Christoph Otte
Spatio-Temporal Deep Learning Models for Tip Force Estimation During Needle Insertion
May 22, 2019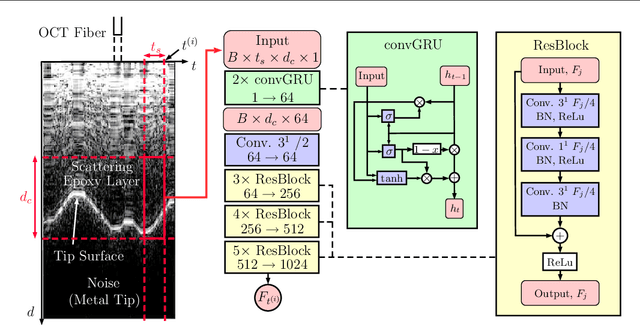
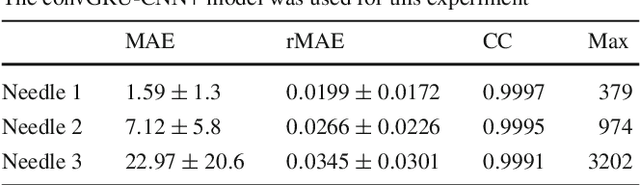
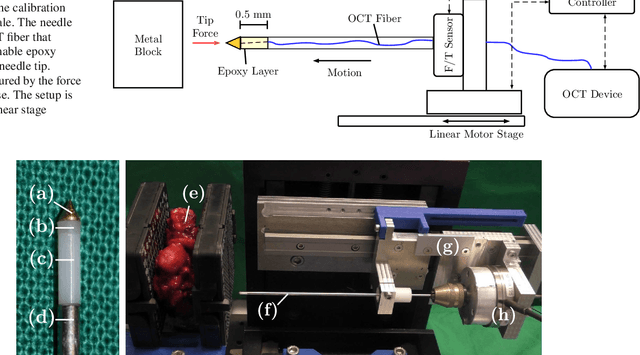
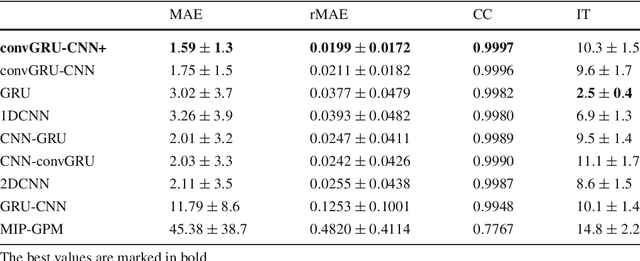
Abstract:Purpose. Precise placement of needles is a challenge in a number of clinical applications such as brachytherapy or biopsy. Forces acting at the needle cause tissue deformation and needle deflection which in turn may lead to misplacement or injury. Hence, a number of approaches to estimate the forces at the needle have been proposed. Yet, integrating sensors into the needle tip is challenging and a careful calibration is required to obtain good force estimates. Methods. We describe a fiber-optical needle tip force sensor design using a single OCT fiber for measurement. The fiber images the deformation of an epoxy layer placed below the needle tip which results in a stream of 1D depth profiles. We study different deep learning approaches to facilitate calibration between this spatio-temporal image data and the related forces. In particular, we propose a novel convGRU-CNN architecture for simultaneous spatial and temporal data processing. Results. The needle can be adapted to different operating ranges by changing the stiffness of the epoxy layer. Likewise, calibration can be adapted by training the deep learning models. Our novel convGRU-CNN architecture results in the lowest mean absolute error of 1.59 +- 1.3 mN and a cross-correlation coefficient of 0.9997, and clearly outperforms the other methods. Ex vivo experiments in human prostate tissue demonstrate the needle's application. Conclusions. Our OCT-based fiber-optical sensor presents a viable alternative for needle tip force estimation. The results indicate that the rich spatio-temporal information included in the stream of images showing the deformation throughout the epoxy layer can be effectively used by deep learning models. Particularly, we demonstrate that the convGRU-CNN architecture performs favorably, making it a promising approach for other spatio-temporal learning problems.
Needle Tip Force Estimation using an OCT Fiber and a Fused convGRU-CNN Architecture
May 30, 2018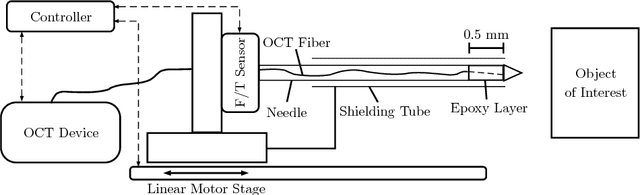

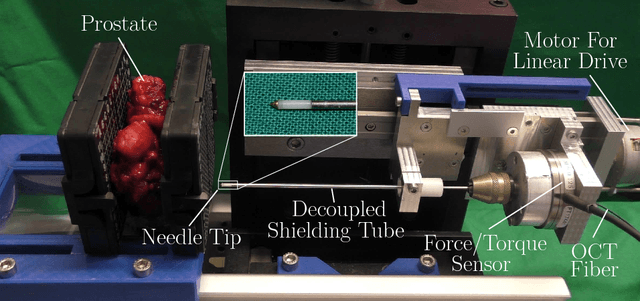
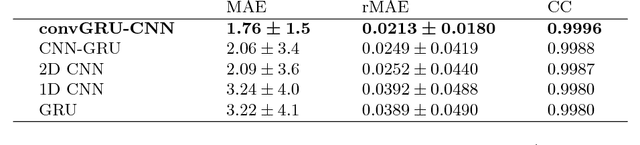
Abstract:Needle insertion is common during minimally invasive interventions such as biopsy or brachytherapy. During soft tissue needle insertion, forces acting at the needle tip cause tissue deformation and needle deflection. Accurate needle tip force measurement provides information on needle-tissue interaction and helps detecting and compensating potential misplacement. For this purpose we introduce an image-based needle tip force estimation method using an optical fiber imaging the deformation of an epoxy layer below the needle tip over time. For calibration and force estimation, we introduce a novel deep learning-based fused convolutional GRU-CNN model which effectively exploits the spatio-temporal data structure. The needle is easy to manufacture and our model achieves a mean absolute error of 1.76 +- 1.5 mN with a cross-correlation coefficient of 0.9996, clearly outperforming other methods. We test needles with different materials to demonstrate that the approach can be adapted for different sensitivities and force ranges. Furthermore, we validate our approach in an ex-vivo prostate needle insertion scenario.
Force Estimation from OCT Volumes using 3D CNNs
Apr 26, 2018



Abstract:\textit{Purpose} Estimating the interaction forces of instruments and tissue is of interest, particularly to provide haptic feedback during robot assisted minimally invasive interventions. Different approaches based on external and integrated force sensors have been proposed. These are hampered by friction, sensor size, and sterilizability. We investigate a novel approach to estimate the force vector directly from optical coherence tomography image volumes. \textit{Methods} We introduce a novel Siamese 3D CNN architecture. The network takes an undeformed reference volume and a deformed sample volume as an input and outputs the three components of the force vector. We employ a deep residual architecture with bottlenecks for increased efficiency. We compare the Siamese approach to methods using difference volumes and two-dimensional projections. Data was generated using a robotic setup to obtain ground truth force vectors for silicon tissue phantoms as well as porcine tissue. \textit{Results} Our method achieves a mean average error of 7.7 +- 4.3 mN when estimating the force vector. Our novel Siamese 3D CNN architecture outperforms single-path methods that achieve a mean average error of 11.59 +- 6.7 mN. Moreover, the use of volume data leads to significantly higher performance compared to processing only surface information which achieves a mean average error of 24.38 +- 22.0 mN. Based on the tissue dataset, our methods shows good generalization in between different subjects. \textit{Conclusions} We propose a novel image-based force estimation method using optical coherence tomography. We illustrate that capturing the deformation of subsurface structures substantially improves force estimation. Our approach can provide accurate force estimates in surgical setups when using intraoperative optical coherence tomography.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge