Chengwei Huang
Affine Modulation-based Audiogram Fusion Network for Joint Noise Reduction and Hearing Loss Compensation
Sep 09, 2025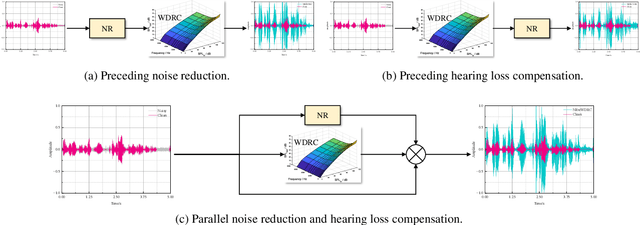
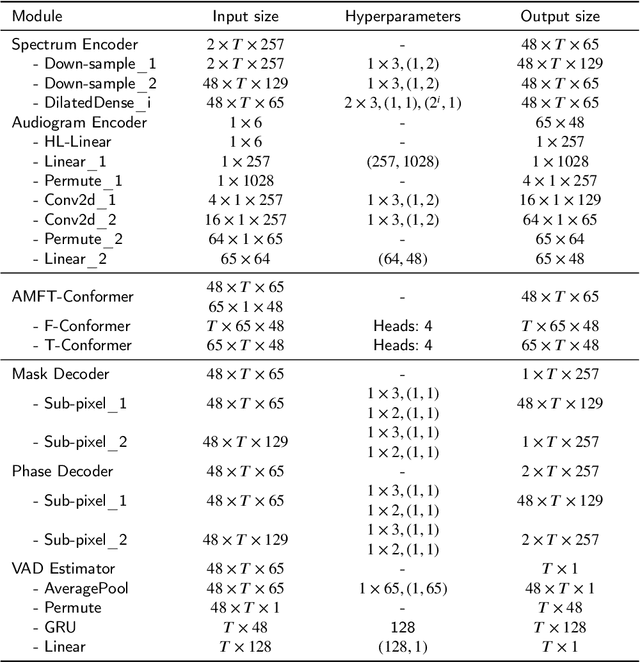
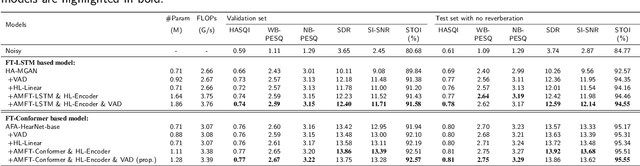
Abstract:Hearing aids (HAs) are widely used to provide personalized speech enhancement (PSE) services, improving the quality of life for individuals with hearing loss. However, HA performance significantly declines in noisy environments as it treats noise reduction (NR) and hearing loss compensation (HLC) as separate tasks. This separation leads to a lack of systematic optimization, overlooking the interactions between these two critical tasks, and increases the system complexity. To address these challenges, we propose a novel audiogram fusion network, named AFN-HearNet, which simultaneously tackles the NR and HLC tasks by fusing cross-domain audiogram and spectrum features. We propose an audiogram-specific encoder that transforms the sparse audiogram profile into a deep representation, addressing the alignment problem of cross-domain features prior to fusion. To incorporate the interactions between NR and HLC tasks, we propose the affine modulation-based audiogram fusion frequency-temporal Conformer that adaptively fuses these two features into a unified deep representation for speech reconstruction. Furthermore, we introduce a voice activity detection auxiliary training task to embed speech and non-speech patterns into the unified deep representation implicitly. We conduct comprehensive experiments across multiple datasets to validate the effectiveness of each proposed module. The results indicate that the AFN-HearNet significantly outperforms state-of-the-art in-context fusion joint models regarding key metrics such as HASQI and PESQ, achieving a considerable trade-off between performance and efficiency. The source code and data will be released at https://github.com/deepnetni/AFN-HearNet.
Sequence-to-Sequence Load Disaggregation Using Multi-Scale Residual Neural Network
Sep 25, 2020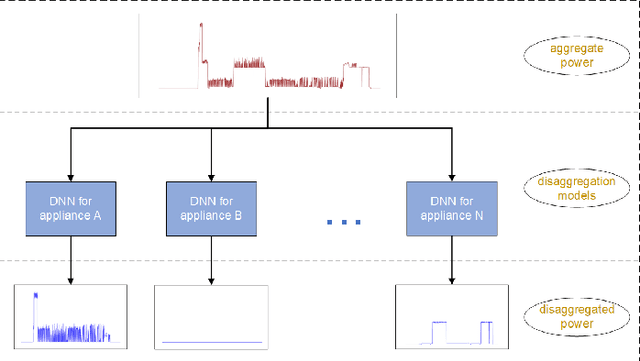
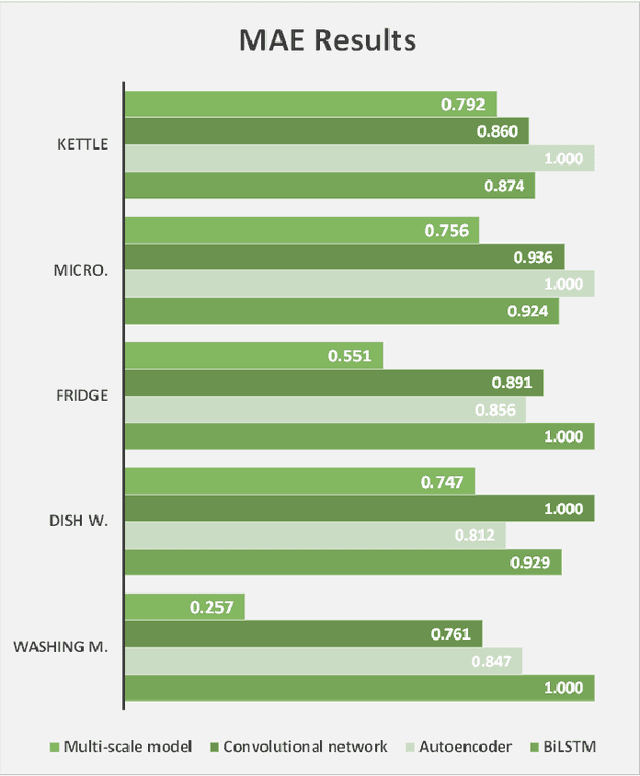
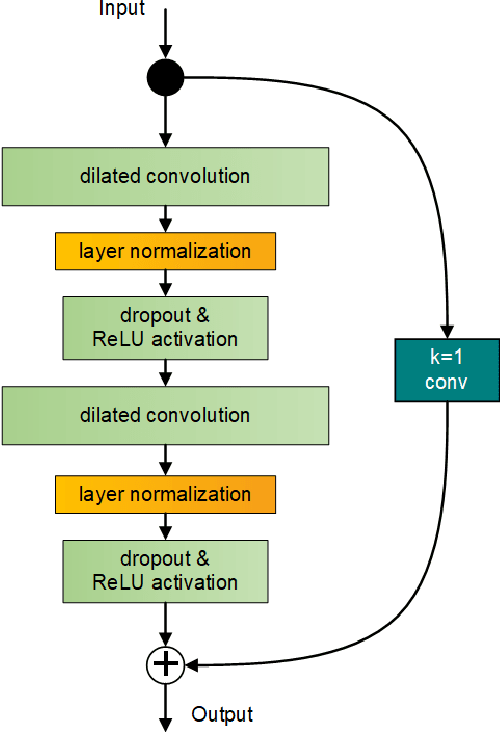
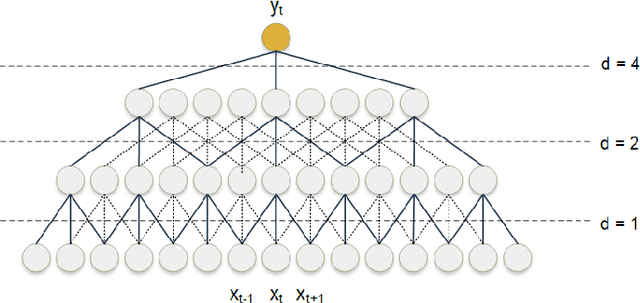
Abstract:With the increased demand on economy and efficiency of measurement technology, Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM) has received more and more attention as a cost-effective way to monitor electricity and provide feedback to users. Deep neural networks has been shown a great potential in the field of load disaggregation. In this paper, firstly, a new convolutional model based on residual blocks is proposed to avoid the degradation problem which traditional networks more or less suffer from when network layers are increased in order to learn more complex features. Secondly, we propose dilated convolution to curtail the excessive quantity of model parameters and obtain bigger receptive field, and multi-scale structure to learn mixed data features in a more targeted way. Thirdly, we give details about generating training and test set under certain rules. Finally, the algorithm is tested on real-house public dataset, UK-DALE, with three existing neural networks. The results are compared and analysed, the proposed model shows improvements on F1 score, MAE as well as model complexity across different appliances.
Personalized Fuzzy Text Search Using Interest Prediction and Word Vectorization
Oct 01, 2017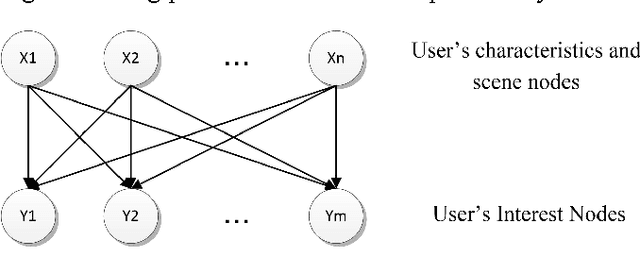
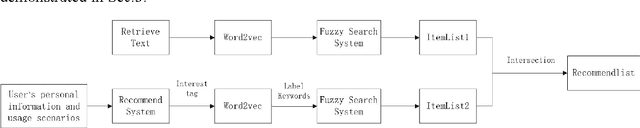
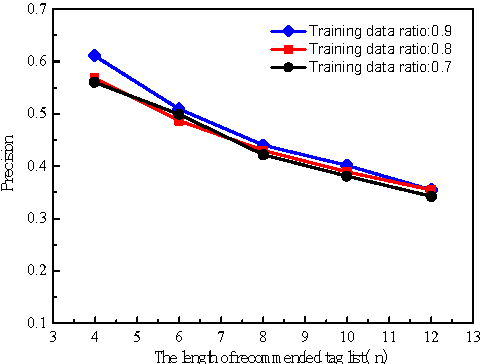
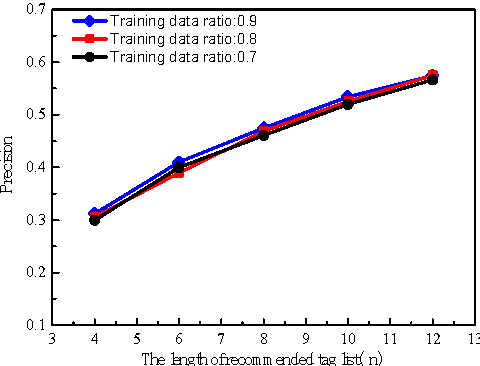
Abstract:In this paper we study the personalized text search problem. The keyword based search method in conventional algorithms has a low efficiency in understanding users' intention since the semantic meaning, user profile, user interests are not always considered. Firstly, we propose a novel text search algorithm using a inverse filtering mechanism that is very efficient for label based item search. Secondly, we adopt the Bayesian network to implement the user interest prediction for an improved personalized search. According to user input, it searches the related items using keyword information, predicted user interest. Thirdly, the word vectorization is used to discover potential targets according to the semantic meaning. Experimental results show that the proposed search engine has an improved efficiency and accuracy and it can operate on embedded devices with very limited computational resources.
Research on several key technologies in practical speech emotion recognition
Sep 27, 2017Abstract:In this dissertation the practical speech emotion recognition technology is studied, including several cognitive related emotion types, namely fidgetiness, confidence and tiredness. The high quality of naturalistic emotional speech data is the basis of this research. The following techniques are used for inducing practical emotional speech: cognitive task, computer game, noise stimulation, sleep deprivation and movie clips. A practical speech emotion recognition system is studied based on Gaussian mixture model. A two-class classifier set is adopted for performance improvement under the small sample case. Considering the context information in continuous emotional speech, a Gaussian mixture model embedded with Markov networks is proposed. A further study is carried out for system robustness analysis. First, noise reduction algorithm based on auditory masking properties is fist introduced to the practical speech emotion recognition. Second, to deal with the complicated unknown emotion types under real situation, an emotion recognition method with rejection ability is proposed, which enhanced the system compatibility against unknown emotion samples. Third, coping with the difficulties brought by a large number of unknown speakers, an emotional feature normalization method based on speaker-sensitive feature clustering is proposed. Fourth, by adding the electrocardiogram channel, a bi-modal emotion recognition system based on speech signals and electrocardiogram signals is first introduced. The speech emotion recognition methods studied in this dissertation may be extended into the cross-language speech emotion recognition and the whispered speech emotion recognition.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge