github.com/stevejpapad/miscaptioned-image-reconstruction
FaceX: Understanding Face Attribute Classifiers through Summary Model Explanations
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:EXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) approaches are widely applied for identifying fairness issues in Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems. However, in the context of facial analysis, existing XAI approaches, such as pixel attribution methods, offer explanations for individual images, posing challenges in assessing the overall behavior of a model, which would require labor-intensive manual inspection of a very large number of instances and leaving to the human the task of drawing a general impression of the model behavior from the individual outputs. Addressing this limitation, we introduce FaceX, the first method that provides a comprehensive understanding of face attribute classifiers through summary model explanations. Specifically, FaceX leverages the presence of distinct regions across all facial images to compute a region-level aggregation of model activations, allowing for the visualization of the model's region attribution across 19 predefined regions of interest in facial images, such as hair, ears, or skin. Beyond spatial explanations, FaceX enhances interpretability by visualizing specific image patches with the highest impact on the model's decisions for each facial region within a test benchmark. Through extensive evaluation in various experimental setups, including scenarios with or without intentional biases and mitigation efforts on four benchmarks, namely CelebA, FairFace, CelebAMask-HQ, and Racial Faces in the Wild, FaceX demonstrates high effectiveness in identifying the models' biases.
MAVias: Mitigate any Visual Bias
Dec 09, 2024Abstract:Mitigating biases in computer vision models is an essential step towards the trustworthiness of artificial intelligence models. Existing bias mitigation methods focus on a small set of predefined biases, limiting their applicability in visual datasets where multiple, possibly unknown biases exist. To address this limitation, we introduce MAVias, an open-set bias mitigation approach leveraging foundation models to discover spurious associations between visual attributes and target classes. MAVias first captures a wide variety of visual features in natural language via a foundation image tagging model, and then leverages a large language model to select those visual features defining the target class, resulting in a set of language-coded potential visual biases. We then translate this set of potential biases into vision-language embeddings and introduce an in-processing bias mitigation approach to prevent the model from encoding information related to them. Our experiments on diverse datasets, including CelebA, Waterbirds, ImageNet, and UrbanCars, show that MAVias effectively detects and mitigates a wide range of biases in visual recognition tasks outperforming current state-of-the-art.
DiMoDif: Discourse Modality-information Differentiation for Audio-visual Deepfake Detection and Localization
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:Deepfake technology has rapidly advanced, posing significant threats to information integrity and societal trust. While significant progress has been made in detecting deepfakes, the simultaneous manipulation of audio and visual modalities, sometimes at small parts but still altering the meaning, presents a more challenging detection scenario. We present a novel audio-visual deepfake detection framework that leverages the inter-modality differences in machine perception of speech, based on the assumption that in real samples - in contrast to deepfakes - visual and audio signals coincide in terms of information. Our framework leverages features from deep networks that specialize in video and audio speech recognition to spot frame-level cross-modal incongruities, and in that way to temporally localize the deepfake forgery. To this end, DiMoDif employs a Transformer encoder-based architecture with a feature pyramid scheme and local attention, and optimizes the detection model through a composite loss function accounting for frame-level detections and fake intervals localization. DiMoDif outperforms the state-of-the-art on the Temporal Forgery Localization task by +47.88% AP@0.75 on AV-Deepfake1M, and performs on-par on LAV-DF. On the Deepfake Detection task, it outperforms the state-of-the-art by +30.5% AUC on AV-Deepfake1M, +2.8% AUC on FakeAVCeleb, and performs on-par on LAV-DF. Code available at https://github.com/mever-team/dimodif.
BAdd: Bias Mitigation through Bias Addition
Aug 21, 2024Abstract:Computer vision (CV) datasets often exhibit biases that are perpetuated by deep learning models. While recent efforts aim to mitigate these biases and foster fair representations, they fail in complex real-world scenarios. In particular, existing methods excel in controlled experiments involving benchmarks with single-attribute injected biases, but struggle with multi-attribute biases being present in well-established CV datasets. Here, we introduce BAdd, a simple yet effective method that allows for learning fair representations invariant to the attributes introducing bias by incorporating features representing these attributes into the backbone. BAdd is evaluated on seven benchmarks and exhibits competitive performance, surpassing state-of-the-art methods on both single- and multi-attribute benchmarks. Notably, BAdd achieves +27.5% and +5.5% absolute accuracy improvements on the challenging multi-attribute benchmarks, FB-Biased-MNIST and CelebA, respectively.
TextureCrop: Enhancing Synthetic Image Detection through Texture-based Cropping
Jul 22, 2024


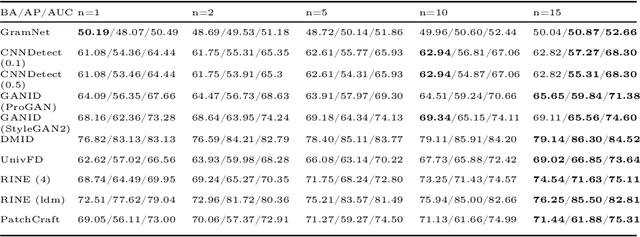
Abstract:Generative AI technologies produce hyper-realistic imagery that can be used for nefarious purposes such as producing misleading or harmful content, among others. This makes Synthetic Image Detection (SID) an essential tool for defending against AI-generated harmful content. Current SID methods typically resize input images to a fixed resolution or perform center-cropping due to computational concerns, leading to challenges in effectively detecting artifacts in high-resolution images. To this end, we propose TextureCrop, a novel image pre-processing technique. By focusing on high-frequency image parts where generation artifacts are prevalent, TextureCrop effectively enhances SID accuracy while maintaining manageable memory requirements. Experimental results demonstrate a consistent improvement in AUC across various detectors by 5.7% compared to center cropping and by 14% compared to resizing, across high-resolution images from the Forensynths and Synthbuster datasets.
Similarity over Factuality: Are we making progress on multimodal out-of-context misinformation detection?
Jul 18, 2024



Abstract:Out-of-context (OOC) misinformation poses a significant challenge in multimodal fact-checking, where images are paired with texts that misrepresent their original context to support false narratives. Recent research in evidence-based OOC detection has seen a trend towards increasingly complex architectures, incorporating Transformers, foundation models, and large language models. In this study, we introduce a simple yet robust baseline, which assesses MUltimodal SimilaritiEs (MUSE), specifically the similarity between image-text pairs and external image and text evidence. Our results demonstrate that MUSE, when used with conventional classifiers like Decision Tree, Random Forest, and Multilayer Perceptron, can compete with and even surpass the state-of-the-art on the NewsCLIPpings and VERITE datasets. Furthermore, integrating MUSE in our proposed "Attentive Intermediate Transformer Representations" (AITR) significantly improved performance, by 3.3% and 7.5% on NewsCLIPpings and VERITE, respectively. Nevertheless, the success of MUSE, relying on surface-level patterns and shortcuts, without examining factuality and logical inconsistencies, raises critical questions about how we define the task, construct datasets, collect external evidence and overall, how we assess progress in the field. We release our code at: https://github.com/stevejpapad/outcontext-misinfo-progress
SDFD: Building a Versatile Synthetic Face Image Dataset with Diverse Attributes
Apr 29, 2024



Abstract:AI systems rely on extensive training on large datasets to address various tasks. However, image-based systems, particularly those used for demographic attribute prediction, face significant challenges. Many current face image datasets primarily focus on demographic factors such as age, gender, and skin tone, overlooking other crucial facial attributes like hairstyle and accessories. This narrow focus limits the diversity of the data and consequently the robustness of AI systems trained on them. This work aims to address this limitation by proposing a methodology for generating synthetic face image datasets that capture a broader spectrum of facial diversity. Specifically, our approach integrates a systematic prompt formulation strategy, encompassing not only demographics and biometrics but also non-permanent traits like make-up, hairstyle, and accessories. These prompts guide a state-of-the-art text-to-image model in generating a comprehensive dataset of high-quality realistic images and can be used as an evaluation set in face analysis systems. Compared to existing datasets, our proposed dataset proves equally or more challenging in image classification tasks while being much smaller in size.
Leveraging Representations from Intermediate Encoder-blocks for Synthetic Image Detection
Feb 29, 2024



Abstract:The recently developed and publicly available synthetic image generation methods and services make it possible to create extremely realistic imagery on demand, raising great risks for the integrity and safety of online information. State-of-the-art Synthetic Image Detection (SID) research has led to strong evidence on the advantages of feature extraction from foundation models. However, such extracted features mostly encapsulate high-level visual semantics instead of fine-grained details, which are more important for the SID task. On the contrary, shallow layers encode low-level visual information. In this work, we leverage the image representations extracted by intermediate Transformer blocks of CLIP's image-encoder via a lightweight network that maps them to a learnable forgery-aware vector space capable of generalizing exceptionally well. We also employ a trainable module to incorporate the importance of each Transformer block to the final prediction. Our method is compared against the state-of-the-art by evaluating it on 20 test datasets and exhibits an average +10.6% absolute performance improvement. Notably, the best performing models require just a single epoch for training (~8 minutes). Code available at https://github.com/mever-team/rine.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge