Chris Francis
Evaluating Co-Creativity using Total Information Flow
Feb 09, 2024



Abstract:Co-creativity in music refers to two or more musicians or musical agents interacting with one another by composing or improvising music. However, this is a very subjective process and each musician has their own preference as to which improvisation is better for some context. In this paper, we aim to create a measure based on total information flow to quantitatively evaluate the co-creativity process in music. In other words, our measure is an indication of how "good" a creative musical process is. Our main hypothesis is that a good musical creation would maximize information flow between the participants captured by music voices recorded in separate tracks. We propose a method to compute the information flow using pre-trained generative models as entropy estimators. We demonstrate how our method matches with human perception using a qualitative study.
SpiroMask: Measuring Lung Function Using Consumer-Grade Masks
Jan 31, 2022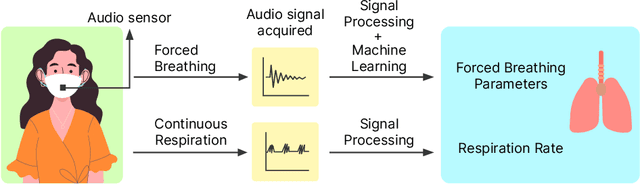
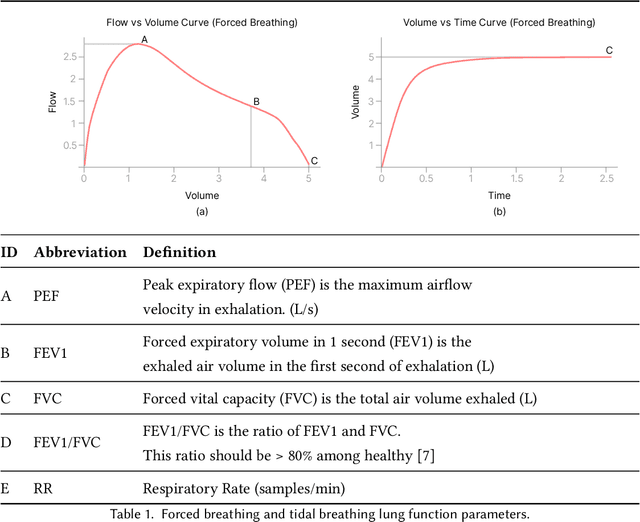
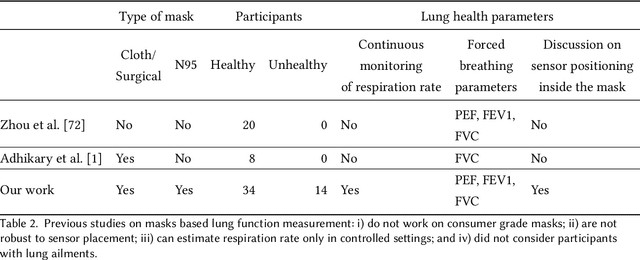
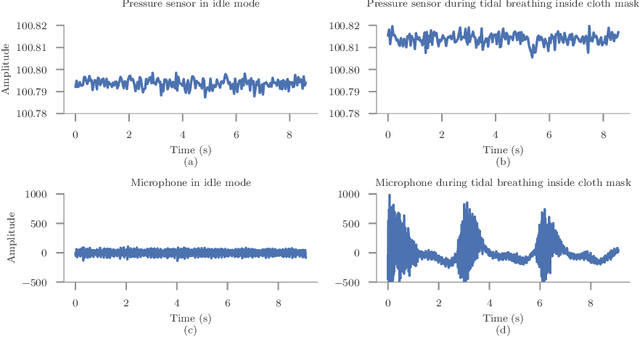
Abstract:According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), 235 million people suffer from respiratory illnesses and four million people die annually due to air pollution. Regular lung health monitoring can lead to prognoses about deteriorating lung health conditions. This paper presents our system SpiroMask that retrofits a microphone in consumer-grade masks (N95 and cloth masks) for continuous lung health monitoring. We evaluate our approach on 48 participants (including 14 with lung health issues) and find that we can estimate parameters such as lung volume and respiration rate within the approved error range by the American Thoracic Society (ATS). Further, we show that our approach is robust to sensor placement inside the mask.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge