Christopher Hojny
On the Expressiveness of Rational ReLU Neural Networks With Bounded Depth
Feb 10, 2025
Abstract:To confirm that the expressive power of ReLU neural networks grows with their depth, the function $F_n = \max \{0,x_1,\ldots,x_n\}$ has been considered in the literature. A conjecture by Hertrich, Basu, Di Summa, and Skutella [NeurIPS 2021] states that any ReLU network that exactly represents $F_n$ has at least $\lceil\log_2 (n+1)\rceil$ hidden layers. The conjecture has recently been confirmed for networks with integer weights by Haase, Hertrich, and Loho [ICLR 2023]. We follow up on this line of research and show that, within ReLU networks whose weights are decimal fractions, $F_n$ can only be represented by networks with at least $\lceil\log_3 (n+1)\rceil$ hidden layers. Moreover, if all weights are $N$-ary fractions, then $F_n$ can only be represented by networks with at least $\Omega( \frac{\ln n}{\ln \ln N})$ layers. These results are a partial confirmation of the above conjecture for rational ReLU networks, and provide the first non-constant lower bound on the depth of practically relevant ReLU networks.
Verifying message-passing neural networks via topology-based bounds tightening
Feb 21, 2024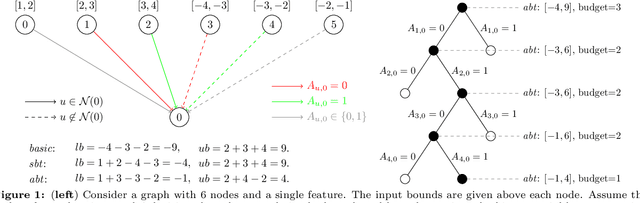
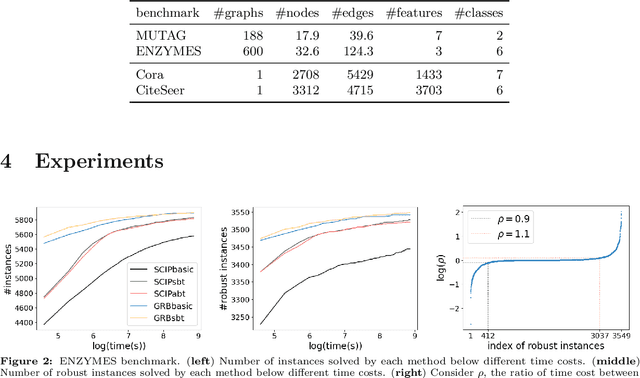
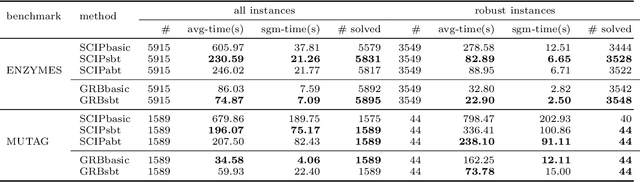
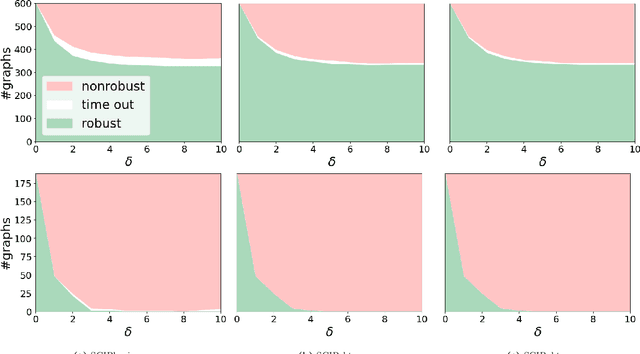
Abstract:Since graph neural networks (GNNs) are often vulnerable to attack, we need to know when we can trust them. We develop a computationally effective approach towards providing robust certificates for message-passing neural networks (MPNNs) using a Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation function. Because our work builds on mixed-integer optimization, it encodes a wide variety of subproblems, for example it admits (i) both adding and removing edges, (ii) both global and local budgets, and (iii) both topological perturbations and feature modifications. Our key technology, topology-based bounds tightening, uses graph structure to tighten bounds. We also experiment with aggressive bounds tightening to dynamically change the optimization constraints by tightening variable bounds. To demonstrate the effectiveness of these strategies, we implement an extension to the open-source branch-and-cut solver SCIP. We test on both node and graph classification problems and consider topological attacks that both add and remove edges.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge