Christoph Beierle
Model Transformations for Ranking Functions and Total Preorders
Mar 26, 2022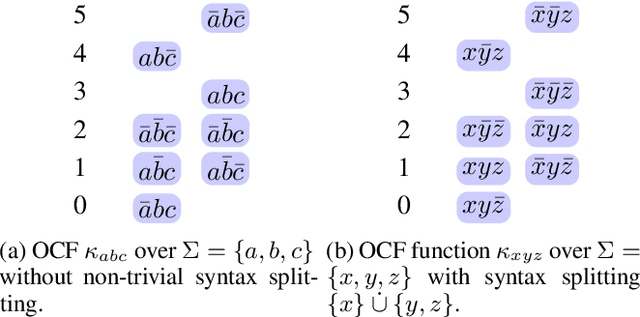
Abstract:In the field of knowledge representation, the considered epistemic states are often based on propositional interpretations, also called worlds. E.g., epistemic states of agents can be modelled by ranking functions or total preorders on worlds. However, there are usually different ways of how to describe a real world situation in a propositional language; this can be seen as different points of view on the same situation. In this paper we introduce the concept of model transformations to convert an epistemic state from one point of view to another point of view, yielding a novel notion of equivalence of epistemic states. We show how the well-known advantages of syntax splitting, originally developed for belief sets and later extended to representation of epistemic states and to nonmonotonic reasoning, can be exploited for belief revision via model transformation by uncovering splittings not being present before. Furthermore, we characterize situations where belief change operators commute with model transformations.
Iterated Belief Change, Computationally
Feb 17, 2022
Abstract:Iterated Belief Change is the research area that investigates principles for the dynamics of beliefs over (possibly unlimited) many subsequent belief changes. In this paper, we demonstrate how iterated belief change is connected to computation. In particular, we show that iterative belief revision is Turing complete, even under the condition that broadly accepted principles like the Darwiche-Pearl postulates for iterated revision hold.
Inference with System W Satisfies Syntax Splitting
Feb 11, 2022
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate inductive inference with system W from conditional belief bases with respect to syntax splitting. The concept of syntax splitting for inductive inference states that inferences about independent parts of the signature should not affect each other. This was captured in work by Kern-Isberner, Beierle, and Brewka in the form of postulates for inductive inference operators expressing syntax splitting as a combination of relevance and independence; it was also shown that c-inference fulfils syntax splitting, while system P inference and system Z both fail to satisfy it. System W is a recently introduced inference system for nonmonotonic reasoning that captures and properly extends system Z as well as c-inference. We show that system W fulfils the syntax splitting postulates for inductive inference operators by showing that it satisfies the required properties of relevance and independence. This makes system W another inference operator besides c-inference that fully complies with syntax splitting, while in contrast to c-inference, also extending rational closure.
A Conditional Perspective on the Logic of Iterated Belief Contraction
Feb 04, 2022



Abstract:In this article, we consider iteration principles for contraction, with the goal of identifying properties for contractions that respect conditional beliefs. Therefore, we investigate and evaluate four groups of iteration principles for contraction which consider the dynamics of conditional beliefs. For all these principles, we provide semantic characterization theorems and provide formulations by postulates which highlight how the change of beliefs and of conditional beliefs is constrained, whenever that is possible. The first group is similar to the syntactic Darwiche-Pearl postulates. As a second group, we consider semantic postulates for iteration of contraction by Chopra, Ghose, Meyer and Wong, and by Konieczny and Pino P\'erez, respectively, and we provide novel syntactic counterparts. Third, we propose a contraction analogue of the independence condition by Jin and Thielscher. For the fourth group, we consider natural and moderate contraction by Nayak. Methodically, we make use of conditionals for contractions, so-called contractionals and furthermore, we propose and employ the novel notion of $ \alpha $-equivalence for formulating some of the new postulates.
Conditional Inference and Activation of Knowledge Entities in ACT-R
Oct 28, 2021



Abstract:Activation-based conditional inference applies conditional reasoning to ACT-R, a cognitive architecture developed to formalize human reasoning. The idea of activation-based conditional inference is to determine a reasonable subset of a conditional belief base in order to draw inductive inferences in time. Central to activation-based conditional inference is the activation function which assigns to the conditionals in the belief base a degree of activation mainly based on the conditional's relevance for the current query and its usage history. Therewith, our approach integrates several aspects of human reasoning into expert systems such as focusing, forgetting, and remembering.
On Limited Non-Prioritised Belief Revision Operators with Dynamic Scope
Aug 17, 2021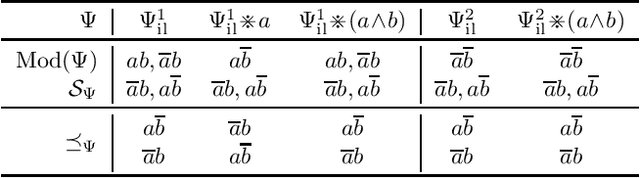
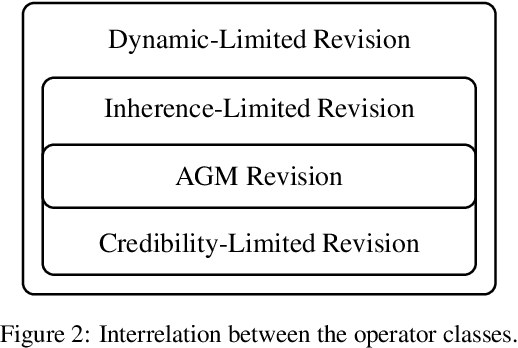
Abstract:The research on non-prioritized revision studies revision operators which do not accept all new beliefs. In this paper, we contribute to this line of research by introducing the concept of dynamic-limited revision, which are revisions expressible by a total preorder over a limited set of worlds. For a belief change operator, we consider the scope, which consists of those beliefs which yield success of revision. We show that for each set satisfying single sentence closure and disjunction completeness there exists a dynamic-limited revision having the union of this set with the beliefs set as scope. We investigate iteration postulates for belief and scope dynamics and characterise them for dynamic-limited revision. As an application, we employ dynamic-limited revision to studying belief revision in the context of so-called inherent beliefs, which are beliefs globally accepted by the agent. This leads to revision operators which we call inherence-limited. We present a representation theorem for inherence-limited revision, and we compare these operators and dynamic-limited revision with the closely related credible-limited revision operators.
Using Finite-State Machines to Automatically Scan Classical Greek Hexameter
Jan 22, 2021



Abstract:This paper presents a fully automatic approach to the scansion of Classical Greek hexameter verse. In particular, the paper describes an algorithm that uses deterministic finite-state automata and local linguistic rules to implement a targeted search for valid spondeus patterns and, in addition, a weighted finite-state transducer to correct and complete partial analyses and to reject invalid candidates. The paper also details the results of an empirical evaluation of the annotation quality resulting from this approach on hand-annotated data. It is shown that a finite-state approach provides quick and linguistically sound analyses of hexameter verses as well as an efficient formalisation of linguistic knowledge. The project code is available (see https://github.com/anetschka/greek_scansion).
Descriptor Revision for Conditionals: Literal Descriptors and Conditional Preservation
Jun 02, 2020
Abstract:Descriptor revision by Hansson is a framework for addressing the problem of belief change. In descriptor revision, different kinds of change processes are dealt with in a joint framework. Individual change requirements are qualified by specific success conditions expressed by a belief descriptor, and belief descriptors can be combined by logical connectives. This is in contrast to the currently dominating AGM paradigm shaped by Alchourr\'on, G\"ardenfors, and Makinson, where different kinds of changes, like a revision or a contraction, are dealt with separately. In this article, we investigate the realisation of descriptor revision for a conditional logic while restricting descriptors to the conjunction of literal descriptors. We apply the principle of conditional preservation developed by Kern-Isberner to descriptor revision for conditionals, show how descriptor revision for conditionals under these restrictions can be characterised by a constraint satisfaction problem, and implement it using constraint logic programming. Since our conditional logic subsumes propositional logic, our approach also realises descriptor revision for propositional logic.
Nonmonotonic Inferences with Qualitative Conditionals based on Preferred Structures on Worlds
May 26, 2020


Abstract:A conditional knowledge base R is a set of conditionals of the form "If A, the usually B". Using structural information derived from the conditionals in R, we introduce the preferred structure relation on worlds. The preferred structure relation is the core ingredient of a new inference relation called system W inference that inductively completes the knowledge given explicitly in R. We show that system W exhibits desirable inference properties like satisfying system P and avoiding, in contrast to e.g. system Z, the drowning problem. It fully captures and strictly extends both system Z and skeptical c-inference. In contrast to skeptical c-inference, it does not require to solve a complex constraint satisfaction problem, but is as tractable as system Z.
A Conditional Perspective for Iterated Belief Contraction
Nov 20, 2019

Abstract:According to Boutillier, Darwiche, Pearl and others, principles for iterated revision can be characterised in terms of changing beliefs about conditionals. For iterated contraction a similar formulation is not known. This is especially because for iterated belief change the connection between revision and contraction via the Levi and Harper identity is not straightforward, and therefore, characterisation results do not transfer easily between iterated revision and contraction. In this article, we develop an axiomatisation of iterated contraction in terms of changing conditional beliefs. We prove that the new set of postulates conforms semantically to the class of operators like the ones given by Konieczny and Pino P\'erez for iterated contraction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge