Chih-Fan Chen
Face Beautification: Beyond Makeup Transfer
Dec 11, 2019



Abstract:Facial appearance plays an important role in our social lives. Subjective perception of women's beauty depends on various face-related (e.g., skin, shape, hair) and environmental (e.g., makeup, lighting, angle) factors. Similar to cosmetic surgery in the physical world, virtual face beautification is an emerging field with many open issues to be addressed. Inspired by the latest advances in style-based synthesis and face beauty prediction, we propose a novel framework of face beautification. For a given reference face with a high beauty score, our GAN-based architecture is capable of translating an inquiry face into a sequence of beautified face images with referenced beauty style and targeted beauty score values. To achieve this objective, we propose to integrate both style-based beauty representation (extracted from the reference face) and beauty score prediction (trained on SCUT-FBP database) into the process of beautification. Unlike makeup transfer, our approach targets at many-to-many (instead of one-to-one) translation where multiple outputs can be defined by either different references or varying beauty scores. Extensive experimental results are reported to demonstrate the effectiveness and flexibility of the proposed face beautification framework.
Digital Twin: Acquiring High-Fidelity 3D Avatar from a Single Image
Dec 07, 2019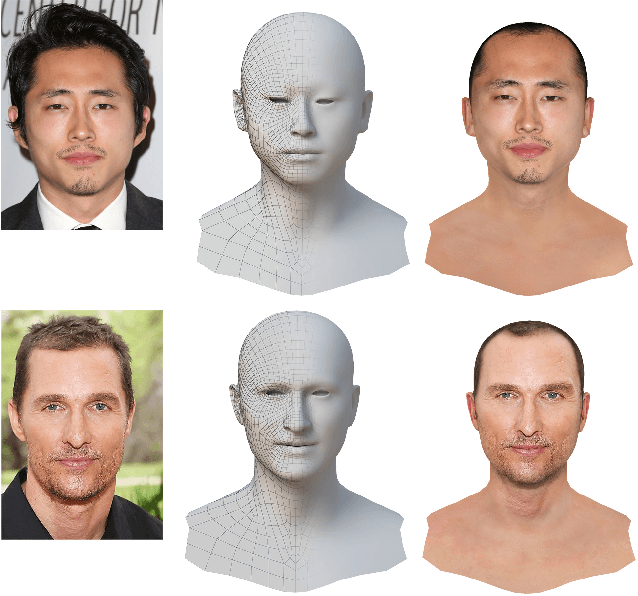
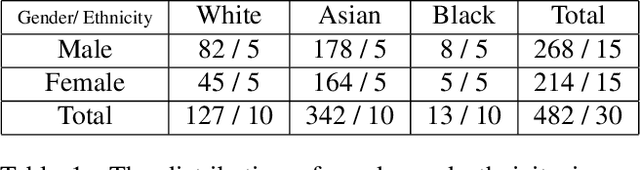
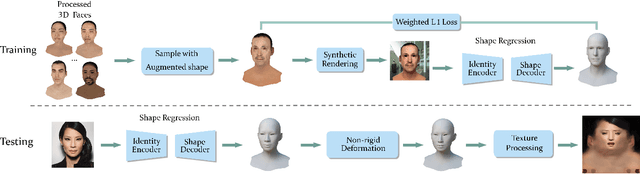
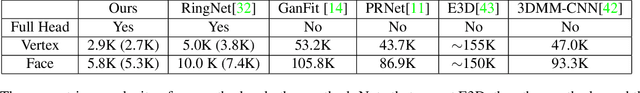
Abstract:We present an approach to generate high fidelity 3D face avatar with a high-resolution UV texture map from a single image. To estimate the face geometry, we use a deep neural network to directly predict vertex coordinates of the 3D face model from the given image. The 3D face geometry is further refined by a non-rigid deformation process to more accurately capture facial landmarks before texture projection. A key novelty of our approach is to train the shape regression network on facial images synthetically generated using a high-quality rendering engine. Moreover, our shape estimator fully leverages the discriminative power of deep facial identity features learned from millions of facial images. We have conducted extensive experiments to demonstrate the superiority of our optimized 2D-to-3D rendering approach, especially its excellent generalization property on real-world selfie images. Our proposed system of rendering 3D avatars from 2D images has a wide range of applications from virtual/augmented reality (VR/AR) and telepsychiatry to human-computer interaction and social networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge