Che Lin
THeGAU: Type-Aware Heterogeneous Graph Autoencoder and Augmentation
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks (HGNNs) are effective for modeling Heterogeneous Information Networks (HINs), which encode complex multi-typed entities and relations. However, HGNNs often suffer from type information loss and structural noise, limiting their representational fidelity and generalization. We propose THeGAU, a model-agnostic framework that combines a type-aware graph autoencoder with guided graph augmentation to improve node classification. THeGAU reconstructs schema-valid edges as an auxiliary task to preserve node-type semantics and introduces a decoder-driven augmentation mechanism to selectively refine noisy structures. This joint design enhances robustness, accuracy, and efficiency while significantly reducing computational overhead. Extensive experiments on three benchmark HIN datasets (IMDB, ACM, and DBLP) demonstrate that THeGAU consistently outperforms existing HGNN methods, achieving state-of-the-art performance across multiple backbones.
FinNuE: Exposing the Risks of Using BERTScore for Numerical Semantic Evaluation in Finance
Nov 13, 2025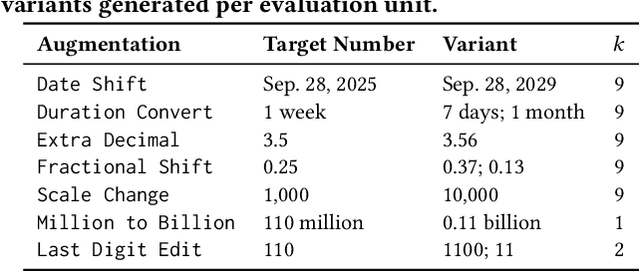

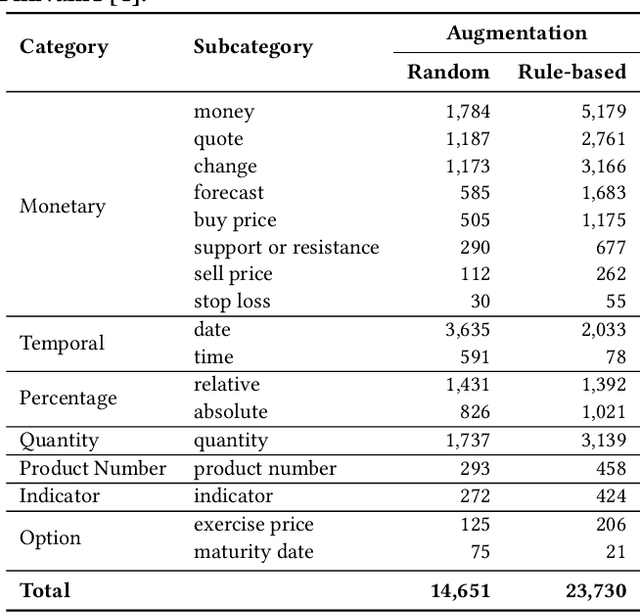
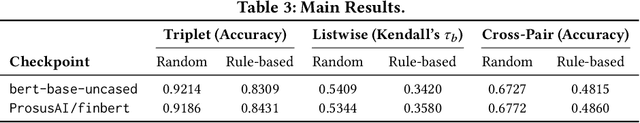
Abstract:BERTScore has become a widely adopted metric for evaluating semantic similarity between natural language sentences. However, we identify a critical limitation: BERTScore exhibits low sensitivity to numerical variation, a significant weakness in finance where numerical precision directly affects meaning (e.g., distinguishing a 2% gain from a 20% loss). We introduce FinNuE, a diagnostic dataset constructed with controlled numerical perturbations across earnings calls, regulatory filings, social media, and news articles. Using FinNuE, demonstrate that BERTScore fails to distinguish semantically critical numerical differences, often assigning high similarity scores to financially divergent text pairs. Our findings reveal fundamental limitations of embedding-based metrics for finance and motivate numerically-aware evaluation frameworks for financial NLP.
MedFuse: Multiplicative Embedding Fusion For Irregular Clinical Time Series
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Clinical time series derived from electronic health records (EHRs) are inherently irregular, with asynchronous sampling, missing values, and heterogeneous feature dynamics. While numerical laboratory measurements are highly informative, existing embedding strategies usually combine feature identity and value embeddings through additive operations, which constrains their ability to capture value-dependent feature interactions. We propose MedFuse, a framework for irregular clinical time series centered on the MuFuse (Multiplicative Embedding Fusion) module. MuFuse fuses value and feature embeddings through multiplicative modulation, preserving feature-specific information while modeling higher-order dependencies across features. Experiments on three real-world datasets covering both intensive and chronic care show that MedFuse consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on key predictive tasks. Analysis of the learned representations further demonstrates that multiplicative fusion enhances expressiveness and supports cross-dataset pretraining. These results establish MedFuse as a generalizable approach for modeling irregular clinical time series.
Style4Rec: Enhancing Transformer-based E-commerce Recommendation Systems with Style and Shopping Cart Information
Jan 16, 2025



Abstract:Understanding users' product preferences is essential to the efficacy of a recommendation system. Precision marketing leverages users' historical data to discern these preferences and recommends products that align with them. However, recent browsing and purchase records might better reflect current purchasing inclinations. Transformer-based recommendation systems have made strides in sequential recommendation tasks, but they often fall short in utilizing product image style information and shopping cart data effectively. In light of this, we propose Style4Rec, a transformer-based e-commerce recommendation system that harnesses style and shopping cart information to enhance existing transformer-based sequential product recommendation systems. Style4Rec represents a significant step forward in personalized e-commerce recommendations, outperforming benchmarks across various evaluation metrics. Style4Rec resulted in notable improvements: HR@5 increased from 0.681 to 0.735, NDCG@5 increased from 0.594 to 0.674, and MRR@5 increased from 0.559 to 0.654. We tested our model using an e-commerce dataset from our partnering company and found that it exceeded established transformer-based sequential recommendation benchmarks across various evaluation metrics. Thus, Style4Rec presents a significant step forward in personalized e-commerce recommendation systems.
Scalable Numerical Embeddings for Multivariate Time Series: Enhancing Healthcare Data Representation Learning
May 26, 2024Abstract:Multivariate time series (MTS) data, when sampled irregularly and asynchronously, often present extensive missing values. Conventional methodologies for MTS analysis tend to rely on temporal embeddings based on timestamps that necessitate subsequent imputations, yet these imputed values frequently deviate substantially from their actual counterparts, thereby compromising prediction accuracy. Furthermore, these methods typically fail to provide robust initial embeddings for values infrequently observed or even absent within the training set, posing significant challenges to model generalizability. In response to these challenges, we propose SCAlable Numerical Embedding (SCANE), a novel framework that treats each feature value as an independent token, effectively bypassing the need for imputation. SCANE regularizes the traits of distinct feature embeddings and enhances representational learning through a scalable embedding mechanism. Coupling SCANE with the Transformer Encoder architecture, we develop the Scalable nUMerical eMbeddIng Transformer (SUMMIT), which is engineered to deliver precise predictive outputs for MTS characterized by prevalent missing entries. Our experimental validation, conducted across three disparate electronic health record (EHR) datasets marked by elevated missing value frequencies, confirms the superior performance of SUMMIT over contemporary state-of-the-art approaches addressing similar challenges. These results substantiate the efficacy of SCANE and SUMMIT, underscoring their potential applicability across a broad spectrum of MTS data analytical tasks.
SynHIN: Generating Synthetic Heterogeneous Information Network for Explainable AI
Jan 07, 2024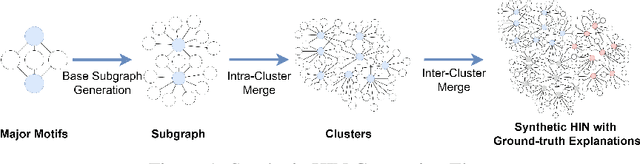
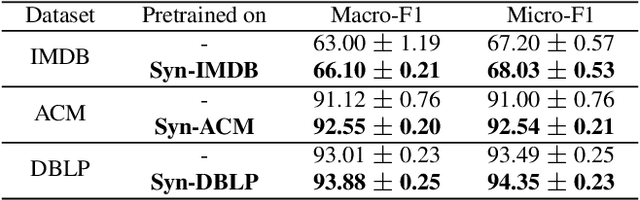
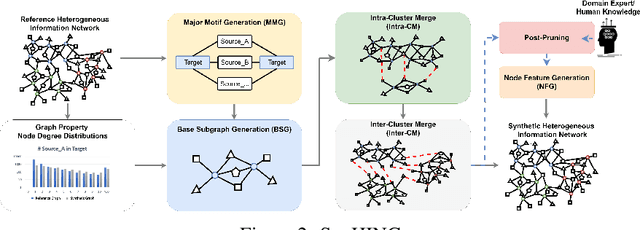
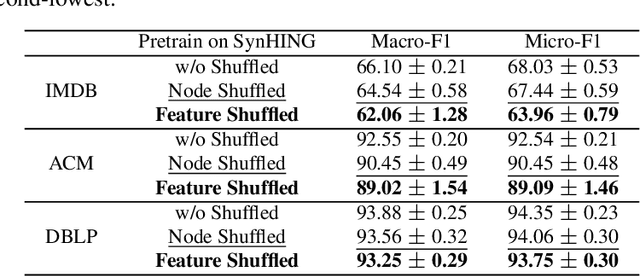
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) excel in various domains, from detecting e-commerce spam to social network classification problems. However, the lack of public graph datasets hampers research progress, particularly in heterogeneous information networks (HIN). The demand for datasets for fair HIN comparisons is growing due to advancements in GNN interpretation models. In response, we propose SynHIN, a unique method for generating synthetic heterogeneous information networks. SynHIN identifies motifs in real-world datasets, summarizes graph statistics, and constructs a synthetic network. Our approach utilizes In-Cluster and Out-Cluster Merge modules to build the synthetic HIN from primary motif clusters. After In/Our-Cluster mergers and a post-pruning process fitting the real dataset constraints, we ensure the synthetic graph statistics align closely with the reference one. SynHIN generates a synthetic heterogeneous graph dataset for node classification tasks, using the primary motif as the explanation ground truth. It can adapt and address the lack of heterogeneous graph datasets and motif ground truths, proving beneficial for assessing heterogeneous graph neural network explainers. We further present a benchmark dataset for future heterogeneous graph explainer model research. Our work marks a significant step towards explainable AI in HGNNs.
A GAN Approach for Node Embedding in Heterogeneous Graphs Using Subgraph Sampling
Dec 11, 2023Abstract:Our research addresses class imbalance issues in heterogeneous graphs using graph neural networks (GNNs). We propose a novel method combining the strengths of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) with GNNs, creating synthetic nodes and edges that effectively balance the dataset. This approach directly targets and rectifies imbalances at the data level. The proposed framework resolves issues such as neglecting graph structures during data generation and creating synthetic structures usable with GNN-based classifiers in downstream tasks. It processes node and edge information concurrently, improving edge balance through node augmentation and subgraph sampling. Additionally, our framework integrates a threshold strategy, aiding in determining optimal edge thresholds during training without time-consuming parameter adjustments. Experiments on the Amazon and Yelp Review datasets highlight the effectiveness of the framework we proposed, especially in minority node identification, where it consistently outperforms baseline models across key performance metrics, demonstrating its potential in the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge