Chengzhi Shi
H-SPLID: HSIC-based Saliency Preserving Latent Information Decomposition
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:We introduce H-SPLID, a novel algorithm for learning salient feature representations through the explicit decomposition of salient and non-salient features into separate spaces. We show that H-SPLID promotes learning low-dimensional, task-relevant features. We prove that the expected prediction deviation under input perturbations is upper-bounded by the dimension of the salient subspace and the Hilbert-Schmidt Independence Criterion (HSIC) between inputs and representations. This establishes a link between robustness and latent representation compression in terms of the dimensionality and information preserved. Empirical evaluations on image classification tasks show that models trained with H-SPLID primarily rely on salient input components, as indicated by reduced sensitivity to perturbations affecting non-salient features, such as image backgrounds. Our code is available at https://github.com/neu-spiral/H-SPLID.
Spectral Survival Analysis
May 28, 2025Abstract:Survival analysis is widely deployed in a diverse set of fields, including healthcare, business, ecology, etc. The Cox Proportional Hazard (CoxPH) model is a semi-parametric model often encountered in the literature. Despite its popularity, wide deployment, and numerous variants, scaling CoxPH to large datasets and deep architectures poses a challenge, especially in the high-dimensional regime. We identify a fundamental connection between rank regression and the CoxPH model: this allows us to adapt and extend the so-called spectral method for rank regression to survival analysis. Our approach is versatile, naturally generalizing to several CoxPH variants, including deep models. We empirically verify our method's scalability on multiple real-world high-dimensional datasets; our method outperforms legacy methods w.r.t. predictive performance and efficiency.
Learning Set Functions with Implicit Differentiation
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Ou et al. (2022) introduce the problem of learning set functions from data generated by a so-called optimal subset oracle. Their approach approximates the underlying utility function with an energy-based model, whose parameters are estimated via mean-field variational inference. Ou et al. (2022) show this reduces to fixed point iterations; however, as the number of iterations increases, automatic differentiation quickly becomes computationally prohibitive due to the size of the Jacobians that are stacked during backpropagation. We address this challenge with implicit differentiation and examine the convergence conditions for the fixed-point iterations. We empirically demonstrate the efficiency of our method on synthetic and real-world subset selection applications including product recommendation, set anomaly detection and compound selection tasks.
A Segmentation-Oriented Inter-Class Transfer Method: Application to Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Jun 20, 2019


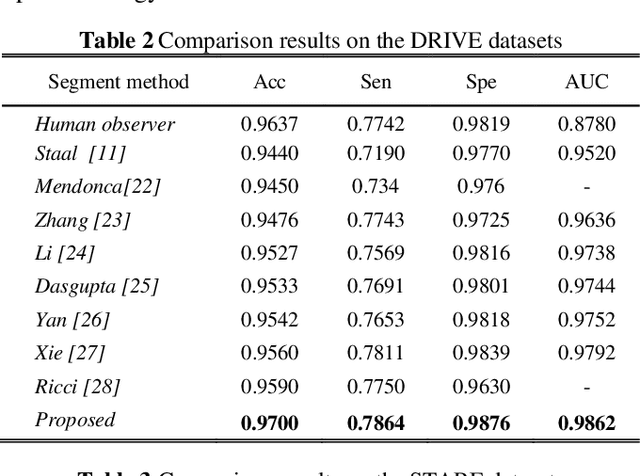
Abstract:Retinal vessel segmentation, as a principal nonintrusive diagnose method for ophthalmology diseases or diabetics, suffers from data scarcity due to requiring pixel-wise labels. In this paper, we proposed a convenient patch-based two-stage transfer method. First, based on the information bottleneck theory, we insert one dimensionality-reduced layer for task-specific feature space. Next, the semi-supervised clustering is conducted to select instances, from different sources databases, possessing similarities in the feature space. Surprisingly, we empirically demonstrate that images from different classes possessing similarities contribute to better performance than some same-class instances. The proposed framework achieved an accuracy of 97%, 96.8%, and 96.77% on DRIVE, STARE, and HRF respectively, outperforming current methods and independent human observers (DRIVE (96.37%) and STARE (93.39%)).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge