Chokri Ben Amar
REGIM
Three dimensional Deep Learning approach for remote sensing image classification
Jun 15, 2018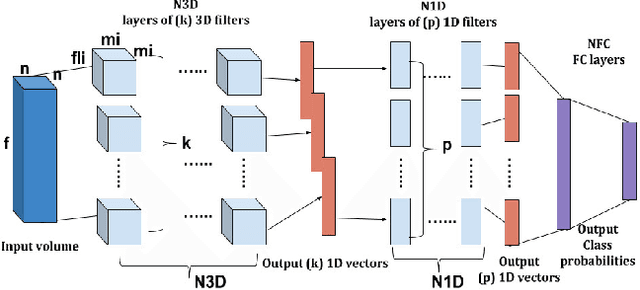
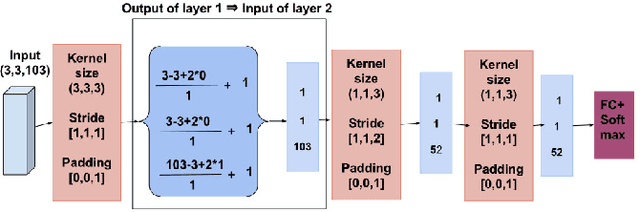
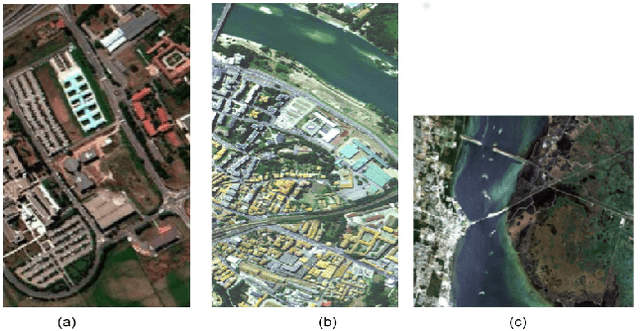
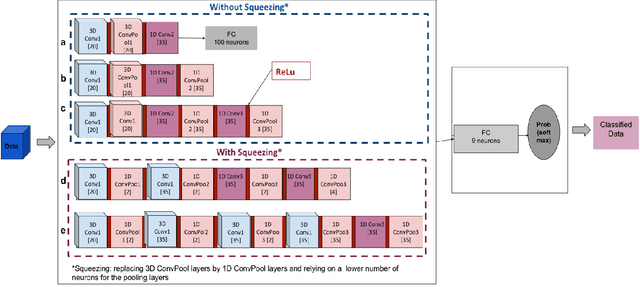
Abstract:Recently, a variety of approaches has been enriching the field of Remote Sensing (RS) image processing and analysis. Unfortunately, existing methods remain limited faced to the rich spatio-spectral content of today's large datasets. It would seem intriguing to resort to Deep Learning (DL) based approaches at this stage with regards to their ability to offer accurate semantic interpretation of the data. However, the specificity introduced by the coexistence of spectral and spatial content in the RS datasets widens the scope of the challenges presented to adapt DL methods to these contexts. Therefore, the aim of this paper is firstly to explore the performance of DL architectures for the RS hyperspectral dataset classification and secondly to introduce a new three-dimensional DL approach that enables a joint spectral and spatial information process. A set of three-dimensional schemes is proposed and evaluated. Experimental results based on well knownhyperspectral datasets demonstrate that the proposed method is able to achieve a better classification rate than state of the art methods with lower computational costs.
Deep Learning for Saliency Prediction in Natural Video
Apr 27, 2016


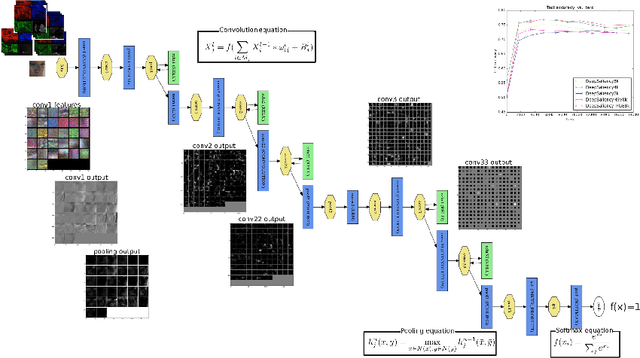
Abstract:The purpose of this paper is the detection of salient areas in natural video by using the new deep learning techniques. Salient patches in video frames are predicted first. Then the predicted visual fixation maps are built upon them. We design the deep architecture on the basis of CaffeNet implemented with Caffe toolkit. We show that changing the way of data selection for optimisation of network parameters, we can save computation cost up to 12 times. We extend deep learning approaches for saliency prediction in still images with RGB values to specificity of video using the sensitivity of the human visual system to residual motion. Furthermore, we complete primary colour pixel values by contrast features proposed in classical visual attention prediction models. The experiments are conducted on two publicly available datasets. The first is IRCCYN video database containing 31 videos with an overall amount of 7300 frames and eye fixations of 37 subjects. The second one is HOLLYWOOD2 provided 2517 movie clips with the eye fixations of 19 subjects. On IRCYYN dataset, the accuracy obtained is of 89.51%. On HOLLYWOOD2 dataset, results in prediction of saliency of patches show the improvement up to 2% with regard to RGB use only. The resulting accuracy of 76, 6% is obtained. The AUC metric in comparison of predicted saliency maps with visual fixation maps shows the increase up to 16% on a sample of video clips from this dataset.
A new scheme of signature extraction for iris authentication
Feb 17, 2013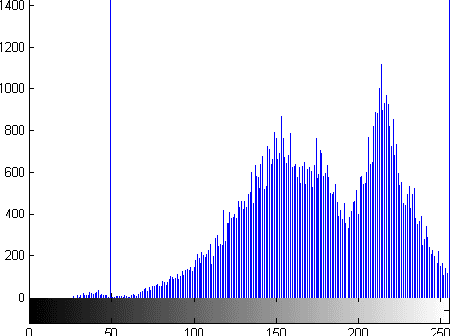
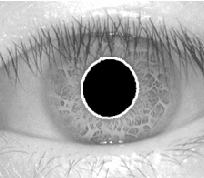

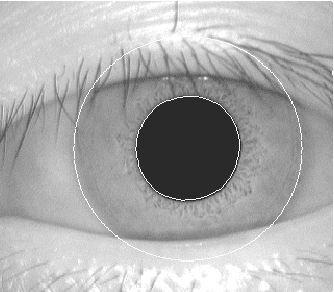
Abstract:Iris recognition, a relatively new biometric technology, has great advantages, such as variability, stability and security, thus is the most promising for high security environment. Iris recognition is proposed in this report. We describe some methods, the first one is based on grey level histogram to extract the pupil, the second is based on elliptic and parabolic HOUGH transformation to determinate the edge of iris, upper and lower eyelids, the third we used 2D Gabor Wavelets to encode the iris and finally we used the Hamming distance for authentication.
* 7 pages, 13 figures,International Multi-Conference on Systems Signals and Devices
Multi-input Multi-output Beta Wavelet Network: Modeling of Acoustic Units for Speech Recognition
Nov 08, 2012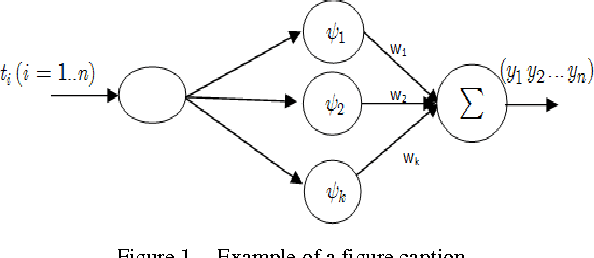
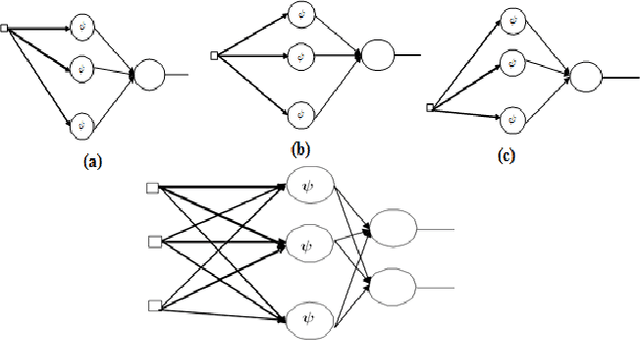
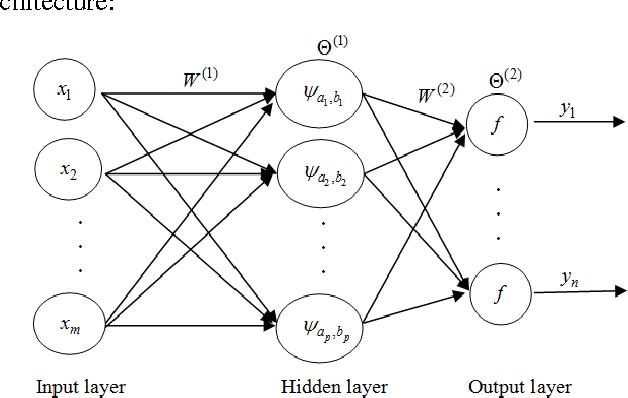
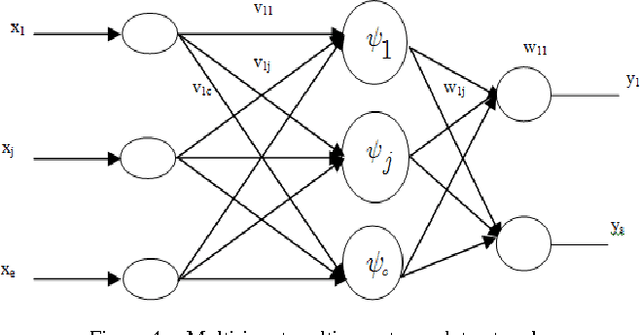
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel architecture of wavelet network called Multi-input Multi-output Wavelet Network MIMOWN as a generalization of the old architecture of wavelet network. This newel prototype was applied to speech recognition application especially to model acoustic unit of speech. The originality of our work is the proposal of MIMOWN to model acoustic unit of speech. This approach was proposed to overcome limitation of old wavelet network model. The use of the multi-input multi-output architecture will allows training wavelet network on various examples of acoustic units.
* 7 pages, 10 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge